Intro
Discover 5 metronidazole uses, including treating infections, parasites, and STDs, with this antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication, effective against bacterial vaginosis, giardiasis, and trichomoniasis.
The importance of understanding various medical treatments and their applications cannot be overstated. One such medication that has been widely used for decades is Metronidazole. Known for its effectiveness against a range of infections, Metronidazole has become a staple in many medical practices. Its versatility and broad spectrum of activity make it a valuable asset in the fight against infectious diseases. As we delve into the uses of Metronidazole, it becomes clear that this medication plays a critical role in treating various conditions that affect millions of people worldwide.
Metronidazole's mechanism of action involves interfering with the DNA of microbial cells, ultimately leading to their death. This process is crucial in combating infections caused by anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. The medication's ability to penetrate deep into tissues and reach the site of infection makes it highly effective in treating a variety of conditions. From gastrointestinal infections to skin and tissue infections, Metronidazole has proven to be a reliable treatment option. Its uses extend beyond these areas, showcasing the medication's versatility and importance in modern medicine.
The applications of Metronidazole are diverse and have been extensively studied. By examining the different uses of this medication, healthcare professionals and patients can better understand its benefits and potential side effects. This knowledge is essential in ensuring that Metronidazole is used effectively and safely. As research continues to uncover new aspects of Metronidazole's uses, its significance in the medical community is likely to grow. With its broad spectrum of activity and proven track record, Metronidazole remains a vital component in the treatment of various infections.
Introduction to Metronidazole
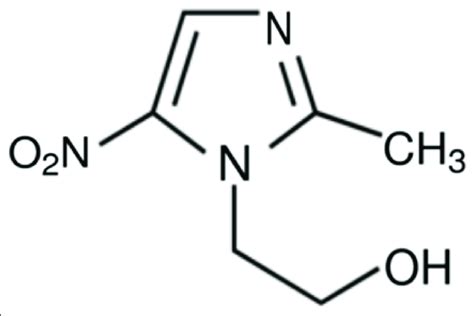
How Metronidazole Works
Metronidazole's mechanism of action involves the reduction of its nitro group, which occurs in the presence of low redox potential. This reduction leads to the formation of reactive intermediates that damage the DNA of microbial cells, ultimately resulting in their death. The medication's ability to target anaerobic bacteria and protozoa makes it highly effective in treating infections caused by these microorganisms. By understanding how Metronidazole works, healthcare professionals can better appreciate its uses and potential applications in the treatment of various conditions.Uses of Metronidazole

Treatment of Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis is a common condition characterized by an imbalance of vaginal flora, leading to symptoms such as abnormal discharge and odor. Metronidazole is often prescribed to treat this condition, either alone or in combination with other medications. Its effectiveness in reducing symptoms and eradicating the underlying infection has made Metronidazole a first-line treatment option for bacterial vaginosis.Metronidazole in the Treatment of Infections

Precautions and Side Effects
While Metronidazole is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, as well as metallic taste and headache. In rare cases, Metronidazole can cause more serious side effects, such as seizures and peripheral neuropathy. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and treatment duration to minimize the risk of side effects.Metronidazole Resistance and Future Directions
Combination Therapy and Novel Treatment Options
Combination therapy, which involves the use of Metronidazole in conjunction with other medications, may offer a solution to the problem of antibiotic resistance. By targeting multiple pathways and mechanisms, combination therapy can reduce the risk of resistance and improve treatment outcomes. Novel treatment options, such as antimicrobial peptides and phage therapy, are also being explored as potential alternatives to traditional antibiotics.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

Future Perspectives and Recommendations
Future perspectives on Metronidazole's uses and limitations will depend on ongoing research and the development of new treatment options. Recommendations for the use of Metronidazole should be based on current evidence and guidelines, taking into account the medication's potential benefits and risks. By working together to address the challenges posed by antibiotic resistance, healthcare professionals can ensure that Metronidazole remains a valuable treatment option for generations to come.Final Considerations and Reflections

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Metronidazole in the comments section below. Your input and feedback are invaluable in helping us better understand the uses and limitations of this medication. Please feel free to share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and let us work together to promote a greater understanding of Metronidazole and its role in modern medicine.
What is Metronidazole used for?
+Metronidazole is used to treat various infections caused by bacteria and protozoa, including bacterial vaginosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and infections caused by anaerobic bacteria.
How does Metronidazole work?
+Metronidazole works by damaging the DNA of microbial cells, thereby inhibiting their growth and proliferation. Its mechanism of action involves the reduction of its nitro group, which occurs in the presence of low redox potential.
What are the common side effects of Metronidazole?
+Common side effects of Metronidazole include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, as well as metallic taste and headache. In rare cases, Metronidazole can cause more serious side effects, such as seizures and peripheral neuropathy.
Can Metronidazole be used in combination with other medications?
+Yes, Metronidazole can be used in combination with other medications to treat various infections. Combination therapy may offer a solution to the problem of antibiotic resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
What is the future of Metronidazole in the treatment of infections?
+The future of Metronidazole in the treatment of infections will depend on ongoing research and the development of new treatment options. As antibiotic resistance continues to grow, it is essential to address this challenge and explore novel treatment options to ensure that Metronidazole remains a valuable treatment option.
