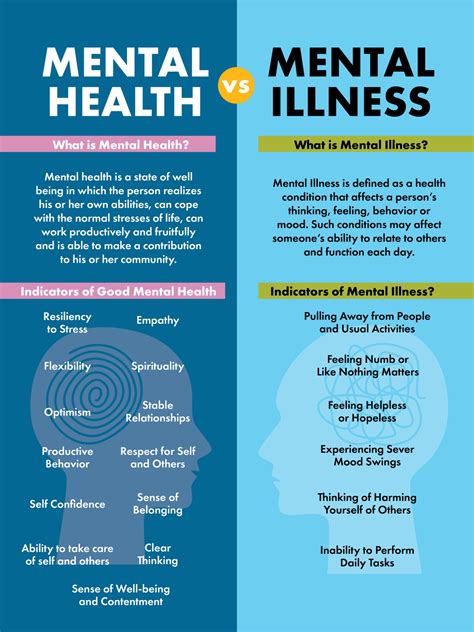
Intro
Discover insights on Mental Health Medical Conditions, including symptoms, treatments, and management of anxiety, depression, and trauma, promoting holistic well-being and stress relief.
Mental health is a vital aspect of our overall well-being, and it is essential to acknowledge that mental health medical conditions are just as significant as physical health conditions. In recent years, there has been a growing awareness and recognition of the importance of mental health, and this has led to a reduction in stigma and an increase in people seeking help. However, there is still much work to be done to ensure that mental health medical conditions are understood, diagnosed, and treated effectively.
The importance of mental health cannot be overstated, as it affects every aspect of our lives, from our relationships and work performance to our overall quality of life. Mental health medical conditions can have a significant impact on an individual's daily life, causing symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and mood swings. If left untreated, these conditions can lead to more severe problems, including social isolation, substance abuse, and even suicidal thoughts. It is crucial, therefore, to prioritize mental health and seek help when needed.
Mental health medical conditions are complex and multifaceted, and they can be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Some of the most common mental health medical conditions include depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. Each of these conditions has its unique set of symptoms and treatment options, and it is essential to work with a mental health professional to develop a personalized treatment plan. By seeking help and support, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms, develop coping strategies, and improve their overall mental health and well-being.
Mental Health Medical Conditions Overview
Mental health medical conditions can be broadly categorized into several types, including mood disorders, anxiety disorders, personality disorders, and psychotic disorders. Mood disorders, such as depression and bipolar disorder, are characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and mood swings. Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder and panic disorder, are marked by excessive worry, fear, and anxiety. Personality disorders, such as borderline personality disorder and narcissistic personality disorder, are characterized by persistent patterns of thoughts and behaviors that deviate from societal norms. Psychotic disorders, including schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder, are marked by hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
Types of Mental Health Medical Conditions
Mental health medical conditions can be further subdivided into several subtypes, each with its unique set of symptoms and treatment options. For example, depression can be classified into major depressive disorder, persistent depressive disorder, and postpartum depression. Anxiety disorders can be categorized into generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. Personality disorders can be divided into borderline personality disorder, narcissistic personality disorder, and obsessive-compulsive personality disorder.Causes and Risk Factors of Mental Health Medical Conditions

Mental health medical conditions are complex and multifaceted, and they can be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Genetic factors, such as family history and genetic predisposition, can play a significant role in the development of mental health medical conditions. Environmental factors, including trauma, stress, and social isolation, can also contribute to the development of mental health medical conditions. Psychological factors, such as low self-esteem, negative thinking patterns, and coping mechanisms, can also increase the risk of developing mental health medical conditions.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors can play a significant role in the development of mental health medical conditions. For example, individuals with a family history of depression or anxiety disorders are more likely to develop these conditions themselves. Genetic predisposition can also increase the risk of developing mental health medical conditions, particularly in individuals who have experienced trauma or stress.Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, including trauma, stress, and social isolation, can also contribute to the development of mental health medical conditions. Trauma, such as physical or emotional abuse, can increase the risk of developing mental health medical conditions, particularly post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Stress, including work-related stress or financial stress, can also contribute to the development of mental health medical conditions, particularly anxiety disorders. Social isolation, including loneliness and lack of social support, can also increase the risk of developing mental health medical conditions, particularly depression.Symptoms and Diagnosis of Mental Health Medical Conditions
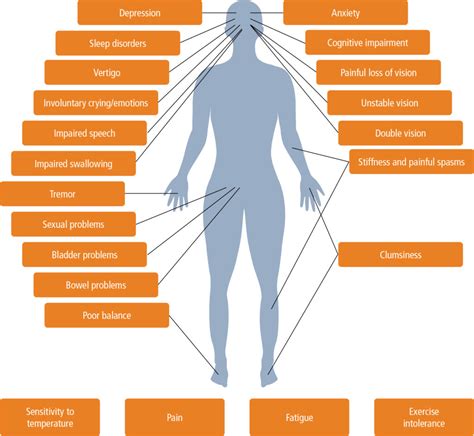
Mental health medical conditions can manifest in different ways, and symptoms can vary depending on the specific condition. Common symptoms of mental health medical conditions include:
- Mood changes, such as depression, anxiety, or irritability
- Changes in appetite or sleep patterns
- Fatigue or low energy
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Social withdrawal or isolation
- Substance abuse or addiction
Diagnosing mental health medical conditions can be complex, and it often requires a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional. The diagnostic process typically involves:
- A physical exam to rule out underlying medical conditions
- A psychological evaluation, including a clinical interview and assessment tools
- A review of medical and mental health history
- A discussion of symptoms and treatment options
Diagnostic Criteria
Diagnostic criteria for mental health medical conditions are outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). The DSM-5 provides standardized criteria for diagnosing mental health medical conditions, including symptoms, severity, and duration. Mental health professionals use the DSM-5 to diagnose mental health medical conditions and develop personalized treatment plans.Treatment Options for Mental Health Medical Conditions
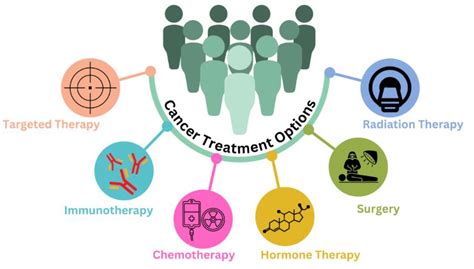
Treatment options for mental health medical conditions can vary depending on the specific condition and individual needs. Common treatment options include:
- Medications, such as antidepressants or antipsychotics
- Psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or psychodynamic therapy
- Lifestyle changes, including exercise, healthy eating, and stress management
- Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or mindfulness-based stress reduction
Medications
Medications can be effective in managing symptoms of mental health medical conditions. Antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. Antipsychotics, such as risperidone or olanzapine, can help manage symptoms of psychotic disorders, including schizophrenia.Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, including CBT or psychodynamic therapy, can help individuals understand and manage their symptoms. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors, while psychodynamic therapy explores the underlying causes of symptoms and behaviors.Coping Mechanisms and Self-Help Strategies

Coping mechanisms and self-help strategies can be effective in managing symptoms of mental health medical conditions. Common coping mechanisms include:
- Exercise, including walking, running, or yoga
- Mindfulness, including meditation or deep breathing
- Social support, including friends, family, or support groups
- Healthy eating, including a balanced diet and regular meals
- Stress management, including time management or relaxation techniques
Self-Help Strategies
Self-help strategies, including self-care and self-compassion, can also be effective in managing symptoms of mental health medical conditions. Self-care involves engaging in activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction, such as reading, listening to music, or taking a warm bath. Self-compassion involves treating oneself with kindness, understanding, and patience, particularly during difficult times.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

Mental health medical conditions are complex and multifaceted, and they can have a significant impact on an individual's daily life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for mental health medical conditions, individuals can take the first step towards seeking help and support. It is essential to prioritize mental health and seek help when needed, as early intervention and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with mental health medical conditions. How have you or a loved one been affected by mental health medical conditions? What coping mechanisms and self-help strategies have you found to be effective? Share your story and help raise awareness about the importance of mental health.
What are mental health medical conditions?
+Mental health medical conditions are complex and multifaceted conditions that affect an individual's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
What are the symptoms of mental health medical conditions?
+Symptoms of mental health medical conditions can vary depending on the specific condition, but common symptoms include mood changes, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, fatigue, and social withdrawal.
How are mental health medical conditions diagnosed?
+Mental health medical conditions are diagnosed through a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional, including a physical exam, psychological evaluation, and review of medical and mental health history.
