Intro
The midodrine drug class is a crucial aspect of medical treatment, particularly for individuals dealing with orthostatic hypotension, a condition characterized by a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing. This condition can lead to dizziness, lightheadedness, and even fainting, significantly impacting the quality of life. Understanding the midodrine drug class and its role in managing such conditions is essential for both medical professionals and patients alike.
Orthostatic hypotension can result from various factors, including prolonged bed rest, dehydration, and certain neurological disorders. The midodrine drug class, specifically midodrine hydrochloride, is an alpha-1 adrenergic agonist that works by constricting blood vessels, which in turn increases blood pressure. This mechanism of action helps alleviate the symptoms associated with orthostatic hypotension, providing patients with greater stability and reducing the risk of falls.
The importance of the midodrine drug class extends beyond the treatment of orthostatic hypotension. It also highlights the broader issue of blood pressure regulation and the various pharmacological interventions available to manage conditions related to blood pressure abnormalities. As research continues to uncover the complexities of cardiovascular diseases, the role of drugs like midodrine in clinical practice is likely to evolve, offering new avenues for treatment and management.
Introduction to Midodrine
Midodrine is a synthetic compound that acts as an alpha-adrenergic agonist. Its primary use is in the treatment of orthostatic hypotension, where it helps to increase blood pressure by causing vasoconstriction. The drug is orally administered and is known for its relatively rapid onset of action, making it a valuable option for managing acute episodes of orthostatic hypotension. Understanding the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of midodrine is crucial for optimizing its therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
Pharmacological Profile
The pharmacological profile of midodrine includes its mechanism of action, absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Midodrine's action as an alpha-1 adrenergic agonist leads to the constriction of blood vessels, thereby increasing peripheral resistance and blood pressure. This effect is particularly beneficial in patients with orthostatic hypotension, as it helps to reduce the symptoms associated with low blood pressure upon standing.Benefits of Midodrine

The benefits of midodrine in managing orthostatic hypotension are well-documented. By increasing blood pressure, midodrine reduces the risk of dizziness and fainting, improving the patient's ability to perform daily activities without interruption. Additionally, midodrine's relatively simple dosing regimen and oral administration make it a convenient treatment option for patients.
Improvement in Quality of Life
One of the significant benefits of midodrine is its impact on the quality of life for patients with orthostatic hypotension. By alleviating the symptoms of low blood pressure, midodrine enables patients to engage in physical activities and social interactions without the fear of sudden dizziness or fainting. This improvement in mobility and confidence can have a profound effect on a patient's overall well-being and psychological health.Working Mechanism of Midodrine
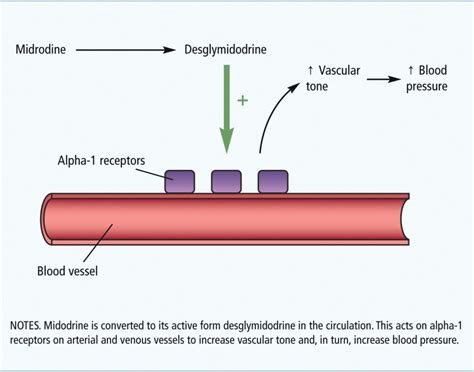
The working mechanism of midodrine involves its action on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, which are found in the smooth muscle of blood vessels. Upon binding to these receptors, midodrine causes the smooth muscle to contract, leading to vasoconstriction. This constriction of blood vessels increases peripheral resistance, which in turn elevates blood pressure. The increase in blood pressure helps to counteract the effects of orthostatic hypotension, providing symptomatic relief to patients.
Steps Involved in Midodrine Action
The steps involved in midodrine action include: - Oral administration of midodrine - Absorption of midodrine into the bloodstream - Distribution of midodrine to its site of action (alpha-1 adrenergic receptors in blood vessels) - Binding of midodrine to alpha-1 adrenergic receptors - Contraction of smooth muscle in blood vessels (vasoconstriction) - Increase in peripheral resistance and blood pressureSide Effects and Precautions

While midodrine is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some patients. Common side effects include supine hypertension (high blood pressure when lying down), piloerection (goosebumps), and pruritus (itching). To minimize the risk of side effects, patients should be closely monitored, especially during the initial phase of treatment. It is also crucial for patients to follow the prescribed dosing regimen and to report any adverse effects to their healthcare provider promptly.
Precautions for Use
Precautions for the use of midodrine include: - Monitoring blood pressure regularly - Avoiding lying down for at least 4 hours after taking midodrine - Gradually increasing the dose to minimize side effects - Informing the healthcare provider about any other medications being taken - Reporting any signs of supine hypertension or other adverse effectsPractical Examples and Statistical Data
Studies have shown that midodrine can significantly improve symptoms of orthostatic hypotension in patients. For example, a clinical trial demonstrated that patients treated with midodrine experienced a substantial reduction in dizziness and fainting episodes compared to those receiving a placebo. Statistical data from such studies highlight the efficacy of midodrine in managing orthostatic hypotension and underscore its value as a therapeutic option.
Case Studies
Case studies involving patients with orthostatic hypotension have provided valuable insights into the effectiveness of midodrine. These studies often involve patients who have not responded adequately to other treatments and have shown that midodrine can offer significant symptom relief. By examining the outcomes of these case studies, healthcare providers can better understand how to optimize midodrine therapy for their patients.SEO Optimization for Midodrine

To ensure that information about midodrine reaches the widest possible audience, SEO optimization is crucial. This involves using relevant keywords, such as "midodrine drug class," "orthostatic hypotension treatment," and "alpha-1 adrenergic agonist," in a balanced and natural manner throughout the content. By doing so, individuals searching for information on these topics can easily find comprehensive and accurate resources.
Keyword Density and Synonyms
Maintaining an optimal keyword density of 1-2% is essential for SEO optimization. This means that for every 100 words of content, the target keyword (e.g., "midodrine") should appear 1-2 times. Using synonyms and related phrases, such as "blood pressure medication" or "orthostatic intolerance treatment," can also enhance SEO relevance without resorting to keyword stuffing.Encouraging Engagement

As we conclude our discussion on the midodrine drug class, it's essential to encourage engagement and further exploration of this topic. We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about midodrine and its use in treating orthostatic hypotension. By fostering a community of individuals interested in learning more about this critical aspect of healthcare, we can promote a deeper understanding of the midodrine drug class and its potential to improve the lives of those affected by orthostatic hypotension.
Call to Action
We encourage all readers to engage with this content by commenting below, sharing this article with others who might benefit from the information, or seeking out additional resources to learn more about midodrine and orthostatic hypotension. Together, we can create a more informed and supportive community for those navigating the complexities of blood pressure regulation and its treatment.What is the primary use of midodrine?
+Midodrine is primarily used to treat orthostatic hypotension, a condition characterized by a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing.
How does midodrine work?
+Midodrine works as an alpha-1 adrenergic agonist, causing the constriction of blood vessels, which increases blood pressure and alleviates the symptoms of orthostatic hypotension.
What are the common side effects of midodrine?
+Common side effects of midodrine include supine hypertension, piloerection, and pruritus. Patients should be closely monitored, especially during the initial phase of treatment, to minimize the risk of these side effects.
