Intro
Discover 5 key facts about Motrin, a popular pain reliever, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to safely manage pain and reduce inflammation with ibuprofen-based medications.
Pain relief is an essential aspect of healthcare, and medications like Motrin play a significant role in managing various types of pain. Motrin, also known as ibuprofen, is a widely used over-the-counter medication that helps alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and lower fever. Understanding the facts about Motrin can help individuals use it effectively and safely.
The importance of knowing how to use Motrin and its potential interactions cannot be overstated. With so many people relying on this medication for pain relief, it's crucial to delve into the specifics of what Motrin is, how it works, and what precautions should be taken. From its active ingredients to potential side effects, exploring the facets of Motrin can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Motrin's mechanism of action and its benefits make it a staple in many medicine cabinets. However, like any medication, it's not without its risks and considerations. By examining the aspects of Motrin, including its uses, dosage, and interactions, readers can gain a comprehensive understanding of this common pain reliever. This knowledge is key to using Motrin responsibly and maximizing its benefits while minimizing its risks.
Introduction to Motrin
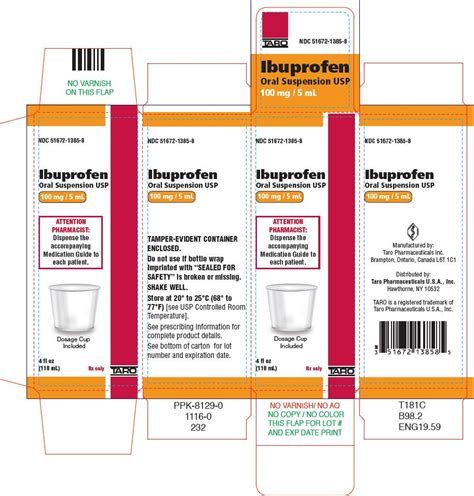
History of Motrin
The development of Motrin dates back to the 1960s, when a team of researchers at the Boots Company in the United Kingdom was working on a new class of pain relievers. The team, led by Dr. Stewart Adams, discovered that ibuprofen was a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, which made it an effective treatment for pain and inflammation. Motrin was first introduced in the United Kingdom in 1969 and later became available in the United States in 1974.How Motrin Works

Mechanisms of Action
The mechanisms of action of Motrin involve the inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, which are responsible for the production of prostaglandins. COX-1 is involved in the maintenance of normal physiological functions, such as the protection of the stomach lining, while COX-2 is involved in the production of prostaglandins in response to inflammation. Motrin inhibits both COX-1 and COX-2, which can lead to a range of effects, including pain relief, reduced inflammation, and decreased fever.Benefits of Motrin

Common Uses
Motrin is commonly used to treat a range of conditions, including: * Headaches * Arthritis * Menstrual cramps * Back pain * Fever reduction It is also used to relieve pain and inflammation associated with injuries, such as sprains and strains.Risks and Side Effects

Precautions and Interactions
Motrin can interact with a range of medications, including blood thinners, diabetes medications, and blood pressure medications. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking Motrin, especially if you are taking any other medications. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as stomach ulcers, kidney disease, and asthma, should use Motrin with caution.Dosage and Administration
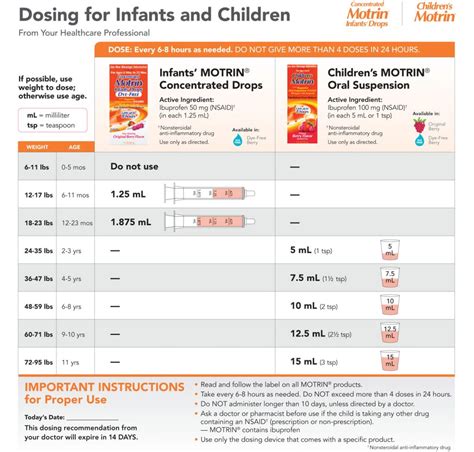
Overdose and Toxicity
In cases of overdose or toxicity, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Symptoms of overdose can include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and abdominal pain. In severe cases, it can lead to more serious complications, such as stomach ulcers, kidney damage, and respiratory depression.Alternatives to Motrin
Natural Alternatives
There are also several natural alternatives to Motrin, including herbal remedies, such as willow bark and turmeric, and dietary changes, such as increasing omega-3 fatty acid intake. While these alternatives may not be as effective as Motrin, they can be a useful addition to your pain relief regimen.Conclusion and Future Directions

As research continues to evolve, it is likely that new and more effective alternatives to Motrin will become available. In the meantime, it is essential to use Motrin responsibly and to follow the recommended guidelines to minimize the risk of side effects and maximize its benefits.
What is Motrin used for?
+Motrin is used to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and lower fever. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as headaches, arthritis, and menstrual cramps.
How does Motrin work?
+Motrin works by blocking the production of prostaglandins, which are chemicals in the body that cause pain and inflammation. It inhibits the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which is responsible for the production of prostaglandins.
What are the side effects of Motrin?
+The side effects of Motrin can include stomach upset, nausea, dizziness, and allergic reactions. In rare cases, it can also cause more serious side effects, such as stomach ulcers, kidney damage, and respiratory depression.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of Motrin and its uses. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with Motrin, please don't hesitate to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote responsible use of medications like Motrin and improve overall health and well-being.
