Intro
Discover 5 ways MRI scan brain technology improves diagnosis, treatment, and brain health, using functional MRI, diffusion MRI, and magnetic resonance angiography to detect conditions like stroke, tumors, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans of the brain are a crucial diagnostic tool in modern medicine, offering detailed images of the brain's structure and function. These scans are vital for diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of conditions, from strokes and brain tumors to neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease. The importance of MRI scans in healthcare cannot be overstated, as they provide healthcare professionals with the information needed to make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans. The ability to non-invasively visualize the brain and its various components has revolutionized the field of neurology, enabling earlier interventions and improving patient outcomes.
The process of undergoing an MRI scan is relatively straightforward, though it does require some preparation. Patients are typically asked to remove any metal objects, such as jewelry or glasses, and change into a hospital gown. The scan itself involves lying on a table that slides into a large, cylindrical machine. The machine uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate images of the brain, which are then interpreted by a radiologist. Despite the complexity of the technology, the experience for the patient is generally comfortable and painless, though some may feel claustrophobic or experience noise discomfort due to the loud banging sounds the machine makes during the scanning process.
The significance of MRI scans in medical diagnostics is underscored by their versatility and the breadth of information they can provide. From identifying structural abnormalities to assessing the brain's functional activity, MRI technology has become indispensable in clinical practice. Its applications span various medical specialties, including neurology, neurosurgery, psychiatry, and radiology, each benefiting from the detailed insights MRI scans offer into brain health and disease. Moreover, advances in MRI technology continue to expand its capabilities, enabling higher resolution images, faster scanning times, and new applications in research and clinical care.
Introduction to MRI Scan Brain
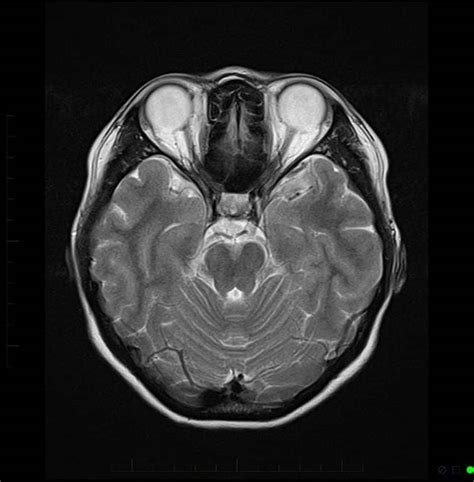
The introduction of MRI scans has marked a significant milestone in medical imaging. By providing clear, detailed pictures of the brain, MRI scans help doctors diagnose and treat medical conditions more effectively. The technology behind MRI scans is based on the principles of nuclear magnetic resonance, where hydrogen nuclei in the body align with a strong magnetic field and are then disturbed by radio waves, producing signals that are used to create detailed images of the brain's anatomy.
How MRI Scan Brain Works
The process of how an MRI scan works involves several key steps. First, the patient is positioned on the MRI table, which then slides into the MRI machine. The machine consists of a strong magnetic field, radiofrequency coils, and a computer system. The magnetic field aligns the hydrogen nuclei in the body, and the radiofrequency coils send and receive radio waves, disturbing the alignment. As the nuclei return to their aligned state, they emit signals, which are picked up by the coils and sent to the computer. The computer then uses these signals to generate detailed images of the brain, which can be viewed from different angles and planes.Benefits of MRI Scan Brain
The benefits of MRI scans of the brain are numerous. They offer a non-invasive way to diagnose a wide range of conditions, reducing the need for more invasive procedures. MRI scans can detect abnormalities in the brain's structure, such as tumors, cysts, and vascular malformations. They can also assess the brain's function, helping in the diagnosis of conditions like stroke, multiple sclerosis, and neurodegenerative diseases. Furthermore, MRI scans are crucial in planning surgical interventions, guiding neurosurgeons during operations, and monitoring the effectiveness of treatments over time.
Steps Involved in MRI Scan Brain
The steps involved in undergoing an MRI scan of the brain include preparation, the scanning process, and image interpretation. Preparation involves removing metal objects, changing into a hospital gown, and, in some cases, receiving a contrast agent to enhance image quality. During the scanning process, the patient lies on the MRI table and is asked to remain still while the machine generates images of the brain. After the scan, a radiologist interprets the images, looking for any abnormalities or signs of disease. The results are then communicated to the patient's healthcare provider, who discusses them with the patient and develops a treatment plan as necessary.Uses of MRI Scan Brain
The uses of MRI scans of the brain are diverse and continue to expand with advances in technology. They are used to diagnose and monitor neurological conditions, plan and guide neurosurgical procedures, and conduct research into brain function and disease. MRI scans can detect early signs of neurological disorders, allowing for early intervention and potentially improving outcomes. They are also invaluable in emergency situations, such as stroke, where timely and accurate diagnosis is critical for effective treatment.
Preparation for MRI Scan Brain
Preparation for an MRI scan of the brain involves several steps to ensure the scan is safe and effective. Patients are asked to remove any metal objects, as these can interfere with the magnetic field. They are also asked about any metal implants, such as pacemakers or artificial joints, which may be contraindications for an MRI scan. In some cases, a contrast agent may be administered to enhance the quality of the images. Patients are advised to arrive early to complete any necessary paperwork and to change into a hospital gown. It's also recommended to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the scan, though this may vary depending on the specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider.Common Uses of MRI Scan Brain
Common uses of MRI scans of the brain include diagnosing and monitoring conditions such as brain tumors, stroke, and multiple sclerosis. They are also used to investigate the cause of symptoms like headaches, dizziness, and seizures. MRI scans can provide detailed information about the brain's structure and function, helping healthcare providers understand the extent of any damage or disease. This information is critical for developing effective treatment plans and for monitoring the progression of conditions over time.
Risks and Side Effects of MRI Scan Brain
While MRI scans are generally safe, there are some risks and side effects to be aware of. The strong magnetic field can interfere with certain metal implants, and the contrast agent used in some scans can cause allergic reactions in a small number of patients. Some patients may experience claustrophobia or discomfort during the scan, though this can often be managed with sedation or the use of an open MRI machine. It's also important to follow the instructions provided by the healthcare provider before and after the scan to minimize any potential risks.Future of MRI Scan Brain

The future of MRI scans of the brain looks promising, with ongoing research aimed at improving image quality, reducing scanning times, and expanding the range of applications. Advances in technology, such as the development of higher field strength magnets and more sophisticated image analysis software, are expected to enhance the diagnostic capabilities of MRI scans. Additionally, the integration of MRI with other imaging modalities, such as PET scans, is opening up new possibilities for functional brain imaging and the study of brain diseases.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, MRI scans of the brain are a powerful diagnostic tool that has revolutionized the field of neurology. Their ability to provide detailed images of the brain's structure and function has enabled healthcare providers to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions more effectively. As technology continues to advance, the potential applications of MRI scans will only continue to grow, offering new hope for patients with neurological disorders and advancing our understanding of the brain and its many mysteries.To further explore the topic and address any questions you might have, let's examine some frequently asked questions about MRI scans of the brain.
What is an MRI scan, and how does it work?
+An MRI scan uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to generate detailed images of the brain's structure and function. It works by aligning the hydrogen nuclei in the body with the magnetic field and then disturbing them with radio waves, producing signals that are used to create images.
Are MRI scans safe, and what are the potential risks?
+MRI scans are generally safe, but there are potential risks to be aware of, including the interference with metal implants and the possibility of allergic reactions to the contrast agent used in some scans. Patients should follow the instructions provided by their healthcare provider to minimize any potential risks.
What are the common uses of MRI scans of the brain?
+MRI scans of the brain are commonly used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as brain tumors, stroke, and multiple sclerosis. They are also used to investigate the cause of symptoms like headaches, dizziness, and seizures, and to guide neurosurgical procedures.
We hope this comprehensive overview of MRI scans of the brain has provided you with valuable insights into this powerful diagnostic tool. Whether you're a healthcare professional, a patient, or simply someone interested in learning more about medical imaging, we encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below. By engaging in a dialogue about the role of MRI scans in healthcare, we can work together to advance our understanding of the brain and improve patient outcomes.
