Intro
Identify 5 myocardial infarction symptoms, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue, to recognize heart attack warning signs, prevent cardiac arrest, and improve cardiovascular health with timely medical intervention.
Myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, is a serious medical condition that occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. The symptoms of myocardial infarction can vary from person to person, but it is essential to recognize the common signs to seek medical attention promptly. In this article, we will delve into the importance of understanding myocardial infarction symptoms, the benefits of early detection, and the steps to take in case of an emergency.
Recognizing the symptoms of myocardial infarction is crucial because it can significantly improve the chances of survival and reduce the risk of complications. According to the American Heart Association, approximately 735,000 Americans experience a heart attack each year, and prompt medical treatment can make a significant difference in outcomes. The symptoms of myocardial infarction can be subtle, and some people may not experience the typical chest pain, making it essential to be aware of the various signs and seek medical help immediately.
The importance of understanding myocardial infarction symptoms cannot be overstated. Early detection and treatment can prevent long-term damage to the heart muscle, reduce the risk of future heart attacks, and improve overall quality of life. Furthermore, recognizing the symptoms of myocardial infarction can also help individuals take preventive measures, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and controlling underlying medical conditions. By being informed and proactive, individuals can reduce their risk of experiencing a heart attack and improve their overall heart health.
Common Myocardial Infarction Symptoms
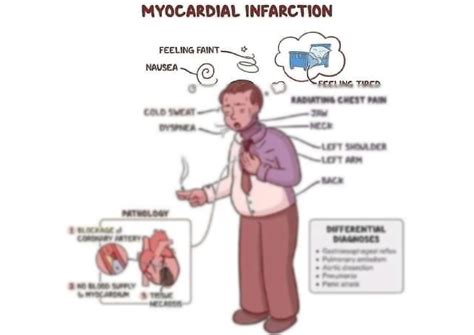
The common symptoms of myocardial infarction include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, lightheadedness or dizziness, nausea or vomiting, and fatigue. Chest pain is the most common symptom, and it can feel like pressure, tightness, or a squeezing sensation in the chest. The pain can radiate to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, and it may be triggered by physical activity or emotional stress. Shortness of breath is another common symptom, and it can occur with or without chest pain. Lightheadedness or dizziness can also occur, especially when standing up or changing positions.
Less Common Symptoms
Some people may experience less common symptoms, such as palpitations or irregular heartbeats, coughing or wheezing, abdominal pain or discomfort, and anxiety or panic. Palpitations or irregular heartbeats can occur when the heart is not beating normally, and it can feel like the heart is skipping beats or beating too quickly. Coughing or wheezing can occur when the heart is not pumping efficiently, and it can lead to fluid buildup in the lungs. Abdominal pain or discomfort can occur when the heart is not getting enough oxygen, and it can feel like a sharp or dull ache in the stomach.Causes and Risk Factors
Myocardial infarction is usually caused by a blockage in the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. The blockage can occur due to a blood clot or the buildup of plaque, which is a mixture of fat, cholesterol, and other substances. The risk factors for myocardial infarction include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a family history of heart disease. High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of blockages, while high cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of blood clots, while diabetes can increase the risk of heart disease.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing myocardial infarction involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and controlling underlying medical conditions. This can include eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress through relaxation techniques. Treatment for myocardial infarction usually involves medications to dissolve blood clots, improve blood flow, and reduce pain. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove blockages or repair damaged heart tissue.Diagnosis and Testing

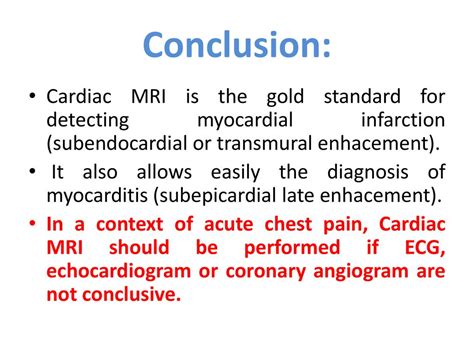
Diagnosing myocardial infarction usually involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The doctor may listen to the heart and lungs, check blood pressure and pulse, and ask about symptoms and medical history. Diagnostic tests may include electrocardiogram (ECG), blood tests, echocardiogram, and coronary angiogram. An ECG can show abnormal heart rhythms or signs of damage to the heart muscle, while blood tests can detect abnormal levels of enzymes or proteins that indicate heart damage.
Complications and Outlook
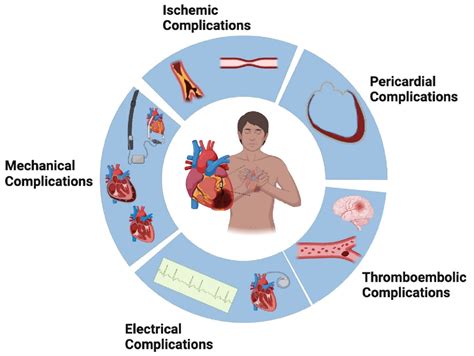
The complications of myocardial infarction can include heart failure, arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest. Heart failure can occur when the heart is not pumping efficiently, and it can lead to fluid buildup in the lungs and other parts of the body. Arrhythmias can occur when the heart is not beating normally, and it can increase the risk of cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest can occur when the heart stops beating suddenly, and it can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.Treatment Options and Recovery
Treatment options for myocardial infarction usually involve a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and surgery. Medications may include blood thinners, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors to improve blood flow, reduce pain, and prevent future heart attacks. Lifestyle changes may include eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress through relaxation techniques. Surgery may be necessary to remove blockages or repair damaged heart tissue.
Rehabilitation and Follow-up Care
Rehabilitation and follow-up care are essential after a heart attack to prevent future complications and improve overall heart health. This may include cardiac rehabilitation programs, which involve exercise, education, and counseling to help individuals recover and manage their condition. Follow-up care may include regular check-ups with the doctor, monitoring of blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and adjustments to medications or lifestyle changes as needed.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, understanding myocardial infarction symptoms is crucial for prompt medical treatment and improved outcomes. By recognizing the common and less common symptoms, individuals can seek medical help immediately and reduce the risk of complications. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and controlling underlying medical conditions can also help prevent myocardial infarction. We encourage readers to share this article with friends and family, and to take the necessary steps to prioritize their heart health.
What are the common symptoms of myocardial infarction?
+The common symptoms of myocardial infarction include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, lightheadedness or dizziness, nausea or vomiting, and fatigue.
How can I prevent myocardial infarction?
+Preventing myocardial infarction involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and controlling underlying medical conditions. This can include eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress through relaxation techniques.
What are the treatment options for myocardial infarction?
+Treatment options for myocardial infarction usually involve a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and surgery. Medications may include blood thinners, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors to improve blood flow, reduce pain, and prevent future heart attacks.
