Intro
Naltrexone used for opioid addiction treatment, blocking cravings and aiding recovery. Effective for alcohol dependence, weight loss, and autoimmune disorders, with benefits including reduced withdrawal symptoms and increased sobriety rates.
The use of naltrexone has been a topic of interest in the medical community for several decades. Initially approved by the FDA in 1984 for the treatment of opioid addiction, naltrexone has since been explored for its potential benefits in addressing various other health conditions. The importance of understanding the applications and mechanisms of naltrexone cannot be overstated, as it offers insights into innovative approaches to managing complex diseases. By delving into the world of naltrexone, we can uncover the intricacies of its effects on the human body and the vast array of conditions it may help alleviate.
The versatility of naltrexone is rooted in its ability to interact with opioid receptors in the brain, which play a crucial role in pain perception, mood regulation, and addiction. This interaction can lead to significant improvements in patients suffering from conditions that were once thought to be unrelated to opioid receptor activity. As research continues to unravel the mysteries of naltrexone's effects, its potential as a therapeutic agent expands, offering hope to individuals dealing with a range of debilitating conditions. From addiction and chronic pain to autoimmune diseases and mental health disorders, the applications of naltrexone are diverse and multifaceted.
The journey into the realm of naltrexone's uses is not only about understanding its medical applications but also about appreciating the complexity of human biology and the intricate balance of neurotransmitters and receptors that govern our well-being. As we explore the various facets of naltrexone's role in healthcare, we are reminded of the importance of ongoing research and the need for a comprehensive approach to managing health conditions. By embracing the potential of naltrexone and other innovative treatments, we can work towards a future where a broader range of effective, personalized therapeutic options are available to those in need.
Naltrexone Mechanism of Action
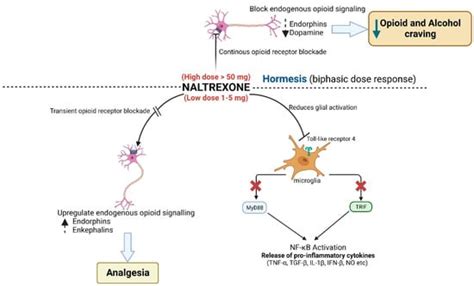
Opioid Receptor Blockade
Naltrexone's primary action is as an opioid receptor antagonist, specifically targeting mu, delta, and kappa receptors. The mu receptors are primarily responsible for the analgesic (pain-relieving) and euphoric effects of opioids, making them a key target for treating opioid addiction. Delta receptors are involved in mood modulation and emotional response, while kappa receptors have roles in stress response and dysphoria (a state of unease). By blocking these receptors, naltrexone can have a profound impact on both the physical and psychological aspects of opioid use and other conditions influenced by opioid receptor activity.Applications of Naltrexone

Treatment of Opioid Addiction
Naltrexone is perhaps best known for its role in the treatment of opioid addiction. It works by blocking the effects of opioids at their receptor sites and reducing the craving for opioids. This can be particularly effective in preventing relapse in individuals who have undergone detoxification. Naltrexone can be administered orally or via a monthly injection, providing a sustained release of the medication and improving adherence to treatment.Alcohol Dependence
In addition to its use in opioid addiction, naltrexone has been found to be beneficial in the treatment of alcohol dependence. It can reduce the craving for alcohol and block the rewarding aspects of drinking, thereby aiding in the reduction of alcohol consumption. The exact mechanism through which naltrexone exerts its effects on alcohol dependence is not fully understood but is believed to involve the modulation of the endogenous opioid system and its interaction with alcohol's effects on the brain.Chronic Pain Management
Naltrexone, particularly in low doses, has been explored for its potential in managing chronic pain. Low-dose naltrexone (LDN) has been used off-label for conditions like fibromyalgia, Crohn's disease, and multiple sclerosis, among others. The rationale behind its use in chronic pain is based on its ability to modulate the immune system and potentially reduce inflammation, as well as its effects on endorphins and the endogenous opioid system, which plays a significant role in pain regulation.Low-Dose Naltrexone (LDN)
Benefits and Mechanisms of LDN
The benefits of LDN are thought to arise from its unique mechanism of action at low doses. Unlike higher doses that block opioid receptors outright, LDN may stimulate the body's natural production of opioids (endorphins) and modulate the immune system. This can lead to anti-inflammatory effects and improved overall well-being. Additionally, LDN has been suggested to have neuroprotective properties, potentially benefiting conditions characterized by neurodegeneration.Potential Side Effects and Considerations

Importance of Patient Selection and Monitoring
The success of naltrexone treatment, whether for addiction or other conditions, heavily relies on proper patient selection and ongoing monitoring. Patients must be opioid-free before starting naltrexone to avoid precipitating withdrawal. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to assess the efficacy of the treatment, manage side effects, and adjust the treatment plan as necessary.Future Directions and Research

Personalized Medicine and Naltrexone
The integration of personalized medicine principles into naltrexone treatment could revolutionize its application. By understanding the genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that influence an individual's response to naltrexone, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to maximize efficacy and minimize side effects. This approach could lead to better outcomes and increased patient satisfaction.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with naltrexone, whether as a healthcare provider, a patient, or a family member of someone who has benefited from this medication. Your insights can help others understand the complexities and benefits of naltrexone treatment. Please comment below, and let's continue the conversation about the evolving role of naltrexone in modern healthcare.
What is naltrexone primarily used for?
+Naltrexone is primarily used for the treatment of opioid addiction. It works by blocking the effects of opioids at their receptor sites, reducing cravings and preventing relapse.
Can naltrexone be used for chronic pain management?
+Yes, naltrexone, particularly in low doses (Low-Dose Naltrexone or LDN), has been explored for its potential in managing chronic pain. It is believed to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation, among other effects.
What are the potential side effects of naltrexone?
+Common side effects of naltrexone include nausea, headache, and dizziness. More serious considerations involve its potential impact on liver function and the risk of opioid overdose if naltrexone is discontinued and opioids are then used.
