Intro
Learn about Necrotizing Enterocolitis, a devastating gut condition causing intestinal necrosis, sepsis, and bowel obstruction, affecting premature infants, with risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, including surgical interventions and supportive care.
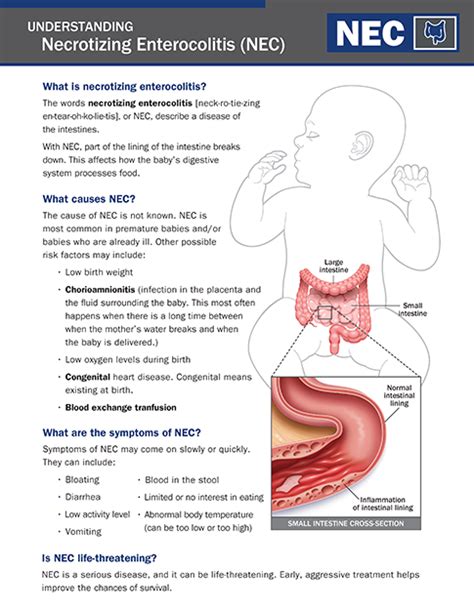
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating and potentially life-threatening condition that primarily affects premature infants. It is characterized by the inflammation and death of intestinal tissue, which can lead to severe complications, including sepsis, intestinal perforation, and death. NEC is a significant concern in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) worldwide, and its incidence has been increasing over the past few decades. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and treatment options for NEC is essential for healthcare professionals and parents of premature infants.
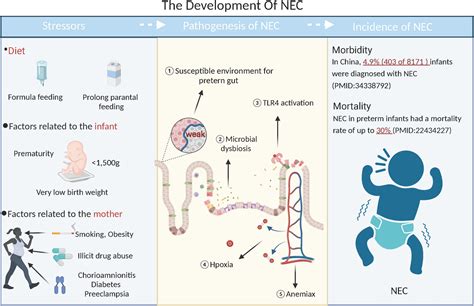
The exact cause of NEC is still not fully understood, but several factors are thought to contribute to its development. These include prematurity, low birth weight, formula feeding, and altered gut microbiota. Premature infants are more susceptible to NEC due to their immature digestive system and compromised immune function. The condition can progress rapidly, making early recognition and treatment crucial to prevent long-term complications. Research has shown that NEC can have a significant impact on the quality of life and long-term health outcomes of affected infants, highlighting the need for effective prevention and treatment strategies.
NEC is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. Healthcare professionals must be aware of the risk factors and clinical signs of NEC, including abdominal distension, vomiting, and bloody stools. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes, and a multidisciplinary team approach is often necessary to manage the condition. Parents of premature infants should be educated about the risks and signs of NEC, as well as the importance of breastfeeding and proper nutrition in preventing the condition. By working together, healthcare professionals and parents can reduce the incidence and severity of NEC, improving the health and well-being of premature infants.
Necrotizing Enterocolitis Causes and Risk Factors
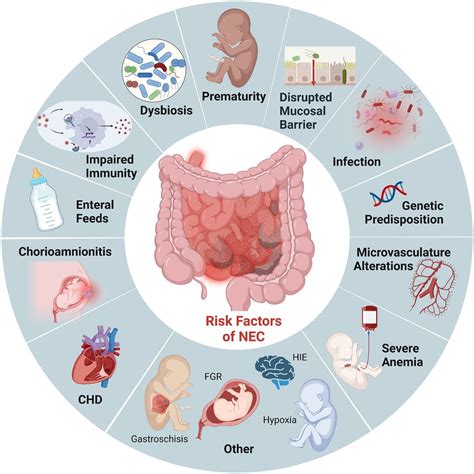
Role of Gut Microbiota in NEC
The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in the development and function of the intestinal tract. An imbalance of the gut microbiota, also known as dysbiosis, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of NEC. Research has shown that premature infants with NEC have altered gut microbiota compared to healthy premature infants. The exact mechanisms by which dysbiosis contributes to NEC are still not fully understood, but it is thought to involve the disruption of the intestinal barrier function and the activation of inflammatory pathways.Necrotizing Enterocolitis Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
Staging of NEC
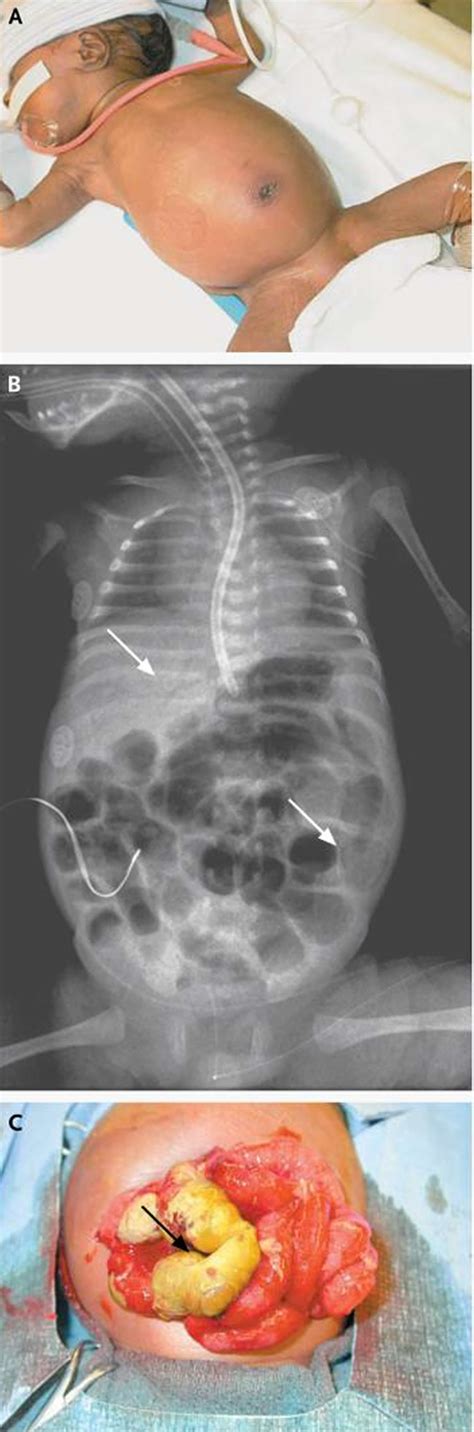
The staging of NEC is based on the severity of the condition, with stage I being the mildest and stage III being the most severe. The staging system is as follows: * Stage I: Suspected NEC, with symptoms such as abdominal distension and vomiting * Stage II: Proven NEC, with symptoms such as bloody stools and pneumatosis intestinalis (air in the intestinal wall) * Stage III: Advanced NEC, with symptoms such as intestinal perforation and peritonitisNecrotizing Enterocolitis Treatment and Management
Role of Breast Milk in NEC Prevention
Breast milk has been shown to have a protective effect against NEC, and its use is recommended for all premature infants. Breast milk contains antibodies and other factors that help to protect the intestinal tract and promote the growth of beneficial gut microbiota. Donor breast milk may be used if a mother is unable to express her own milk, and formula feeding should be avoided whenever possible.Necrotizing Enterocolitis Complications and Long-Term Outcomes
Impact of NEC on Quality of Life
The impact of NEC on quality of life can be significant, with affected infants requiring ongoing medical care and rehabilitation. Parents of infants with NEC may experience stress, anxiety, and uncertainty, and may require support and counseling to cope with the condition. Healthcare professionals must be aware of the potential long-term outcomes of NEC and provide affected infants and their families with comprehensive care and support.Necrotizing Enterocolitis Prevention Strategies
Role of Probiotics in NEC Prevention
Probiotics have been shown to have a potential role in preventing NEC, although more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness. Probiotics are live microorganisms that can help to promote the growth of beneficial gut microbiota and prevent dysbiosis. They may be administered to premature infants to reduce the risk of NEC, although their use should be carefully monitored and evaluated.What is the main cause of Necrotizing Enterocolitis?
+The main cause of Necrotizing Enterocolitis is still not fully understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of factors, including prematurity, low birth weight, formula feeding, and altered gut microbiota.
How is Necrotizing Enterocolitis diagnosed?
+Necrotizing Enterocolitis is diagnosed based on a combination of clinical, laboratory, and imaging findings, including abdominal X-rays and blood tests.
What are the long-term outcomes of Necrotizing Enterocolitis?
+The long-term outcomes of Necrotizing Enterocolitis can be significant, including intestinal stricture, short bowel syndrome, and neurodevelopmental impairment. Affected infants may require ongoing medical care and rehabilitation.
How can Necrotizing Enterocolitis be prevented?
+Necrotizing Enterocolitis can be prevented by promoting breastfeeding, avoiding formula feeding, and minimizing the use of antibiotics. Probiotics and prebiotics may also be used to promote the growth of beneficial gut microbiota and prevent dysbiosis.
What is the role of breast milk in preventing Necrotizing Enterocolitis?
+Breast milk has been shown to have a protective effect against Necrotizing Enterocolitis, and its use is recommended for all premature infants. Breast milk contains antibodies and other factors that help to protect the intestinal tract and promote the growth of beneficial gut microbiota.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of Necrotizing Enterocolitis, its causes, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can reduce the incidence and severity of NEC, improving the health and well-being of premature infants.
