Intro
Discover 5 tips to manage bilirubin levels, reducing jaundice risks. Learn about liver health, bilirubin tests, and natural ways to lower bilirubin counts, promoting healthy bile production and overall well-being.
Bilirubin levels are a crucial aspect of our health, particularly when it comes to liver function and the breakdown of red blood cells. Understanding bilirubin and its impact on our bodies can help us take proactive steps towards maintaining our overall well-being. Bilirubin is a yellow compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in red blood cells. Normally, bilirubin is processed by the liver, and high levels can indicate liver dysfunction or other health issues. In this article, we will delve into the importance of managing bilirubin levels and explore tips on how to keep them in check.
The significance of bilirubin levels cannot be overstated. Elevated bilirubin can lead to jaundice, a condition characterized by a yellowing of the skin and eyes, which can be a symptom of underlying health issues. Furthermore, understanding how to manage bilirubin levels can help in the early detection and treatment of liver diseases, ensuring timely medical intervention. It is essential to recognize the signs of high bilirubin levels and take preventive measures to avoid complications.
Bilirubin management is not just about treating existing conditions but also about adopting a lifestyle that promotes liver health and efficient red blood cell breakdown. This includes dietary changes, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding substances that can harm the liver. By taking a proactive approach, individuals can reduce the risk of developing liver diseases and maintain optimal bilirubin levels. In the following sections, we will explore these strategies in detail, providing readers with practical advice on managing bilirubin levels and promoting overall health.
Understanding Bilirubin
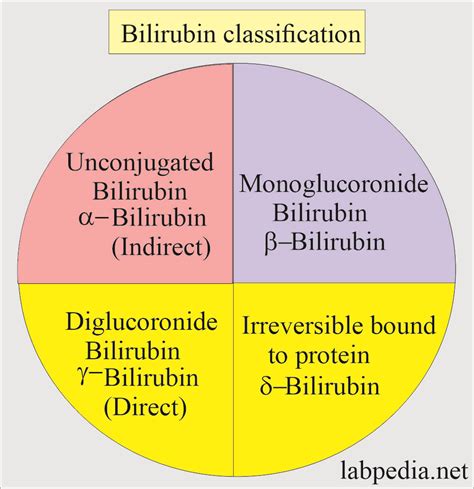
Types of Bilirubin
There are two main types of bilirubin: unconjugated (indirect) and conjugated (direct). Unconjugated bilirubin is the form that has not yet been processed by the liver, while conjugated bilirubin is the water-soluble form that has been processed and is ready to be excreted. Elevated levels of either type can indicate different health issues. For example, high levels of unconjugated bilirubin may suggest a problem with the production or breakdown of red blood cells, while elevated conjugated bilirubin could indicate a liver or bile duct issue.Dietary Changes for Bilirubin Management

Foods to Avoid
Some foods can exacerbate liver problems or increase bilirubin levels. It's advisable to limit or avoid: - Foods high in saturated fats, as they can contribute to liver fat accumulation and worsen liver function. - Processed foods, which often contain high amounts of sodium, sugar, and unhealthy fats that can strain the liver. - Alcohol, as it is directly toxic to liver cells and can impair the liver's ability to process bilirubin.Exercise and Bilirubin Levels
Managing Stress
Stress can have a detrimental effect on overall health, including liver function. Chronic stress can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, which may impair the liver's ability to process bilirubin. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help mitigate these effects. Adequate sleep and a balanced diet also play crucial roles in managing stress levels.Medical Interventions for High Bilirubin
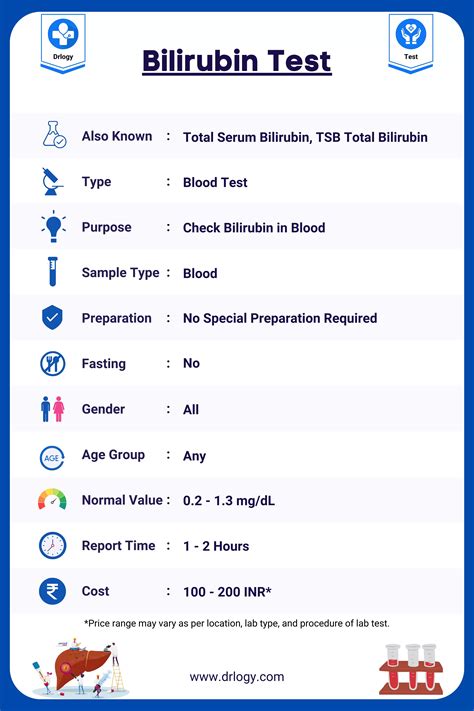
Monitoring Bilirubin Levels
Regular monitoring of bilirubin levels is essential, especially for individuals with a history of liver disease or other conditions that can affect bilirubin metabolism. This involves periodic blood tests to check for levels of direct and indirect bilirubin. Early detection of abnormalities can lead to timely intervention, reducing the risk of serious health issues.Lifestyle Modifications
Support and Community
Living with elevated bilirubin levels or managing liver health can be challenging. Connecting with support groups, either online or in-person, can provide valuable resources, advice, and emotional support. Sharing experiences and learning from others who are facing similar challenges can be incredibly empowering and help individuals stay motivated on their health journey.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on managing bilirubin levels in the comments below. Your insights can help others who are navigating similar health challenges. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with your network to help spread awareness about the importance of liver health and bilirubin management.
What are normal bilirubin levels?
+Normal bilirubin levels typically range from 0.1 to 1.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for adults, though this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory conducting the test.
Can diet alone lower bilirubin levels?
+Diet can play a significant role in managing bilirubin levels, but it may not be enough on its own to lower levels significantly, especially in cases of underlying liver disease or other health issues. A comprehensive approach that includes diet, exercise, and, if necessary, medical treatment is often most effective.
How often should I check my bilirubin levels?
+The frequency of checking bilirubin levels depends on your health status and risk factors. Individuals with a history of liver disease or those who are experiencing symptoms of high bilirubin should consult with their healthcare provider to determine the best schedule for monitoring their bilirubin levels.
