Intro
Discover key Nitrofurantoin facts, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand this antibiotics role in treating urinary tract infections, bladder infections, and other bacterial infections effectively.
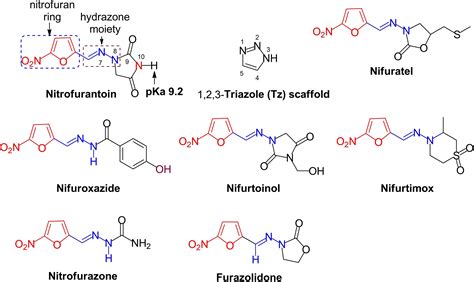
The world of antibiotics is vast and complex, with various medications designed to combat different types of bacterial infections. Among these, Nitrofurantoin stands out as a unique and effective treatment option for certain bacterial infections, particularly those affecting the urinary tract. Its distinct mechanism of action and specific uses set it apart from other antibiotics, making it a crucial component in the fight against antibiotic resistance. Understanding Nitrofurantoin's properties, uses, and side effects is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients, ensuring its safe and effective use.
Nitrofurantoin has been a staple in the treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs) for decades, thanks to its ability to target and eliminate bacteria that cause these infections. Its efficacy against common UTI pathogens, combined with a relatively low risk of promoting antibiotic resistance, makes it a preferred choice for many clinicians. Furthermore, the drug's pharmacokinetics allow it to achieve high concentrations in the urinary tract, enhancing its antibacterial effects in this specific area of the body. Despite its focused use, Nitrofurantoin's importance extends beyond the realm of UTIs, as it contributes to the broader discussion on antibiotic stewardship and responsible prescribing practices.
The importance of Nitrofurantoin in modern medicine cannot be overstated, given the rising concern of antibiotic resistance worldwide. As bacteria evolve to evade the effects of commonly used antibiotics, drugs like Nitrofurantoin offer a vital alternative, helping to preserve the efficacy of our current antibiotic arsenal. Moreover, research into Nitrofurantoin and its mechanisms has provided valuable insights into bacterial resistance patterns, informing strategies to combat this growing health threat. By exploring the multifaceted role of Nitrofurantoin in treating infections and its implications for public health, we can better appreciate the intricacies of antibiotic therapy and the need for judicious drug use.
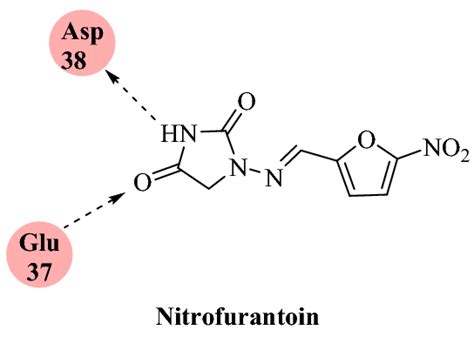
Nitrofurantoin Mechanism of Action
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
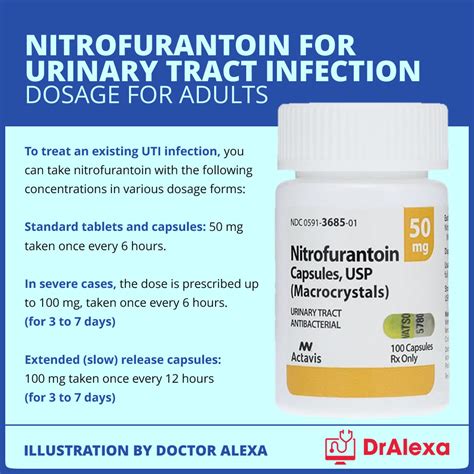
The pharmacokinetics of Nitrofurantoin involve its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Upon oral administration, Nitrofurantoin is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and then distributed throughout the body, with a significant portion being excreted unchanged in the urine. This renal excretion is crucial for its antibacterial effects in the urinary tract. The drug's pharmacodynamics, or its effects on the body, are characterized by its concentration-dependent killing of bacteria, with higher concentrations in the urine leading to more effective bacterial eradication.Nitrofurantoin Uses
Specific Indications
- **Acute Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections:** Nitrofurantoin is indicated for the treatment of acute uncomplicated urinary tract infections, including cystitis. - **Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections:** For patients experiencing recurrent UTIs, Nitrofurantoin can be used as a prophylactic measure to prevent future episodes. - **Pregnancy and Urinary Tract Infections:** Nitrofurantoin is considered safe for use during pregnancy, particularly during the first trimester, making it an option for managing UTIs in pregnant women.Nitrofurantoin Side Effects
Management of Side Effects
- **Dose Adjustment:** Reducing the dose or switching to an alternative antibiotic may alleviate side effects in some patients. - **Symptomatic Treatment:** For mild side effects, symptomatic treatment, such as anti-emetics for nausea, can be effective. - **Monitoring:** Regular monitoring for signs of more severe side effects, such as pulmonary or hepatic toxicity, is crucial for early detection and management.Nitrofurantoin Resistance
Strategies to Combat Resistance
- **Appropriate Use:** Ensuring Nitrofurantoin is used only when necessary and for the appropriate duration can help reduce the selective pressure driving resistance. - **Susceptibility Testing:** Performing susceptibility testing can help identify resistant strains, guiding the choice of alternative antibiotics when necessary. - **Infection Control Practices:** Implementing strict infection control measures in healthcare settings can prevent the spread of resistant organisms.Nitrofurantoin in Pregnancy and Lactation
Considerations for Use in Pregnancy
- **First Trimester:** Nitrofurantoin can be used during the first trimester when the benefits outweigh the risks. - **Near Term:** Close to term, the use of Nitrofurantoin should be avoided due to the potential risk of neonatal hemolysis. - **Lactation:** Nitrofurantoin is excreted in breast milk, but the amounts are considered to be small, and it is generally considered safe for use during lactation.Nitrofurantoin Interactions
Common Interactions
- **Antacids and Sucralfate:** These can decrease the absorption of Nitrofurantoin. - **Metallic Cations:** Magnesium or aluminum-containing products can also interfere with Nitrofurantoin absorption. - **Uricosuric Drugs:** These can increase the risk of crystalluria when used with Nitrofurantoin.As we delve deeper into the world of Nitrofurantoin, it becomes clear that this antibiotic plays a vital role in managing urinary tract infections, while also contributing to the broader efforts against antibiotic resistance. Its unique properties, specific indications, and potential for side effects and interactions all underscore the importance of informed prescribing practices and patient education. By embracing a comprehensive understanding of Nitrofurantoin and its uses, we can work towards more effective and responsible antibiotic use, ultimately protecting the health of individuals and communities alike.
The journey to understand Nitrofurantoin is not just about grasping the intricacies of a single drug; it's about being part of a larger conversation on antibiotic stewardship, public health, and the delicate balance between treating infections and preserving the efficacy of our antibiotic arsenal. As we move forward in this era of increasing antibiotic resistance, the role of Nitrofurantoin, along with other carefully selected antibiotics, will be pivotal in navigating the challenges of infection management.
In wrapping up our exploration of Nitrofurantoin, we invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about this topic. Whether you're a healthcare professional seeking to deepen your understanding of antibiotic therapy or a patient looking for reliable information on your treatment options, your engagement is invaluable. Let's continue the conversation on social media, using hashtags to connect with others interested in antibiotic stewardship and public health. Together, we can foster a community that values informed discussion and promotes the responsible use of antibiotics like Nitrofurantoin.
What is Nitrofurantoin used for?
+Nitrofurantoin is primarily used for the treatment of acute uncomplicated urinary tract infections (uUTIs) and the prevention of recurrent UTIs.
How does Nitrofurantoin work?
+Nitrofurantoin works by damaging bacterial DNA, thereby inhibiting the growth and multiplication of bacteria. This action is specific to certain types of bacteria, particularly those that cause urinary tract infections.
Can Nitrofurantoin be used during pregnancy?
+Yes, Nitrofurantoin is considered relatively safe for use during pregnancy, particularly for the treatment of urinary tract infections. However, its use should be carefully evaluated, considering the potential benefits and risks.
