Intro
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets have been a cornerstone in the management of angina pectoris for decades. Angina pectoris, commonly known as angina, is a condition characterized by chest pain or discomfort due to transient myocardial ischemia. It is a symptom of myocardial oxygen demand exceeding supply, often precipitated by physical exertion or emotional stress. The importance of effective and rapid relief from angina symptoms cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the quality of life and reduces the risk of more severe cardiac events.
The role of nitroglycerin in managing angina is well-established. Nitroglycerin works by relaxing vascular smooth muscle, leading to vasodilation. This action decreases myocardial oxygen demand by reducing preload (the initial stretching of the cardiac myocytes prior to contraction) and, to a lesser extent, afterload (the pressure against which the heart must work to eject blood during systole). Additionally, nitroglycerin can cause dilation of coronary arteries, potentially improving blood flow to ischemic areas of the myocardium. The sublingual form of nitroglycerin is particularly beneficial due to its rapid onset of action, which is crucial for the immediate relief of angina symptoms.
Understanding how nitroglycerin sublingual tablets work and their proper use is essential for patients suffering from angina. The sublingual route of administration allows for the rapid absorption of nitroglycerin into the bloodstream, bypassing first-pass metabolism. This leads to a quick onset of action, typically within 1 to 3 minutes, making it an ideal choice for the acute management of angina attacks. However, it is also important to recognize the potential side effects and contraindications associated with nitroglycerin use, such as headache, hypotension, and interactions with phosphodiesterase inhibitors.
Nitroglycerin Sublingual Tablets Mechanism of Action

The mechanism of action of nitroglycerin sublingual tablets involves the release of nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator. Nitric oxide stimulates the production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in vascular smooth muscle cells, leading to smooth muscle relaxation. This relaxation results in the dilation of blood vessels, which in turn reduces the workload on the heart and decreases the oxygen demand of the myocardium. The rapid vasodilatory effect of nitroglycerin provides quick relief from angina symptoms by improving myocardial oxygen supply and reducing oxygen demand.
Benefits of Nitroglycerin Sublingual Tablets
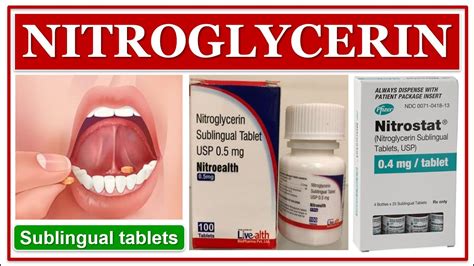
The benefits of nitroglycerin sublingual tablets are multifaceted. They offer a rapid and effective way to manage angina symptoms, improving the patient's quality of life. Key benefits include:
- Rapid onset of action: Providing quick relief from angina pain.
- Ease of use: Sublingual tablets are easy to administer, especially during an angina attack.
- Improved exercise tolerance: By reducing angina frequency and severity, patients can engage in physical activities with more confidence.
- Reduced risk of myocardial infarction: Although not a primary preventive measure, effective management of angina can contribute to a reduced risk of heart attacks by avoiding prolonged ischemic episodes.
Administration and Dosage
The administration of nitroglycerin sublingual tablets is straightforward. Patients are typically advised to sit or lie down and place the tablet under the tongue at the first sign of an angina attack. The tablet should be allowed to dissolve completely without swallowing. If symptoms persist after the initial dose, additional doses can be taken at intervals of approximately 5 minutes, up to a maximum of 3 doses. If pain persists after 3 doses, medical attention should be sought immediately.Side Effects and Contraindications

While nitroglycerin sublingual tablets are effective, they are not without side effects and contraindications. Common side effects include headache, due to the vasodilatory effects, and hypotension, which can lead to dizziness or lightheadedness. Less common but more serious side effects include methemoglobinemia, a condition where an abnormal amount of methemoglobin is produced, reducing the amount of oxygen delivered to the body's tissues. Contraindications include recent use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil), severe anemia, and increased intracranial pressure.
Interactions with Other Medications
Nitroglycerin can interact with various medications, either enhancing its effects or increasing the risk of side effects. For instance, concurrent use with other vasodilators can exacerbate hypotension. Additionally, the use of nitroglycerin with certain antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), may increase the risk of hypotension.Practical Considerations for Patients

For patients prescribed nitroglycerin sublingual tablets, several practical considerations must be kept in mind:
- Storage and Handling: The tablets should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. They should be kept in their original container to protect them from light.
- Expiration Date: Patients should ensure that their supply of nitroglycerin is not past its expiration date, as the efficacy of the medication cannot be guaranteed beyond this point.
- Lifestyle Modifications: While nitroglycerin provides symptom relief, patients should also focus on lifestyle modifications to reduce the frequency and severity of angina attacks. This includes smoking cessation, regular exercise, weight management, and a healthy diet.
Statistical Data on Efficacy
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of nitroglycerin in managing angina. For example, one study found that nitroglycerin sublingual tablets provided relief from angina symptoms in over 90% of patients within 5 minutes of administration. Another study highlighted the importance of nitroglycerin in reducing the frequency of angina attacks, with patients experiencing a significant decrease in episodes per week.Future Directions in Angina Management
As medical science continues to evolve, future directions in angina management may include the development of new vasodilatory agents with improved efficacy and safety profiles. Additionally, advancements in personalized medicine could lead to tailored treatment plans that address the specific pathophysiological mechanisms underlying an individual's angina. The integration of lifestyle interventions, such as stress management and dietary changes, into comprehensive treatment plans is also expected to play a more significant role.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the effectiveness of nitroglycerin, challenges persist in the management of angina, including patient adherence to medication regimens and the presence of comorbid conditions that can complicate treatment. Opportunities for improvement include enhanced patient education, the development of more convenient drug delivery systems, and a greater emphasis on preventive cardiology to reduce the incidence of angina and other cardiovascular diseases.Conclusion and Recommendations

In conclusion, nitroglycerin sublingual tablets remain a vital component in the management of angina pectoris, offering rapid and effective relief from symptoms. However, their use must be balanced with an understanding of potential side effects and contraindications. Patients should be educated on the proper use of these tablets, the importance of adherence to prescribed regimens, and the need for concurrent lifestyle modifications to manage angina effectively. As the field of cardiology continues to advance, it is essential to stay updated on the latest guidelines and treatments for angina, ensuring that patients receive the most effective and personalized care possible.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with nitroglycerin sublingual tablets in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us create content that addresses the needs and concerns of our readers.
What are the common side effects of nitroglycerin sublingual tablets?
+Common side effects include headache and hypotension, which can lead to dizziness or lightheadedness.
How should nitroglycerin sublingual tablets be administered?
+The tablet should be placed under the tongue at the first sign of an angina attack and allowed to dissolve completely without swallowing.
What are the contraindications for the use of nitroglycerin sublingual tablets?
+Contraindications include recent use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors, severe anemia, and increased intracranial pressure.
