Intro
Discover the 5 stages of non-REM sleep, including N1, N2, and N3, and learn about sleep cycles, brain waves, and deep sleep patterns.
The stages of non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) sleep are crucial for our overall health and well-being. Non-REM sleep is divided into three stages, with each stage having distinct brain wave patterns and physiological characteristics. Understanding these stages can help us appreciate the importance of sleep in our lives. In this article, we will delve into the 5 stages of non-REM sleep, exploring their features, functions, and significance.
Non-REM sleep is essential for our physical and mental restoration. During non-REM sleep, our body repairs and regenerates tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens our immune system. Non-REM sleep also plays a critical role in brain development and plasticity, with research suggesting that it helps to clear waste from the brain, including beta-amyloid plaques associated with Alzheimer's disease. Furthermore, non-REM sleep has been linked to improved cognitive function, including attention, memory, and problem-solving skills.
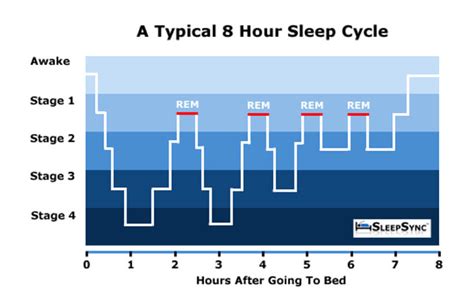
The different stages of non-REM sleep are characterized by distinct brain wave patterns, which can be measured using electroencephalography (EEG). These brain waves are classified into different frequency bands, including delta, theta, and alpha waves. Each stage of non-REM sleep has a unique brain wave signature, which reflects the level of cortical activity and the degree of consciousness. By understanding these brain wave patterns, researchers can gain insights into the neural mechanisms underlying non-REM sleep and its functions.
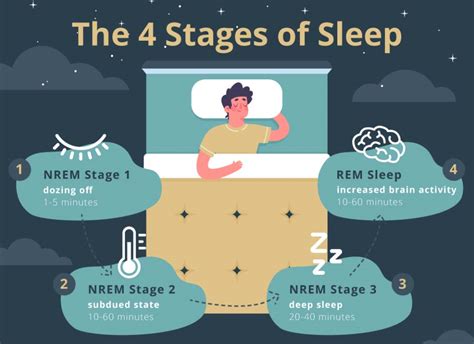
Stage 1 Non-REM Sleep
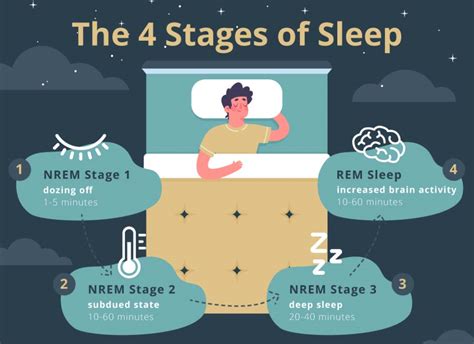
Stage 2 Non-REM Sleep
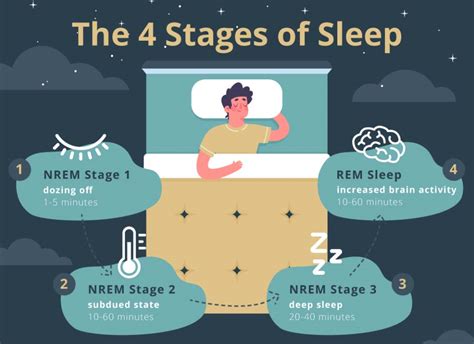
Stage 3 Non-REM Sleep
Functions of Stage 3 Non-REM Sleep
Stage 3 non-REM sleep has several critical functions, including: * Repair and regeneration of tissues * Building and strengthening of bone and muscle * Strengthening of the immune system * Clearance of waste from the brain * Improved cognitive function, including attention, memory, and problem-solving skillsStage 4 Non-REM Sleep
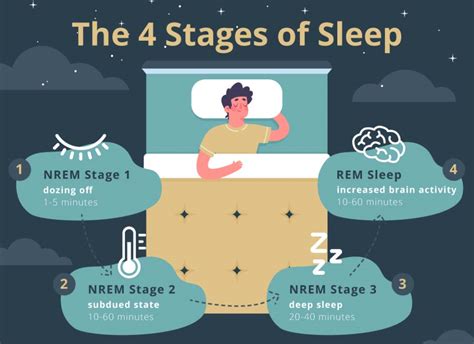
Stage 5 Non-REM Sleep
Benefits of Non-REM Sleep
Non-REM sleep has several benefits, including: * Physical restoration and repair * Improved cognitive function, including attention, memory, and problem-solving skills * Strengthening of the immune system * Clearance of waste from the brain * Improved mood and emotional regulationIn addition to these benefits, non-REM sleep also plays a critical role in brain development and plasticity. Research has shown that non-REM sleep is essential for the consolidation of memories, with the brain replaying and processing previously experienced events during this stage. Non-REM sleep also helps to clear beta-amyloid plaques from the brain, which are associated with Alzheimer's disease.
What is the function of Stage 1 non-REM sleep?
+Stage 1 non-REM sleep is the transition phase between wakefulness and sleep, during which the brain waves slow down, and the individual becomes less responsive to their environment.
What is the characteristic brain wave pattern of Stage 3 non-REM sleep?
+Stage 3 non-REM sleep is characterized by delta waves, which have a frequency of 0.5-4 Hz.
What is the benefit of non-REM sleep for cognitive function?
+Non-REM sleep improves cognitive function, including attention, memory, and problem-solving skills.
In conclusion, the stages of non-REM sleep are critical for our physical and mental restoration. By understanding the different stages of non-REM sleep, we can appreciate the importance of sleep in our lives and take steps to prioritize sleep and maintain good sleep hygiene. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with non-REM sleep in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to explore other articles on sleep and cognitive function, and to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about the importance of sleep.
