Intro
Master your 5 A1c range with expert tips, managing blood sugar levels, diabetes control, and healthy glucose monitoring for optimal results.
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is crucial for individuals with diabetes. The A1c test is a vital tool in managing the condition, providing a snapshot of average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. Understanding the A1c range and how to manage it can significantly impact the quality of life for those living with diabetes. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the A1c range, its implications for health, and provide valuable tips on how to maintain a healthy A1c level.
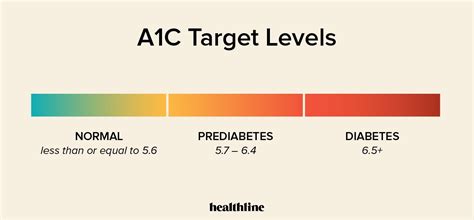
The A1c test measures the percentage of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells. This measurement gives healthcare providers insight into how well diabetes is being managed. For people without diabetes, a normal A1c range is typically below 5.7%. For those with diabetes, the goal is often set below 7%, though this can vary based on individual health goals and risk factors. Managing A1c levels is not just about achieving a number; it's about reducing the risk of long-term complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage.
Understanding one's A1c range and working towards managing it effectively can be empowering. It involves a combination of medication, diet, exercise, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly. The journey to maintaining a healthy A1c level requires dedication, support, and the right strategies. By focusing on lifestyle changes and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can better manage their diabetes and improve their overall health. The goal is not just to control blood sugar levels but to enhance the quality of life, ensuring that diabetes does not define one's potential or well-being.
A1c Range Explained
Importance of A1c Testing
A1c testing is not just a diagnostic tool but a critical component of diabetes management. It provides a broader view of blood sugar control compared to daily glucose monitoring, which only offers a snapshot of the current glucose level. Regular A1c tests help in assessing the effectiveness of the current treatment plan, guiding adjustments in medication, diet, or exercise as needed. Moreover, achieving and maintaining a healthy A1c level can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, improving long-term health outcomes.Tips for Managing A1c Levels

Benefits of Healthy A1c Levels
Maintaining a healthy A1c level has numerous benefits, including reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications. These complications can affect various parts of the body, including the eyes (leading to diabetic retinopathy), kidneys (nephropathy), nerves (neuropathy), and heart (increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke). By managing A1c levels effectively, individuals can also improve their quality of life, enhance their physical and mental well-being, and reduce healthcare costs associated with managing complications.Lifestyle Changes for Better A1c Management

Technological Tools for A1c Management
Technology has revolutionized diabetes management, offering a range of tools and devices that can help monitor and control blood glucose levels. These include: - **Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)**: CGMs provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night, offering insights into glucose trends and patterns. - **Insulin Pumps**: Insulin pumps allow for more precise insulin dosing and can be programmed to deliver insulin continuously (basal rate) and in boluses (before meals). - **Mobile Apps**: Various mobile apps are designed to help track blood glucose levels, carbohydrate intake, physical activity, and medication adherence. They can also provide reminders and offer educational content to support diabetes management.Nutritional Strategies for A1c Control

Physical Activity and A1c Management
Regular physical activity is essential for managing A1c levels. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, helping the body to more effectively use insulin. Types of physical activity that can benefit A1c management include: - **Aerobic Exercise**: Activities like walking, cycling, and swimming can improve cardiovascular health and lower blood glucose levels. - **Resistance Training**: Building muscle through resistance exercises can improve insulin sensitivity and help with weight management. - **High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)**: HIIT involves short bursts of high-intensity exercise followed by brief periods of rest. It can be particularly effective in improving insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular health.Psychological Aspects of A1c Management

Future Directions in A1c Management
The future of A1c management holds promise with advancements in technology, medication, and our understanding of diabetes pathophysiology. Emerging trends include: - **Personalized Medicine**: Tailoring treatment plans to the individual's genetic profile, lifestyle, and health status. - **Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diabetes Management**: Using AI to analyze data from glucose monitors, insulin pumps, and mobile apps to predict blood glucose levels and provide personalized recommendations. - **Stem Cell Research**: Exploring the potential of stem cells in regenerating pancreatic beta cells, which could potentially cure type 1 diabetes.Conclusion and Next Steps

As you continue on your journey to manage your A1c levels and improve your overall health, remember the importance of staying informed, connected, and proactive. Share your experiences, ask questions, and seek support from healthcare professionals and community resources. Together, we can strive towards better health outcomes and a brighter future for those living with diabetes.
What is a normal A1c range for individuals without diabetes?
+A normal A1c level for individuals without diabetes is typically below 5.7%.
How often should I get an A1c test if I have diabetes?
+The frequency of A1c tests can vary depending on the individual's health status and how well their diabetes is managed. Generally, it is recommended to get an A1c test at least twice a year if your diabetes is well-controlled, and more frequently if your treatment plan is being adjusted or if you are not meeting your blood glucose targets.
Can lifestyle changes alone lower my A1c level?
+Yes, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular physical activity, weight loss (if needed), and not smoking can significantly lower your A1c level. For some individuals, especially those with prediabetes or newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes alone may be enough to manage their condition and lower their A1c level.
