Intro
Discover the normal B12 level range and understand vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms, causes, and diagnosis, including methylmalonic acid and homocysteine tests, to maintain optimal health.
Maintaining adequate levels of vitamin B12 is crucial for the proper functioning of the human body. Vitamin B12 plays a significant role in the production of red blood cells, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to various health issues, including anemia, fatigue, and neurological problems. Understanding the normal B12 level range is essential for identifying potential deficiencies and taking corrective measures. In this article, we will delve into the importance of vitamin B12, the normal B12 level range, and the factors that influence these levels.
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that is naturally found in animal products, such as meat, fish, and dairy products. The human body requires vitamin B12 to produce red blood cells, which carry oxygen to different parts of the body. Vitamin B12 also plays a crucial role in the maintenance of the nervous system and the synthesis of DNA. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to a range of health problems, including weakness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, a vitamin B12 deficiency can cause neurological problems, such as numbness and tingling in the hands and feet.
The normal B12 level range is typically measured in picograms per milliliter (pg/mL) or nanograms per liter (ng/L). The normal range for vitamin B12 levels can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors. Generally, a normal vitamin B12 level is considered to be between 200 and 900 pg/mL. Levels below 200 pg/mL are considered deficient, while levels above 900 pg/mL are considered elevated. It is essential to note that vitamin B12 levels can fluctuate over time, and a single test result may not accurately reflect an individual's vitamin B12 status.
Vitamin B12 Level Ranges
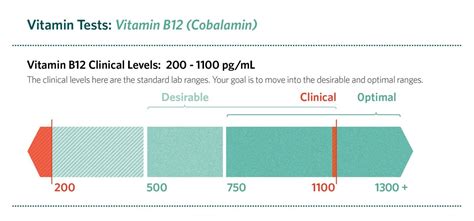
Factors that Influence Vitamin B12 Levels
Several factors can influence vitamin B12 levels, including diet, age, and certain medical conditions. For example, individuals who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet may be at risk of vitamin B12 deficiency, as plant-based foods are not natural sources of vitamin B12. Older adults may also be at risk of vitamin B12 deficiency, as the ability to absorb vitamin B12 from food decreases with age. Certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease and Crohn's disease, can also interfere with vitamin B12 absorption.Vitamin B12 Deficiency
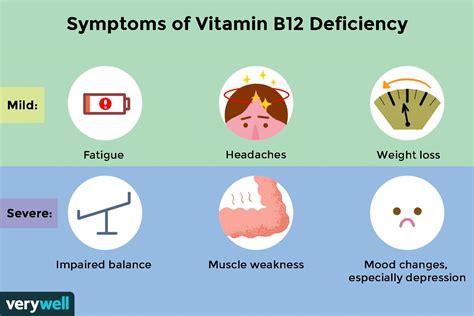
Treatment Options for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Treatment for vitamin B12 deficiency typically involves supplementing with vitamin B12 supplements or injections. The type and duration of treatment depend on the underlying cause of the deficiency and the individual's overall health status. In some cases, dietary changes may be recommended to help increase vitamin B12 intake. For example, individuals who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet may be advised to consume fortified plant-based milk or take vitamin B12 supplements.Vitamin B12 Toxicity

Risks and Complications of Vitamin B12 Toxicity
The risks and complications of vitamin B12 toxicity are relatively rare, but they can be serious. For example, high levels of vitamin B12 can increase the risk of liver damage and other health problems. In severe cases, vitamin B12 toxicity can cause seizures, coma, and even death. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any vitamin B12 supplements or injections to determine the safe and effective dosage.Importance of Vitamin B12 Testing
How to Prepare for Vitamin B12 Testing
Preparing for vitamin B12 testing is relatively straightforward. Individuals are typically required to fast for several hours before the test to ensure accurate results. In some cases, individuals may be required to stop taking certain medications or supplements that can interfere with the test results. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the specific preparation requirements for vitamin B12 testing.Normal B12 Level Range in Different Age Groups
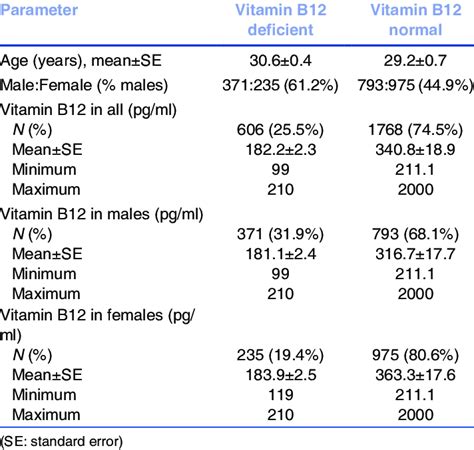
Normal B12 Level Range in Infants and Children
The normal B12 level range in infants and children is typically higher than in adults. Infants require around 0.4-1.2 mcg of vitamin B12 per day, while children require around 1.2-2.4 mcg per day. Breast milk is a rich source of vitamin B12, and breastfed infants typically have higher levels of vitamin B12 than formula-fed infants.Normal B12 Level Range in Adults
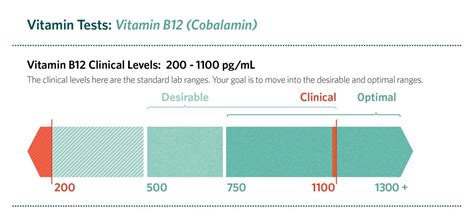
Normal B12 Level Range in Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
Pregnant and breastfeeding women require higher levels of vitamin B12 to support fetal growth and development. The normal B12 level range in pregnant women is typically between 200 and 900 pg/mL, while breastfeeding women require around 2.6-2.8 mcg of vitamin B12 per day.Conclusion and Recommendations
Final Thoughts
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the importance of vitamin B12 and the normal B12 level range. We encourage readers to take an active role in maintaining their vitamin B12 levels and to consult with a healthcare professional if they have any concerns. By prioritizing vitamin B12, individuals can support optimal health and reduce the risk of deficiency and toxicity.What is the normal B12 level range?
+The normal B12 level range is typically between 200 and 900 pg/mL.
What are the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency?
+The symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
How can I maintain optimal vitamin B12 levels?
+Individuals can maintain optimal vitamin B12 levels by prioritizing vitamin B12-rich foods, considering supplements or injections if necessary, and undergoing regular testing to monitor vitamin B12 levels.
