Intro
Learn about normal blood glucose levels, blood sugar control, and glucose monitoring to manage diabetes and prediabetes, maintaining healthy glucose levels.
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When blood glucose levels are within a normal range, the body functions properly, and the risk of developing chronic diseases is reduced. On the other hand, abnormal blood glucose levels can lead to serious health complications, such as diabetes, heart disease, and nerve damage. In this article, we will delve into the importance of normal blood glucose levels, their benefits, and provide guidance on how to maintain them.
The human body is designed to regulate blood glucose levels within a narrow range. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach, releases insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the blood. As glucose enters the cells, blood glucose levels decrease. Conversely, when we fast or haven't eaten for a while, the pancreas releases glucagon, a hormone that stimulates the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, increasing blood glucose levels. This delicate balance is essential for maintaining normal blood glucose levels.
Understanding normal blood glucose levels is vital for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Normal blood glucose levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as food intake, physical activity, and sleep patterns. For individuals without diabetes, normal blood glucose levels are typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) when fasting and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. It's essential to note that these values can vary slightly depending on the individual and the laboratory conducting the test.
Benefits of Normal Blood Glucose Levels

Reducing the Risk of Chronic Diseases
Normal blood glucose levels can significantly reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. High blood glucose levels can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs, increasing the risk of these conditions. By maintaining normal blood glucose levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing these diseases and improve their overall health.Improving Energy Levels
Normal blood glucose levels can improve energy levels by allowing the body to efficiently use glucose for energy. When blood glucose levels are within a normal range, the body can transport glucose to cells, where it is converted into energy. This can improve physical performance, reduce fatigue, and enhance overall well-being.Maintaining Normal Blood Glucose Levels
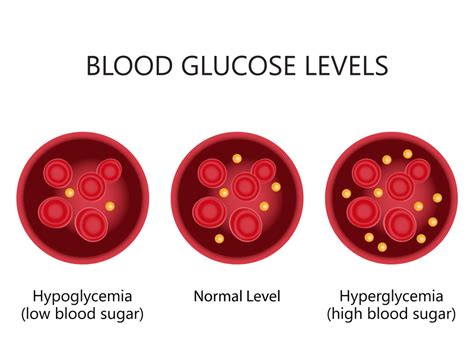
Healthy Eating Habits
Healthy eating habits play a crucial role in maintaining normal blood glucose levels. A balanced diet that is rich in whole foods can help regulate blood glucose levels and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Some tips for healthy eating include: * Eating regular meals to maintain stable blood glucose levels * Choosing whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins * Limiting sugary drinks and foods high in added sugars * Drinking plenty of water to stay hydratedRegular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Some tips for regular physical activity include: * Aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week * Incorporating strength-training exercises into your routine * Finding activities that you enjoy, such as walking, jogging, or cyclingMonitoring Blood Glucose Levels
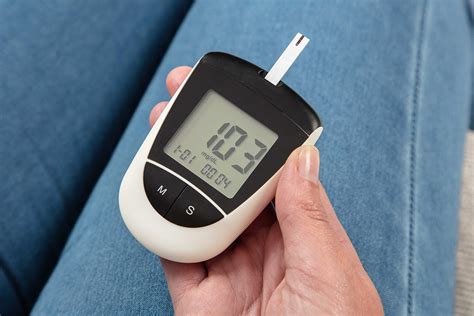
Fasting Blood Glucose Tests
Fasting blood glucose tests measure blood glucose levels after an overnight fast. This test is typically performed in the morning, before eating or drinking anything. Fasting blood glucose tests can help diagnose diabetes and monitor blood glucose control.Postprandial Blood Glucose Tests
Postprandial blood glucose tests measure blood glucose levels after eating. This test can help individuals understand how their body responds to different foods and carbohydrates. Postprandial blood glucose tests can also help monitor blood glucose control and adjust treatment plans as needed.Treatment Options for Abnormal Blood Glucose Levels
Medications
Medications, such as metformin or sulfonylureas, can help regulate blood glucose levels. These medications work by improving insulin sensitivity, reducing glucose production in the liver, or increasing insulin secretion.Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy involves injecting insulin into the body to help regulate blood glucose levels. Insulin therapy is typically used for individuals with type 1 diabetes or those with type 2 diabetes who require insulin to control their blood glucose levels.Prevention and Early Detection

Risk Factors for Diabetes
Individuals with certain risk factors, such as a family history of diabetes, obesity, or physical inactivity, are more likely to develop diabetes. It's essential for these individuals to be aware of their risk factors and take steps to reduce their risk.Screening for Diabetes
Screening for diabetes is essential for early detection and treatment. Individuals with risk factors for diabetes should be screened regularly, and those with symptoms of diabetes should seek medical attention immediately.What are normal blood glucose levels?
+Normal blood glucose levels are typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL when fasting and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating.
How can I maintain normal blood glucose levels?
+Maintaining normal blood glucose levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and stress management.
What are the benefits of normal blood glucose levels?
+Maintaining normal blood glucose levels offers numerous benefits, including reducing the risk of chronic diseases, improving energy levels, and enhancing cognitive function.
How can I monitor my blood glucose levels?
+Monitoring blood glucose levels can be done through fasting blood glucose tests, postprandial blood glucose tests, or continuous glucose monitoring systems.
What are the treatment options for abnormal blood glucose levels?
+Treatment options for abnormal blood glucose levels depend on the individual's specific needs and medical history, and may include medications, insulin therapy, or lifestyle modifications.
In conclusion, maintaining normal blood glucose levels is essential for overall health and well-being. By understanding the benefits of normal blood glucose levels, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and monitoring blood glucose levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases and improve their overall health. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on maintaining normal blood glucose levels, and to take action today to prioritize your health and well-being.
