Intro
Learn the normal blood glucose level range and understand healthy blood sugar levels, glucose tolerance, and glycemic control to manage diabetes and prediabetes effectively.
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. The level of glucose in the blood is tightly regulated by the body's homeostatic mechanisms, and any significant deviations from the normal range can lead to various health problems. In this article, we will delve into the importance of normal blood glucose levels, the factors that influence them, and the consequences of abnormal blood glucose levels.
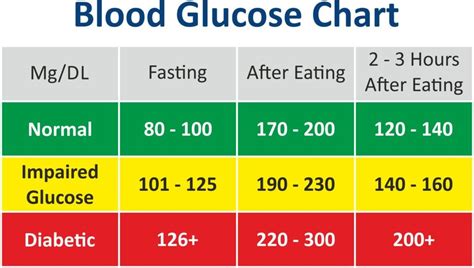
The normal blood glucose level range is a critical aspect of health that is often overlooked until it becomes a problem. The body's ability to regulate blood glucose levels is essential for maintaining energy homeostasis, preventing complications, and ensuring proper bodily functions. The normal range for blood glucose levels is typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), although this can vary slightly depending on the individual, their diet, and their physical activity level. Understanding the factors that influence blood glucose levels and the consequences of abnormal levels is vital for maintaining optimal health.
The importance of normal blood glucose levels cannot be overstated. When blood glucose levels are within the normal range, the body's cells can function properly, and energy is produced efficiently. However, when blood glucose levels are consistently high or low, it can lead to a range of health problems, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurological damage. Furthermore, abnormal blood glucose levels can also affect cognitive function, mood, and overall quality of life. Therefore, it is essential to understand the factors that influence blood glucose levels and take steps to maintain normal levels.
Understanding Blood Glucose Levels

Factors That Influence Blood Glucose Levels
Several factors can influence blood glucose levels, including: * Diet: The type and amount of carbohydrates consumed can significantly impact blood glucose levels. * Physical activity: Regular physical activity can help to lower blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity. * Stress: Chronic stress can raise blood glucose levels and worsen insulin resistance. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood glucose regulation and increase the risk of developing insulin resistance. * Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and some psychiatric medications, can raise blood glucose levels.Normal Blood Glucose Level Range

Consequences of Abnormal Blood Glucose Levels
Abnormal blood glucose levels can have serious consequences, including: * Diabetes: Consistently high blood glucose levels can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. * Cardiovascular disease: High blood glucose levels can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease. * Neurological damage: High blood glucose levels can damage nerves and increase the risk of neurological disorders, such as neuropathy and dementia. * Cognitive impairment: Abnormal blood glucose levels can affect cognitive function, including memory, attention, and decision-making.Maintaining Normal Blood Glucose Levels
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for maintaining normal levels and preventing complications. There are several ways to monitor blood glucose levels, including: * Fasting blood glucose tests: Measure blood glucose levels after an overnight fast. * Postprandial blood glucose tests: Measure blood glucose levels after eating a meal. * Continuous glucose monitoring: Use a device to track blood glucose levels throughout the day. * Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) tests: Measure average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with maintaining normal blood glucose levels in the comments below. Have you found any particularly effective strategies for regulating your blood glucose levels? Do you have any questions or concerns about blood glucose levels or diabetes? Share your story and help others who may be struggling with similar issues.
What is the normal range for blood glucose levels?
+The normal range for blood glucose levels is typically between 70 and 140 mg/dL, although this can vary slightly depending on the individual, their diet, and their physical activity level.
What are the consequences of consistently high blood glucose levels?
+Consistently high blood glucose levels can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, neurological damage, and cognitive impairment.
How can I maintain normal blood glucose levels?
+Maintaining normal blood glucose levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, including eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and getting enough sleep.
