Intro
Learn about the normal glucose range, blood sugar levels, and glucose monitoring to manage diabetes and prediabetes, understanding glycemic control and healthy glucose targets.
Maintaining a normal glucose range is crucial for overall health and well-being. Glucose, a type of sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. The body regulates blood glucose levels through a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and hormones like insulin and glucagon. Understanding the normal glucose range and its significance can help individuals take proactive steps to manage their blood sugar levels and prevent related health issues.
The importance of maintaining a normal glucose range cannot be overstated. When blood glucose levels are within the normal range, the body functions optimally, and the risk of developing conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and certain neurological disorders is minimized. On the other hand, consistently high or low blood glucose levels can lead to serious health complications, including organ damage, nerve damage, and even death. Therefore, it is essential to comprehend the factors that influence blood glucose levels and learn how to maintain them within a healthy range.
The normal glucose range varies slightly depending on the time of day, meal consumption, and individual factors like age and physical activity level. Generally, a normal fasting blood glucose level is between 70 and 99 mg/dL, while a normal postprandial (after meal) blood glucose level is less than 140 mg/dL. These values are critical for diagnosing and managing diabetes, as well as for assessing the risk of developing insulin resistance and other metabolic disorders. By understanding these values and taking steps to maintain a healthy glucose range, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing these conditions and promote overall well-being.
Understanding Blood Glucose Levels

Factors Influencing Blood Glucose Levels
Several factors can impact blood glucose levels, including: * Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods can cause a rapid increase in blood glucose levels. * Physical activity: Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, reducing blood glucose levels. * Stress: Chronic stress can raise blood glucose levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones like cortisol. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood glucose regulation, leading to increased levels. * Certain medications: Some medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric drugs, can increase blood glucose levels.Maintaining a Normal Glucose Range

Benefits of Maintaining a Normal Glucose Range
Maintaining a normal glucose range offers numerous benefits, including: * Reduced risk of developing diabetes and related complications * Improved heart health and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease * Enhanced cognitive function and reduced risk of neurological disorders * Increased energy levels and improved overall physical performance * Reduced risk of certain cancers, such as pancreatic cancerDietary Strategies for Maintaining a Normal Glucose Range

Physical Activity and Blood Glucose Levels
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a normal glucose range. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. Additionally, incorporate strength-training exercises, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), and other forms of physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels.Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
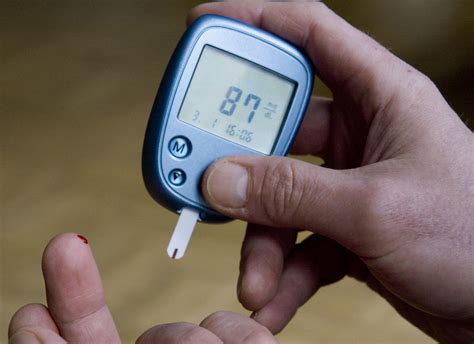
Interpreting Blood Glucose Results
Interpreting blood glucose results requires understanding the normal glucose range and the factors that influence blood glucose levels. Use the following guidelines to interpret blood glucose results: * Fasting blood glucose: 70-99 mg/dL * Postprandial blood glucose: less than 140 mg/dL * Random blood glucose: less than 140 mg/dLManaging Stress and Sleep for a Normal Glucose Range

Strategies for Managing Stress
Use the following strategies to manage stress and maintain a normal glucose range: * Meditation: practice mindfulness meditation or guided meditation * Yoga: engage in yoga practices like Hatha, Vinyasa, or Restorative yoga * Deep breathing exercises: practice diaphragmatic breathing or box breathing * Physical activity: engage in regular physical activity to reduce stress and improve moodConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on maintaining a normal glucose range. How do you manage your blood glucose levels? What strategies have you found most effective? Share your comments below and help others learn from your experiences.
What is the normal glucose range for adults?
+The normal glucose range for adults is between 70 and 99 mg/dL for fasting blood glucose and less than 140 mg/dL for postprandial blood glucose.
How can I maintain a normal glucose range?
+Maintain a normal glucose range by incorporating dietary strategies, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep into daily life. Monitor blood glucose levels regularly and adjust lifestyle factors as needed.
What are the benefits of maintaining a normal glucose range?
+Maintaining a normal glucose range offers numerous benefits, including reduced risk of developing diabetes and related complications, improved heart health, and enhanced cognitive function.
