Intro
Learn normal glucose reading levels, optimal blood sugar ranges, and healthy targets for fasting, postprandial, and random glucose tests to manage diabetes and prediabetes effectively.
Maintaining normal glucose reading levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Glucose, a type of sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When glucose levels are within a normal range, the body functions properly, and the risk of developing various health problems is minimized. On the other hand, abnormal glucose levels can lead to serious health issues, such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. In this article, we will delve into the importance of normal glucose reading levels, the factors that affect them, and the ways to maintain optimal glucose levels.
Glucose levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Normal glucose reading levels vary depending on the time of day, the last meal, and other factors. For example, glucose levels tend to be higher after eating and lower after fasting. Understanding normal glucose reading levels is essential for individuals with diabetes or those who are at risk of developing the condition. By monitoring glucose levels regularly, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication to maintain optimal glucose control.
The importance of normal glucose reading levels cannot be overstated. When glucose levels are within a normal range, the body's cells receive the energy they need to function properly. This, in turn, helps to maintain healthy blood vessels, nerves, and organs. On the other hand, high or low glucose levels can lead to a range of health problems, including nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision loss. Furthermore, abnormal glucose levels can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. By maintaining normal glucose reading levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing these health problems and enjoy overall better health and well-being.
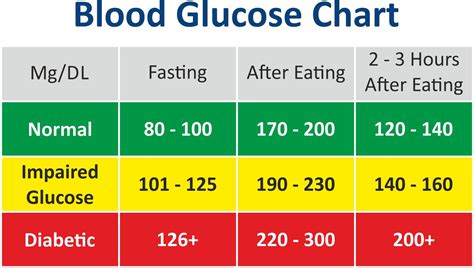
Normal Glucose Reading Levels: What Are They?

Factors That Affect Glucose Levels
Several factors can affect glucose levels, including diet, exercise, medication, and stress. For example, eating foods that are high in sugar and carbohydrates can cause glucose levels to rise, while regular exercise can help to lower glucose levels. Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can also affect glucose levels. Stress can also raise glucose levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline.How to Maintain Normal Glucose Reading Levels
Benefits of Maintaining Normal Glucose Reading Levels
Maintaining normal glucose reading levels has numerous benefits, including: * Reduced risk of developing diabetes and related health problems * Improved energy levels and overall health and well-being * Lower risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions * Improved cognitive function and reduced risk of dementia * Healthier blood vessels, nerves, and organsMonitoring Glucose Levels
Interpreting Glucose Test Results
Interpreting glucose test results requires understanding the different types of tests and their corresponding reference ranges. Here are some general guidelines: * FPG test: Less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) is normal, 100-125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L) is impaired fasting glucose, and 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) or higher is diabetes. * OGTT: Less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) is normal, 140-199 mg/dL (7.8-11 mmol/L) is impaired glucose tolerance, and 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher is diabetes. * Random plasma glucose test: Less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) is normal, 140-199 mg/dL (7.8-11 mmol/L) is impaired glucose regulation, and 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher is diabetes.Treatment Options for Abnormal Glucose Levels
Complications of Abnormal Glucose Levels
Abnormal glucose levels can lead to a range of complications, including: * Diabetes: High glucose levels can damage the pancreas and lead to diabetes. * Heart disease: High glucose levels can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. * Kidney disease: High glucose levels can damage the kidneys and lead to kidney failure. * Nerve damage: High glucose levels can damage the nerves and lead to numbness, tingling, and pain.Prevention Strategies

Risk Factors for Abnormal Glucose Levels
Risk factors for abnormal glucose levels include: * Family history of diabetes * Obesity * Physical inactivity * Unhealthy diet * Age: Risk increases with age, especially after 45 years * Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and American Indians, are at higher riskConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with maintaining normal glucose reading levels in the comments section below. Your feedback and insights can help others who are struggling with glucose control. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with your friends and family on social media.
What are normal glucose reading levels?
+Normal glucose reading levels vary depending on the time of day and other factors. For individuals without diabetes, normal glucose levels are typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL (3.9 and 5.5 mmol/L) when fasting and less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) two hours after eating.
How can I maintain normal glucose reading levels?
+Maintaining normal glucose reading levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits and, if necessary, medication. This includes eating a healthy, balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, getting enough sleep each night, and managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
What are the complications of abnormal glucose levels?
+Abnormal glucose levels can lead to a range of complications, including diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. High glucose levels can damage the pancreas, blood vessels, nerves, and organs, leading to serious health problems.
