Intro
A newborn baby's temperature is a vital sign that healthcare providers closely monitor to ensure the baby's health and well-being. Normal newborn temperature is an essential aspect of neonatal care, and any deviations from the normal range can indicate potential health issues. In this article, we will delve into the world of newborn temperature, exploring its importance, the normal temperature range, and the factors that can influence it.
Newborn babies are vulnerable to temperature fluctuations due to their immature thermoregulation mechanisms. The first few days of life are critical, and maintaining a stable body temperature is crucial for the baby's overall health. Healthcare providers use various methods to monitor a newborn's temperature, including axillary, rectal, and tympanic measurements. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, but they all provide valuable insights into the baby's thermal status.
The normal temperature range for newborns is between 97.7°F (36.5°C) and 99.5°F (37.5°C). This range may vary slightly depending on the measurement method and the baby's age. It is essential to note that newborns can quickly become hypothermic or hyperthermic due to their high surface-to-volume ratio and limited thermoregulatory capabilities. Healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring temperature and taking prompt action if any deviations from the normal range are detected.
Importance of Normal Newborn Temperature
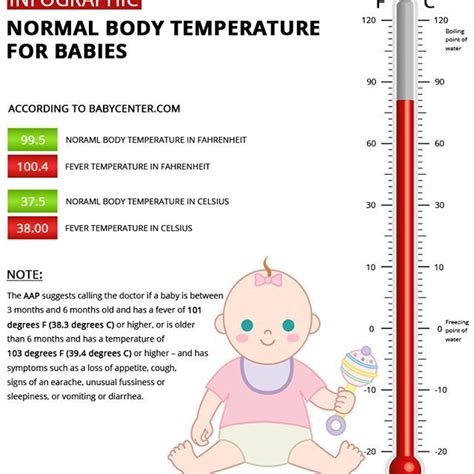
Factors Influencing Newborn Temperature
Several factors can influence a newborn's temperature, including environmental temperature, clothing, and medical conditions. Premature babies are more susceptible to temperature fluctuations due to their immature thermoregulation mechanisms and limited body fat. Additionally, babies with certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or adrenal insufficiency, may have impaired thermoregulation, making it challenging to maintain a normal body temperature.Monitoring Newborn Temperature
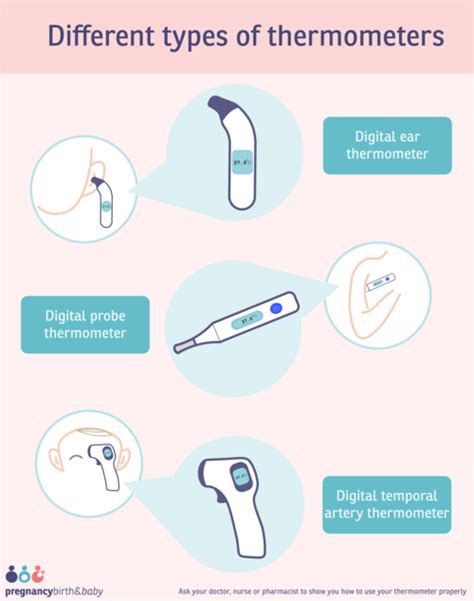
Thermoregulation Mechanisms
Newborns have immature thermoregulation mechanisms, which make them vulnerable to temperature fluctuations. The hypothalamus, the part of the brain that regulates body temperature, is not fully developed in newborns, making it challenging for them to maintain a stable body temperature. Additionally, newborns have a high surface-to-volume ratio, which means they lose heat quickly. Healthcare providers must be aware of these factors and take steps to ensure that the baby's environment is warm and stable.Consequences of Abnormal Newborn Temperature

Prevention and Treatment
Preventing and treating abnormal newborn temperature is crucial to ensuring the baby's health and well-being. Healthcare providers can take several steps to prevent abnormal newborn temperature, including: * Maintaining a warm and stable environment * Using warm blankets or clothing to keep the baby warm * Monitoring the baby's temperature closely * Providing adequate nutrition and hydration * Avoiding overheating or overcooling the babyParental Education and Awareness
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, normal newborn temperature is a vital aspect of neonatal care, and any deviations from the normal range can indicate potential health issues. Healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring temperature and taking prompt action if any deviations from the normal range are detected. Future research should focus on developing more effective methods for monitoring and maintaining normal newborn temperature, as well as educating parents and healthcare providers on the importance of thermoregulation in newborns.What is the normal temperature range for newborns?
+The normal temperature range for newborns is between 97.7°F (36.5°C) and 99.5°F (37.5°C).
What are the consequences of abnormal newborn temperature?
+Abnormal newborn temperature can have serious consequences, including hypothermia, hyperthermia, increased risk of infection, and respiratory distress.
How can parents maintain normal newborn temperature?
+Parents can maintain normal newborn temperature by keeping the baby warm, monitoring the baby's temperature closely, and providing adequate nutrition and hydration.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into the importance of normal newborn temperature. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with your friends and family. Remember, maintaining a normal newborn temperature is crucial for the baby's health and well-being, and it requires the collective effort of healthcare providers and parents. By working together, we can ensure that newborns receive the best possible care and start their lives on a healthy and happy note.
