Intro
Discover the normal potassium level range and learn about hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, and electrolyte balance for optimal health, with symptoms and treatment options for potassium imbalance conditions.
Maintaining the right balance of electrolytes in the body is crucial for various bodily functions, including nerve function, muscle contraction, and heart function. One of the key electrolytes is potassium, an essential mineral that plays a significant role in maintaining fluid balance, regulating blood pressure, and supporting overall health. Understanding the normal potassium level range is vital for diagnosing and managing conditions related to potassium imbalance.
Potassium levels in the body are tightly regulated, and even slight deviations from the normal range can have significant consequences. The normal potassium level range varies slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, but generally, it falls between 3.5 and 5.0 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L) of blood. This range may vary slightly depending on the testing method and the laboratory's reference values. It's essential to note that potassium levels can fluctuate throughout the day due to various factors such as diet, medication, and hormonal changes.
The importance of maintaining potassium levels within the normal range cannot be overstated. Potassium helps regulate the heartbeat, ensuring that it remains steady and strong. It also facilitates the transmission of nerve impulses, allowing for proper muscle function and contraction. Furthermore, potassium plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood pressure, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, and supporting bone health. With the numerous functions that potassium performs in the body, it's clear that understanding and maintaining normal potassium levels is essential for overall health and well-being.
Understanding Potassium Level Ranges

Understanding the different ranges of potassium levels is crucial for diagnosis and treatment. Hypokalemia refers to lower than normal potassium levels, typically below 3.5 mEq/L. This condition can lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, constipation, and heart arrhythmias. On the other hand, hyperkalemia refers to higher than normal potassium levels, typically above 5.0 mEq/L. This condition can cause cardiac arrhythmias, muscle weakness, and in severe cases, cardiac arrest. It's essential to recognize the symptoms of both conditions and seek medical attention if they occur.
Factors Affecting Potassium Levels
Several factors can affect potassium levels, including diet, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. A diet rich in potassium can help maintain healthy levels, while a diet lacking in potassium can lead to deficiency. Certain medications, such as diuretics, can cause potassium loss, leading to hypokalemia. Underlying medical conditions, such as kidney disease, can also impact potassium levels, as the kidneys play a crucial role in regulating electrolyte balance.Causes of Abnormal Potassium Levels
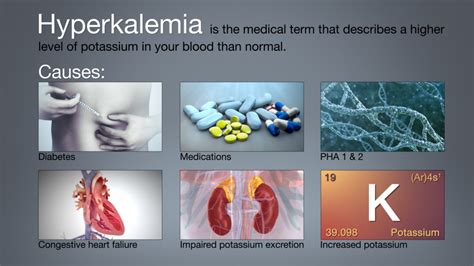
Abnormal potassium levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including excessive potassium loss, inadequate potassium intake, and certain medical conditions. Excessive potassium loss can occur due to vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive sweating. Inadequate potassium intake can result from a diet lacking in potassium-rich foods or certain medical conditions that impair potassium absorption. Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, adrenal gland disorders, and hormonal imbalances, can also affect potassium levels.
Symptoms of Potassium Imbalance
The symptoms of potassium imbalance can vary depending on the severity and duration of the condition. Mild hypokalemia may not produce any noticeable symptoms, while severe hypokalemia can cause muscle weakness, fatigue, and heart arrhythmias. Hyperkalemia can cause cardiac arrhythmias, muscle weakness, and in severe cases, cardiac arrest. It's essential to recognize the symptoms of potassium imbalance and seek medical attention if they occur.Diagnosis and Treatment of Potassium Imbalance

Diagnosing potassium imbalance typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. A blood test can measure potassium levels, and additional tests may be ordered to determine the underlying cause of the imbalance. Treatment for potassium imbalance depends on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Mild hypokalemia may be treated with dietary changes and potassium supplements, while severe hypokalemia may require intravenous potassium administration. Hyperkalemia may be treated with medications that help remove excess potassium from the body or diuretics to increase potassium excretion.
Prevention of Potassium Imbalance
Preventing potassium imbalance involves maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying medical conditions. A diet rich in potassium can help maintain healthy levels, and including potassium-rich foods such as bananas, leafy greens, and sweet potatoes can help prevent deficiency. Staying hydrated can help prevent excessive potassium loss, and managing underlying medical conditions can help prevent potassium imbalance.Potassium-Rich Foods

Including potassium-rich foods in the diet can help maintain healthy potassium levels. Some potassium-rich foods include:
- Bananas
- Leafy greens such as spinach and kale
- Sweet potatoes
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds such as almonds and pumpkin seeds
- Fatty fish such as salmon
- Legumes such as white beans and lentils
- Whole grains such as brown rice and quinoa
Potassium Supplements
While dietary changes can help maintain healthy potassium levels, potassium supplements may be necessary in certain situations. Potassium supplements can help treat hypokalemia, and they may be recommended for individuals with certain medical conditions or those taking medications that cause potassium loss. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking potassium supplements, as excessive potassium intake can cause hyperkalemia.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, maintaining normal potassium levels is essential for overall health and well-being. Understanding the normal potassium level range, recognizing the symptoms of potassium imbalance, and seeking medical attention if they occur can help prevent complications. Including potassium-rich foods in the diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying medical conditions can help prevent potassium imbalance. By taking these steps, individuals can help maintain healthy potassium levels and reduce the risk of related complications.
What is the normal potassium level range?
+The normal potassium level range is typically between 3.5 and 5.0 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L) of blood.
What are the symptoms of hypokalemia?
+The symptoms of hypokalemia can include muscle weakness, fatigue, constipation, and heart arrhythmias.
How can I prevent potassium imbalance?
+Preventing potassium imbalance involves maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying medical conditions.
What are some potassium-rich foods?
+Potassium-rich foods include bananas, leafy greens, sweet potatoes, avocados, nuts and seeds, fatty fish, legumes, and whole grains.
Can I take potassium supplements?
+Potassium supplements may be necessary in certain situations, but it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking them.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of normal potassium levels and the importance of maintaining them. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your friends and family to help them understand the importance of potassium for overall health and well-being.
