Intro
Learn about Normal Sedimentation Rate, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) tests, blood sedimentation, and inflammation indicators, to understand healthy sedimentation ranges and diagnostic implications.
The sedimentation rate, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. The normal sedimentation rate can vary depending on age, sex, and other factors, but it is generally considered to be an important indicator of overall health. In this article, we will delve into the details of the normal sedimentation rate, its significance, and what it can reveal about our health.
The sedimentation rate is influenced by several factors, including the presence of inflammation, infection, or autoimmune disorders. When inflammation is present in the body, the red blood cells tend to clump together, causing them to settle more quickly. This is because the inflammatory response triggers the release of certain proteins that make the red blood cells more likely to aggregate. As a result, a high sedimentation rate can indicate the presence of inflammation, while a low sedimentation rate suggests that there is less inflammation present. Understanding the normal sedimentation rate is essential for interpreting the results of this test and making informed decisions about our health.
The normal sedimentation rate is typically considered to be between 0-20 mm/h for adults, although this can vary depending on the laboratory and the specific testing method used. For example, some laboratories may consider a normal sedimentation rate to be between 0-15 mm/h, while others may use a slightly broader range. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the normal sedimentation rate for a specific individual, as this can vary depending on a range of factors, including age, sex, and overall health. By understanding the normal sedimentation rate, we can better appreciate the significance of this test and how it can be used to monitor our health.
What is Sedimentation Rate?
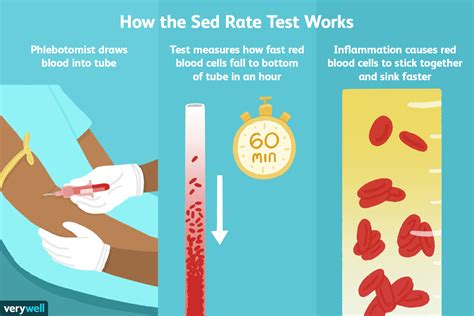
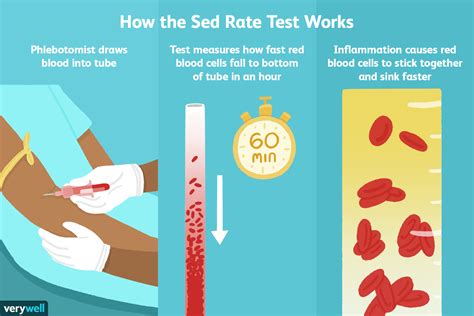
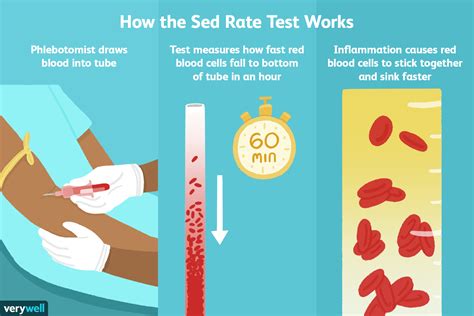
How is Sedimentation Rate Measured?
The sedimentation rate is measured using a blood sample, which is typically drawn from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then placed in a test tube containing an anticoagulant, which prevents the blood from clotting. The test tube is then left to stand for a specified period, usually one hour, allowing the red blood cells to settle. The distance that the red blood cells have settled is then measured and recorded, usually in millimeters per hour (mm/h). This measurement is then compared to a reference range to determine whether the sedimentation rate is within the normal range or not.Factors that Influence Sedimentation Rate

What Does a High Sedimentation Rate Indicate?
A high sedimentation rate can indicate the presence of inflammation, infection, or autoimmune disorders. For example, a sedimentation rate of 40 mm/h or higher may indicate the presence of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or other autoimmune disorders. A high sedimentation rate can also indicate the presence of infection, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis. In some cases, a high sedimentation rate may also indicate the presence of cancer, such as lymphoma or multiple myeloma. However, it is essential to note that a high sedimentation rate is not always a cause for concern, as it can also be influenced by other factors, such as age and sex.What Does a Low Sedimentation Rate Indicate?
How to Lower Sedimentation Rate
There are several ways to lower the sedimentation rate, including reducing inflammation, treating underlying medical conditions, and making lifestyle changes. For example, reducing inflammation by taking anti-inflammatory medications or using alternative therapies such as acupuncture or massage can help to lower the sedimentation rate. Treating underlying medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, can also help to lower the sedimentation rate. Making lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet, can also help to reduce inflammation and lower the sedimentation rate.Normal Sedimentation Rate in Different Age Groups

Normal Sedimentation Rate in Men
The normal sedimentation rate in men is typically considered to be between 0-15 mm/h, although this can vary depending on age and other factors. For example, the normal sedimentation rate in men under the age of 50 is typically considered to be between 0-10 mm/h, while the normal sedimentation rate in men over the age of 50 is typically considered to be between 0-15 mm/h.Normal Sedimentation Rate in Women

Normal Sedimentation Rate in Children
The normal sedimentation rate in children is typically considered to be between 0-10 mm/h, although this can vary depending on age and other factors. For example, the normal sedimentation rate in children under the age of 10 is typically considered to be between 0-5 mm/h, while the normal sedimentation rate in children over the age of 10 is typically considered to be between 0-10 mm/h.Importance of Monitoring Sedimentation Rate
How to Monitor Sedimentation Rate
The sedimentation rate can be monitored by regularly checking the blood test results and comparing them to the reference range. Healthcare professionals may also use other tests, such as the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, to monitor inflammation and adjust treatment as needed. Additionally, patients can monitor their sedimentation rate by keeping track of their symptoms and reporting any changes to their healthcare professional.Conclusion and Next Steps

We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about the normal sedimentation rate and its significance. Additionally, we invite you to comment below with any questions or thoughts you may have on this topic. By working together, we can promote greater understanding and awareness of the importance of monitoring the sedimentation rate and taking steps to maintain good health.
What is the normal sedimentation rate for adults?
+The normal sedimentation rate for adults is typically considered to be between 0-20 mm/h, although this can vary depending on age and other factors.
What does a high sedimentation rate indicate?
+A high sedimentation rate can indicate the presence of inflammation, infection, or autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
How can I lower my sedimentation rate?
+There are several ways to lower the sedimentation rate, including reducing inflammation, treating underlying medical conditions, and making lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet.
