Intro
Discover the normal PT INR value range and understand its significance in blood clotting tests, including prothrombin time, international normalized ratio, and coagulation factors.
Prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR) are crucial blood tests used to evaluate the blood clotting process. These tests are commonly ordered to monitor patients on warfarin therapy, a blood thinner used to prevent and treat blood clots. Understanding the normal PT INR value range is essential for healthcare professionals and patients to ensure proper management of anticoagulation therapy.
The importance of PT INR tests lies in their ability to assess the extrinsic and common pathways of blood coagulation. By measuring the time it takes for blood to clot, these tests provide valuable information about the effectiveness of warfarin therapy and the risk of bleeding or thrombosis. Patients with abnormal PT INR values may require adjustments to their medication dosage to achieve optimal anticoagulation.
The relevance of PT INR tests extends beyond warfarin therapy, as they are also used to diagnose and monitor various bleeding and clotting disorders, such as liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, and inherited coagulopathies. Moreover, PT INR tests are essential in surgical settings, where patients may require temporary cessation of anticoagulation therapy to minimize bleeding risks during procedures.
Understanding PT INR Values

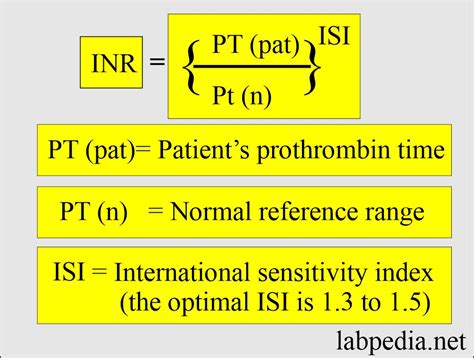
PT INR values are calculated by comparing the patient's prothrombin time to a standard reference value. The resulting ratio is then normalized to account for variations in thromboplastin reagents used in different laboratories. A normal PT INR value range typically falls between 0.9 and 1.1, indicating that the blood is clotting normally. However, the target PT INR range may vary depending on the specific clinical context, such as mechanical heart valves, atrial fibrillation, or deep vein thrombosis.
Target PT INR Ranges
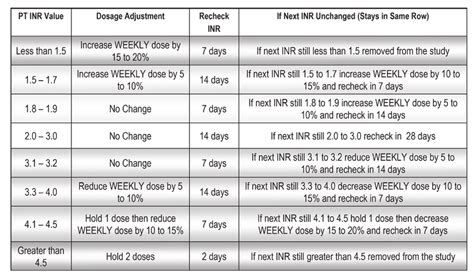
The American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) and other professional organizations have established guidelines for target PT INR ranges in various clinical scenarios:
- Mechanical heart valves: 2.0-3.0
- Atrial fibrillation: 2.0-3.0
- Deep vein thrombosis: 2.0-3.0
- Pulmonary embolism: 2.0-3.0
- Stroke prevention: 1.5-2.5
Interpreting PT INR Results
Interpreting PT INR results requires careful consideration of the patient's clinical context, medication regimen, and laboratory values. Here are some general guidelines for interpreting PT INR results:
- PT INR < 0.9: Subtherapeutic, may indicate increased risk of thrombosis
- PT INR 0.9-1.1: Normal, no action required
- PT INR 1.1-1.5: Slightly elevated, may require dosage adjustment
- PT INR 1.5-2.0: Therapeutic, optimal anticoagulation
- PT INR 2.0-3.0: Therapeutic, optimal anticoagulation
- PT INR > 3.0: Supratherapeutic, may indicate increased risk of bleeding
Factors Affecting PT INR Values
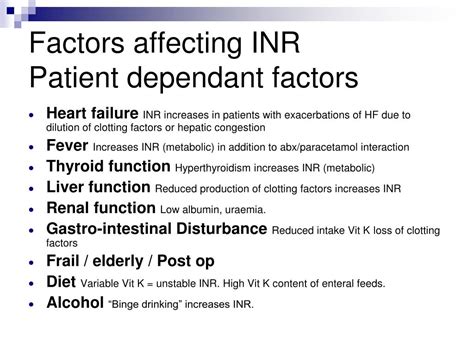
Several factors can affect PT INR values, including:
- Warfarin dosage and compliance
- Vitamin K intake
- Liver function
- Kidney function
- Other medications (e.g., antibiotics, antiplatelet agents)
- Dietary factors (e.g., cranberry juice, grapefruit)
Managing Abnormal PT INR Values
Abnormal PT INR values require prompt attention to minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis. Here are some general guidelines for managing abnormal PT INR values:
- PT INR < 0.9: Increase warfarin dosage, monitor closely
- PT INR > 3.0: Decrease warfarin dosage, monitor closely
- PT INR 1.1-1.5: Monitor closely, consider dosage adjustment
- PT INR 1.5-2.0: Continue current warfarin dosage, monitor closely
Monitoring PT INR Values
Regular monitoring of PT INR values is essential to ensure optimal anticoagulation and minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis. The frequency of monitoring depends on the patient's clinical context, warfarin dosage, and laboratory values. Here are some general guidelines for monitoring PT INR values:
- Initial monitoring: Every 2-3 days
- Stable patients: Every 4-6 weeks
- Unstable patients: Every 1-2 weeks
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, understanding normal PT INR value ranges is crucial for optimal management of anticoagulation therapy. By recognizing the importance of PT INR tests, interpreting results, and managing abnormal values, healthcare professionals can minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis and improve patient outcomes. Future directions in PT INR management may include the development of new anticoagulants, point-of-care testing, and personalized medicine approaches.
What is the normal PT INR value range?
+The normal PT INR value range typically falls between 0.9 and 1.1.
What are the target PT INR ranges for different clinical scenarios?
+The target PT INR ranges vary depending on the clinical context, such as mechanical heart valves (2.0-3.0), atrial fibrillation (2.0-3.0), and deep vein thrombosis (2.0-3.0).
How often should PT INR values be monitored?
+The frequency of monitoring depends on the patient's clinical context, warfarin dosage, and laboratory values, ranging from every 2-3 days to every 4-6 weeks.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with PT INR management in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with your colleagues and social networks. Together, we can promote optimal anticoagulation therapy and improve patient outcomes.
