Intro
Discover Norvasc, a calcium channel blocker in the drug class, used to treat hypertension and angina, with benefits including lowered blood pressure and improved cardiovascular health through vasodilation and reduced cardiac workload.
The Norvasc drug class is a topic of great importance, particularly for individuals dealing with hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions. Norvasc, generically known as amlodipine, falls under a specific category of medications designed to manage and treat high blood pressure and angina. Understanding the drug class of Norvasc is crucial for patients, as it helps them comprehend how the medication works, its potential side effects, and how it interacts with other drugs. This knowledge empowers patients to take a more active role in their health management, ensuring they receive the most effective treatment while minimizing risks.
The classification of Norvasc as a calcium channel blocker (CCB) indicates its mechanism of action, which involves the relaxation of blood vessels to improve blood flow and reduce blood pressure. This is a critical aspect of managing hypertension, as high blood pressure can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. By understanding the drug class of Norvasc, healthcare providers can also make informed decisions about prescribing the right medication for their patients, taking into account factors such as the patient's medical history, current health status, and potential drug interactions.
Furthermore, the importance of the Norvasc drug class extends beyond the management of hypertension and angina. It highlights the significance of pharmacological classification in guiding therapeutic decisions. The drug class of a medication is not just a technical detail; it is a crucial piece of information that influences how medications are prescribed, monitored, and adjusted to achieve optimal patient outcomes. As the field of pharmacology continues to evolve, with new medications and drug classes being developed, understanding the classification of drugs like Norvasc becomes increasingly important for advancing patient care and improving health outcomes.
Norvasc Mechanism of Action
The effects of Norvasc are not limited to blood pressure reduction. Its vasodilatory properties also contribute to the relief of angina symptoms by reducing myocardial oxygen demand through afterload reduction. This dual effect makes Norvasc a valuable therapeutic option for patients with both hypertension and angina, allowing for the management of multiple cardiovascular conditions with a single medication.
Benefits of Norvasc
The benefits of Norvasc are multifaceted, reflecting its efficacy in managing hypertension and angina, as well as its safety profile and ease of use. Some of the key benefits include: - **Effective Blood Pressure Control:** Norvasc has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure in patients with hypertension, reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications. - **Angina Relief:** By reducing myocardial oxygen demand, Norvasc helps alleviate symptoms of angina, improving the quality of life for patients with this condition. - **Once-Daily Dosing:** The pharmacokinetic properties of Norvasc allow for once-daily dosing, which can improve patient compliance with treatment regimens. - **Safety Profile:** Norvasc has a well-established safety profile, with side effects that are generally mild and transient.Norvasc Side Effects
Less Common Side Effects
Less common but more serious side effects of Norvasc can include: - **Hypotension:** Excessive lowering of blood pressure can lead to dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting. - **Worsening Angina:** In rare cases, Norvasc can cause or worsen angina, particularly if used without a nitrate. - **Liver Enzyme Elevations:** Monitoring of liver enzymes may be necessary, as Norvasc can cause elevations in these enzymes.Norvasc Interactions

Precautions and Warnings
Precautions and warnings associated with Norvasc use include: - **Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:** Norvasc should be used with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as its effects on the fetus or baby are not fully understood. - **Hypersensitivity Reactions:** Patients who are allergic to amlodipine or other dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers should not use Norvasc. - **Pediatric Use:** The safety and efficacy of Norvasc in pediatric patients have not been established.Norvasc Dosage
Dosage Adjustments
Dosage adjustments may be necessary in certain patient populations, such as: - **Elderly Patients:** Lower doses may be recommended due to decreased clearance of the drug. - **Patients with Hepatic Impairment:** Dose reduction may be necessary, as amlodipine is metabolized by the liver.Norvasc Overdose

Emergency Procedures
Emergency procedures in the case of a Norvasc overdose include: - **Immediate Medical Attention:** Patients should seek immediate medical attention if they suspect an overdose. - **Cardiovascular Monitoring:** Continuous monitoring of cardiovascular status is crucial to promptly identify and manage any complications.Norvasc Alternatives
Comparison of Alternatives
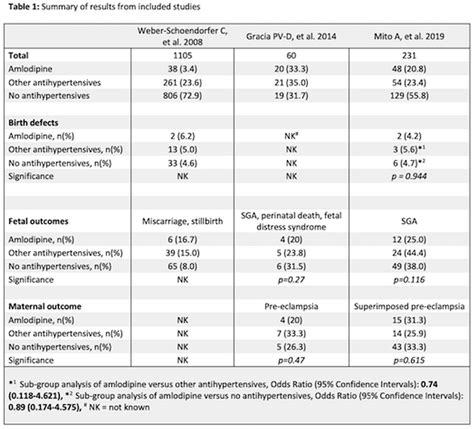
A comparison of Norvasc alternatives may consider factors such as: - **Efficacy:** The ability of the medication to lower blood pressure or relieve angina symptoms. - **Side Effect Profile:** The types and frequencies of side effects associated with each medication. - **Cost and Accessibility:** The affordability and availability of the medication.What is the primary mechanism of action of Norvasc?
+Norvasc primarily acts as a calcium channel blocker, inhibiting the influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscles, thereby causing vasodilation and reducing blood pressure.
What are the common side effects of Norvasc?
+
Can Norvasc be used during pregnancy?
+Norvasc should be used with caution in pregnant women, as its effects on the fetus are not fully understood. It is essential to discuss the risks and benefits with a healthcare provider.
In summary, understanding the Norvasc drug class is essential for the effective management of hypertension and angina. By recognizing its mechanism of action, benefits, potential side effects, and interactions with other medications, patients and healthcare providers can work together to optimize treatment outcomes. As with any medication, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage, monitor for side effects, and seek medical attention if any concerns arise. For those who require alternative treatments, several options are available, each with its own efficacy, side effect profile, and considerations. By staying informed and engaged in their healthcare, individuals can better navigate the complexities of managing cardiovascular conditions and improve their overall well-being. We invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, or seek further clarification on the topics discussed, promoting a community of informed and empowered individuals taking charge of their health.
