Intro
Learn about Oppositional Defiant Disorder in kids, its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, including behavioral therapy and parenting strategies to manage defiant behavior, conduct disorder, and ADHD-like symptoms.
Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) is a type of mental health condition that affects children and adolescents, characterized by a pattern of negative, hostile, and defiant behavior. This condition can be challenging for parents, caregivers, and educators to manage, as it often disrupts daily life and relationships. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ODD is essential for providing effective support and guidance to affected children.
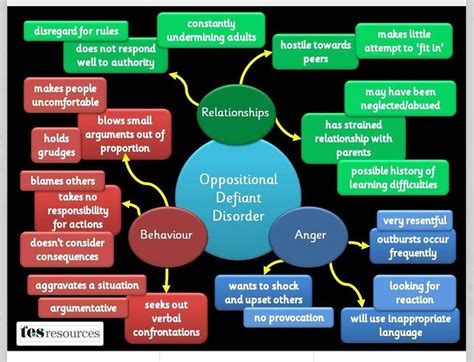
Children with ODD often exhibit behaviors such as arguing with authority figures, refusing to comply with rules, and deliberately annoying others. These behaviors can be frustrating and stressful for those around them, leading to conflicts and strained relationships. It's essential to recognize that ODD is a treatable condition, and with the right approach, children can learn to manage their behaviors and develop more positive relationships with others.
The importance of addressing ODD in children cannot be overstated. If left untreated, ODD can lead to more severe mental health issues, such as conduct disorder, and can also impact a child's social, emotional, and academic development. By understanding the signs and symptoms of ODD, parents and caregivers can take the first step towards seeking help and providing their child with the support they need to thrive.
Understanding Oppositional Defiant Disorder

Causes of Oppositional Defiant Disorder
The exact causes of ODD are not fully understood, but research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and social factors contribute to the development of the condition. Some potential causes of ODD include: * Genetic predisposition: Children with a family history of ODD or other mental health conditions may be more likely to develop the condition. * Brain chemistry: Imbalances in brain chemistry, such as serotonin and dopamine, may contribute to the development of ODD. * Environmental factors: Exposure to trauma, neglect, or abuse can increase the risk of developing ODD. * Social factors: Poor relationships with parents or caregivers, as well as social isolation, can contribute to the development of ODD.Signs and Symptoms of Oppositional Defiant Disorder
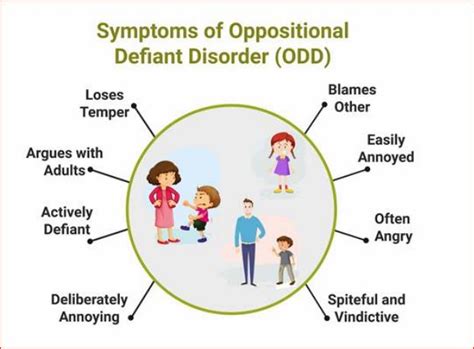
Diagnosing Oppositional Defiant Disorder
Diagnosing ODD can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other mental health conditions. A comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, including a physical exam, psychological evaluation, and behavioral assessment, is necessary to determine if a child has ODD. The diagnostic criteria for ODD include: * A pattern of negative, hostile, and defiant behavior lasting at least six months * At least four symptoms of ODD, such as arguing with authority figures, refusing to comply with rules, and deliberately annoying others * The behavior is not better explained by another mental health condition, such as conduct disorder or bipolar disorderTreatment Options for Oppositional Defiant Disorder

Behavioral Therapy for Oppositional Defiant Disorder
Behavioral therapy is a type of therapy that helps children identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. Some common types of behavioral therapy for ODD include: * Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): This type of therapy helps children identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. * Family therapy: This type of therapy helps families develop more positive relationships and communicate more effectively. * Social skills training: This type of therapy helps children develop social skills, such as sharing, taking turns, and cooperating with others.Managing Oppositional Defiant Disorder in Daily Life
Supporting Children with Oppositional Defiant Disorder
Supporting children with ODD requires a comprehensive approach that includes behavioral therapy, parent training, and medication. Some ways to support children with ODD include: * Providing a stable and predictable environment * Encouraging positive relationships with family and friends * Helping children develop social skills and emotional regulation * Encouraging physical activity and outdoor play * Seeking support from mental health professionals and support groupsConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Oppositional Defiant Disorder in the comments below. Your input can help others better understand the condition and provide support to those who need it. Additionally, if you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to a mental health professional for guidance and support.
What are the symptoms of Oppositional Defiant Disorder?
+The symptoms of Oppositional Defiant Disorder include arguing with authority figures, refusing to comply with rules, deliberately annoying others, blaming others for mistakes, and having a low frustration tolerance.
How is Oppositional Defiant Disorder diagnosed?
+Oppositional Defiant Disorder is diagnosed through a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, including a physical exam, psychological evaluation, and behavioral assessment.
What are the treatment options for Oppositional Defiant Disorder?
+The treatment options for Oppositional Defiant Disorder include behavioral therapy, parent training, and medication. The goal of treatment is to help the child manage their behaviors, develop more positive relationships with others, and improve their overall functioning.
