Intro
Discover the 5 ways an oral glucose test diagnoses diabetes, monitoring blood sugar levels, glucose tolerance, and insulin resistance, with accurate results and medical guidance.
The oral glucose test, also known as the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), is a medical procedure used to assess the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels after consuming a sugary drink. This test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as diabetes, prediabetes, and insulin resistance. Understanding the oral glucose test is crucial for individuals who are at risk of developing these conditions or those who have been diagnosed and are looking to manage their condition effectively. In this article, we will delve into the world of oral glucose testing, exploring its importance, how it works, and the benefits it provides in managing and diagnosing glucose-related health issues.
The importance of the oral glucose test cannot be overstated. It is a straightforward, yet highly effective tool that healthcare providers use to evaluate how well the body can manage blood glucose levels. By administering a controlled amount of glucose and then measuring the body's response, healthcare professionals can identify abnormalities in glucose metabolism, which is critical for early diagnosis and treatment of diabetes and other related conditions. Early detection through tests like the OGTT can significantly improve outcomes for patients, allowing for timely interventions that can prevent or delay the onset of complications associated with diabetes.
The mechanism behind the oral glucose test is relatively simple. The test involves consuming a sweet drink that contains a known amount of glucose. Over the next couple of hours, blood samples are taken at intervals to measure the levels of glucose in the blood. The body's ability to regulate blood glucose levels is primarily managed by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. In healthy individuals, insulin effectively lowers blood glucose levels after a meal. However, in individuals with diabetes or prediabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. The oral glucose test can identify these issues by showing how blood glucose levels change after consuming the glucose drink.
Understanding the Oral Glucose Test Process
The process of undergoing an oral glucose test typically begins with preparation. Patients are usually asked to fast for a certain period before the test, typically overnight, to ensure that the results are not influenced by recent food intake. On the day of the test, a baseline blood sample is taken to measure the fasting glucose level. Then, the patient drinks the glucose solution, and over the next one to two hours, additional blood samples are taken to measure how glucose levels have changed. These measurements are crucial for diagnosing impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes.
Benefits of the Oral Glucose Test
The benefits of the oral glucose test are multifaceted. It provides a clear indication of how the body manages glucose, which is essential for diagnosing diabetes and monitoring its progression. For individuals at risk, early detection through this test can lead to lifestyle changes or interventions that improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, potentially preventing the development of diabetes. Furthermore, for those already diagnosed with diabetes, regular oral glucose tests can help in adjusting treatment plans, ensuring that blood glucose levels are well-managed, and reducing the risk of complications.Preparation for the Oral Glucose Test

Preparation is key when it comes to the oral glucose test. Patients are advised to follow a normal diet for a few days before the test but are required to fast for at least 8 hours before the test. This fasting period is crucial to ensure that the test results accurately reflect the body's response to glucose. Additionally, patients should inform their healthcare provider about any medications they are taking, as some medications can affect blood glucose levels and the results of the test. It's also important to follow any specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider, as the preparation might slightly vary depending on the individual's health status and the purpose of the test.
Interpreting Oral Glucose Test Results
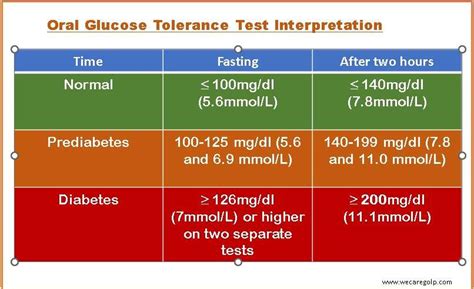
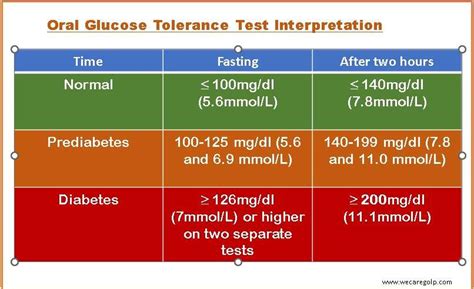
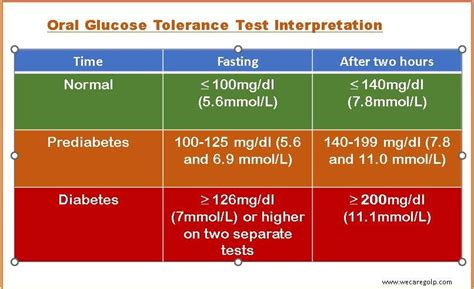
Interpreting the results of the oral glucose test is straightforward. The test measures the body's ability to regulate blood glucose levels after consuming a glucose solution. The results are classified into different categories based on the blood glucose levels measured during the test. For instance, a normal response indicates good glucose tolerance, suggesting that the body is effectively managing blood sugar levels. On the other hand, impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes is diagnosed when blood glucose levels exceed certain thresholds, indicating a problem with insulin production or function. Understanding these results is crucial for healthcare providers to make informed decisions about patient care and treatment.The Role of Oral Glucose Test in Diabetes Management
The oral glucose test plays a significant role in diabetes management. For individuals with diabetes, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential to manage the condition effectively. The oral glucose test, along with other monitoring tools like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG), helps in assessing how different factors such as diet, exercise, and medication affect blood glucose levels. This information is vital for adjusting treatment plans to achieve better glucose control, reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Oral Glucose Test and Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the oral glucose test is used to screen for gestational diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels that are first recognized during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes can pose risks to both the mother and the baby if not managed properly. The test is typically administered between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy. Women with risk factors for gestational diabetes may be tested earlier. The screening involves a preliminary glucose challenge test, and if the results indicate a potential issue, a more detailed glucose tolerance test may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis.Common Misconceptions About the Oral Glucose Test
There are several common misconceptions about the oral glucose test that need to be addressed. One of the most prevalent is the belief that the test is only for individuals who are at high risk of diabetes. While it's true that individuals with risk factors may undergo the test more frequently, the oral glucose test can be an important diagnostic tool for anyone suspected of having impaired glucose regulation. Another misconception is that the test is painful or highly invasive, which is not the case. The test involves drinking a glucose solution and having blood drawn at intervals, which, while not the most pleasant experience, is relatively minor and temporary.
Future Directions in Oral Glucose Testing
The future of oral glucose testing is evolving, with advancements in technology and our understanding of glucose metabolism. New methods and devices are being developed to make glucose monitoring more convenient, less invasive, and more accurate. For example, non-invasive glucose monitoring devices that use optical or other technologies to measure glucose levels without the need for blood draws are under development. These advancements hold promise for improving the diagnostic and monitoring capabilities for diabetes and related conditions, potentially leading to better outcomes for patients.Real-Life Applications of Oral Glucose Test Results

The results of an oral glucose test have real-life applications that can significantly impact an individual's health and wellbeing. For those diagnosed with diabetes or prediabetes, the test results can serve as a wake-up call, prompting lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, and, if necessary, starting medication. For individuals with normal results, the test can provide reassurance and encourage continued healthy habits. Moreover, the test can guide healthcare providers in making informed decisions about patient care, including the need for further testing, medication adjustments, or referrals to specialists.
Oral Glucose Test and Lifestyle Changes
The oral glucose test can be a catalyst for lifestyle changes, especially for individuals with abnormal results. Understanding that the body is not managing glucose effectively can motivate individuals to make significant changes in their diet and exercise habits. For instance, adopting a diet low in added sugars and refined carbohydrates and high in fiber and whole foods can help improve insulin sensitivity. Regular physical activity, such as walking or more intense exercise, can also enhance the body's ability to use insulin effectively. These lifestyle modifications, guided by the results of the oral glucose test, can be powerful tools in managing or even reversing conditions like prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the oral glucose test is a vital tool in the diagnosis and management of diabetes and related conditions. Its ability to assess the body's glucose regulation provides valuable insights into an individual's metabolic health. By understanding the process, benefits, and implications of the oral glucose test, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining good health. Whether it's making informed lifestyle choices or working closely with healthcare providers to manage a diagnosis, the information gleaned from the oral glucose test can be life-changing. As research and technology continue to evolve, the role of the oral glucose test in healthcare will likely expand, offering even more precise and personalized approaches to glucose management and diabetes care.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the oral glucose test in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us create content that addresses the needs and concerns of our readers.
What is the purpose of the oral glucose test?
+The oral glucose test is used to assess the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels after consuming a sugary drink, helping diagnose and monitor conditions like diabetes and prediabetes.
How do I prepare for the oral glucose test?
+To prepare for the test, you typically need to fast for at least 8 hours beforehand and inform your healthcare provider about any medications you're taking. It's also important to follow a normal diet for a few days before the test.
What do the results of the oral glucose test indicate?
+The results indicate how well your body manages blood glucose levels. Normal results suggest good glucose tolerance, while elevated levels can indicate impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes, guiding further treatment or lifestyle changes.
Can the oral glucose test be used during pregnancy?
+Yes, the oral glucose test is used to screen for gestational diabetes during pregnancy, typically between the 24th and 28th weeks. It helps identify women who may need more careful monitoring and treatment to manage their blood sugar levels.
Are there any new developments in oral glucose testing technology?
+Yes, there are ongoing developments in non-invasive glucose monitoring technologies that aim to make testing easier and less painful, potentially improving patient compliance and outcomes in diabetes management.
