Intro
Discover key facts about Oseltamivir, an antiviral medication, including its uses, side effects, and resistance, to understand its role in treating influenza and flu symptoms effectively.
The world of antiviral medications is vast and complex, with various drugs being used to treat a range of viral infections. One such medication that has gained significant attention in recent years is Oseltamivir, commonly known by its brand name Tamiflu. This medication has been widely used to treat and prevent influenza A and B infections. In this article, we will delve into the world of Oseltamivir, exploring its history, mechanism of action, benefits, and potential side effects.
Oseltamivir is a neuraminidase inhibitor, which means it works by blocking the neuraminidase enzyme on the surface of influenza viruses. This enzyme is essential for the virus to spread from infected cells to healthy ones. By inhibiting this enzyme, Oseltamivir prevents the virus from multiplying and spreading, thereby reducing the severity and duration of influenza symptoms. The medication has been shown to be effective in treating influenza A and B infections, including those caused by pandemic strains.
The importance of Oseltamivir lies in its ability to provide a safe and effective treatment option for individuals infected with influenza. Influenza is a highly contagious and potentially life-threatening illness, especially for vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and individuals with underlying health conditions. By reducing the severity and duration of influenza symptoms, Oseltamivir can help prevent complications and reduce the risk of hospitalization and death.
History of Oseltamivir
Benefits of Oseltamivir

Working Mechanism of Oseltamivir
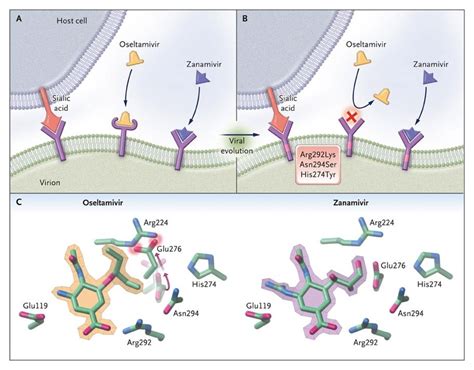
Steps Involved in the Working Mechanism of Oseltamivir
The steps involved in the working mechanism of Oseltamivir include: 1. Binding to the neuraminidase enzyme: Oseltamivir binds to the neuraminidase enzyme on the surface of influenza viruses, preventing the enzyme from functioning properly. 2. Inhibition of viral replication: By inhibiting the neuraminidase enzyme, Oseltamivir prevents the virus from multiplying and spreading, thereby reducing the severity and duration of influenza symptoms. 3. Prevention of viral transmission: Oseltamivir also prevents the transmission of the virus from infected individuals to healthy ones, thereby reducing the spread of influenza.Potential Side Effects of Oseltamivir
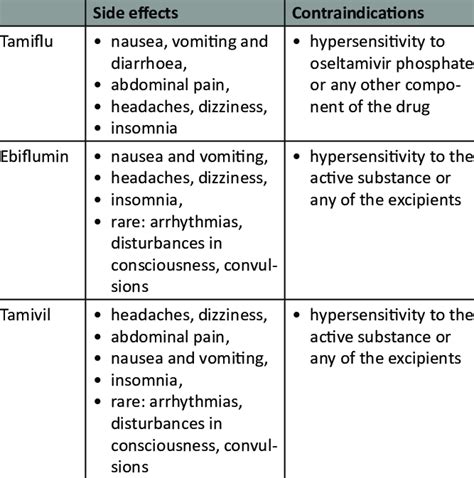
Severe Side Effects of Oseltamivir
In rare cases, Oseltamivir can cause severe side effects, including: * Allergic reactions * Stevens-Johnson syndrome * Toxic epidermal necrolysis * Neuropsychiatric events such as hallucinations and deliriumPrecautions and Contraindications

Conclusion and Future Directions
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Oseltamivir in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one used Oseltamivir to treat or prevent influenza? What were your experiences with the medication? Share your story and help others understand the benefits and potential side effects of Oseltamivir.
What is Oseltamivir used for?
+Oseltamivir is used to treat and prevent influenza A and B infections.
How does Oseltamivir work?
+Oseltamivir works by inhibiting the neuraminidase enzyme on the surface of influenza viruses, preventing the virus from multiplying and spreading.
What are the potential side effects of Oseltamivir?
+The potential side effects of Oseltamivir include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, headache, fatigue, and insomnia. In rare cases, it can cause severe side effects such as allergic reactions and neuropsychiatric events.
Can Oseltamivir be used in pregnant and breastfeeding women?
+Oseltamivir should be used with caution in pregnant and breastfeeding women, as the safety and efficacy of the medication in these populations have not been fully established.
Can Oseltamivir be used to treat other viral infections?
+No, Oseltamivir is specifically designed to treat and prevent influenza A and B infections. It is not effective against other viral infections.
