Intro
Discover key facts about Oxycodone, a potent opioid painkiller, including its uses, risks, and side effects, to understand its impact on health and addiction, amidst the opioid crisis and prescription drug abuse.
The importance of understanding oxycodone cannot be overstated, given its widespread use and potential for abuse. Oxycodone is a powerful opioid medication used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is often prescribed to patients who have undergone surgery, experienced physical trauma, or suffer from chronic pain conditions. However, the misuse of oxycodone has led to a significant increase in opioid-related deaths and addictions, making it a critical public health concern. As we delve into the world of oxycodone, it becomes clear that education and awareness are key to mitigating its risks and ensuring its safe use.
Oxycodone's impact on society is multifaceted, affecting not only individuals but also families, communities, and the healthcare system as a whole. The opioid crisis, which has been exacerbated by the misuse of oxycodone and other opioids, has led to a surge in overdose deaths, emergency department visits, and substance abuse treatment admissions. Furthermore, the economic burden of opioid misuse is substantial, with estimates suggesting that it costs the United States billions of dollars annually in healthcare expenses, lost productivity, and criminal justice expenditures. As we explore the facts surrounding oxycodone, it is essential to consider the broader context and the need for a comprehensive approach to addressing the opioid crisis.
The complexities surrounding oxycodone are numerous, ranging from its pharmacological properties to its social and economic implications. To truly comprehend the significance of oxycodone, it is crucial to examine its history, mechanisms of action, benefits, and risks. By doing so, we can better understand the factors contributing to its misuse and develop effective strategies for preventing addiction, promoting safe use, and supporting those affected by opioid-related disorders. As we navigate the intricacies of oxycodone, we will discover that knowledge is power, and that informed decision-making is essential for mitigating the risks associated with this potent medication.
Introduction to Oxycodone

Pharmacological Properties
The pharmacological properties of oxycodone are characterized by its high affinity for opioid receptors, particularly the mu-receptor subtype. This binding affinity is responsible for its potent analgesic effects, as well as its potential for dependence and addiction. Oxycodone's pharmacokinetic profile is marked by rapid absorption, extensive metabolism, and relatively long elimination half-life, which can contribute to its accumulation in the body and increased risk of adverse effects. Understanding the pharmacological properties of oxycodone is essential for healthcare providers to make informed decisions about its use, dosing, and potential interactions with other medications.Benefits of Oxycodone
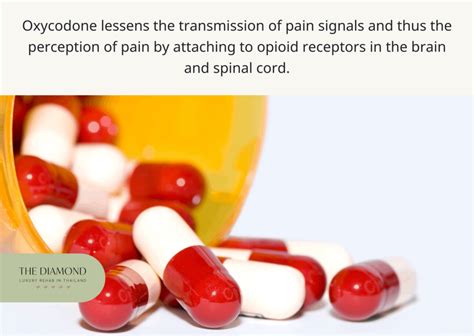
Risks and Side Effects
While oxycodone is an effective medication, it is not without risks and side effects. Some of the potential adverse effects of oxycodone include: * Addiction and dependence: Oxycodone has a high potential for abuse and addiction, particularly when used improperly or in large doses. * Respiratory depression: Oxycodone can slow down breathing rates, leading to respiratory depression, a potentially life-threatening condition. * Constipation: Oxycodone can cause constipation, which can be severe and require medical attention.Working Mechanisms
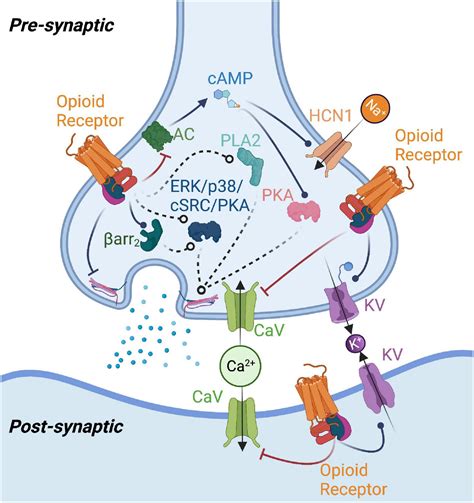
Steps for Safe Use
To ensure the safe use of oxycodone, patients and healthcare providers must follow specific steps, including: 1. Proper dosing: Oxycodone should be taken exactly as prescribed, with careful attention to dosing instructions and potential interactions with other medications. 2. Monitoring: Patients taking oxycodone should be closely monitored for signs of addiction, respiratory depression, and other adverse effects. 3. Storage and disposal: Oxycodone should be stored securely and disposed of properly to prevent misuse and accidental exposure.Practical Examples and Statistical Data

Alternatives and Future Directions
As the opioid crisis continues to evolve, researchers and healthcare providers are exploring alternative treatments and future directions for pain management. Some of these alternatives include: * Non-opioid analgesics: Medications like acetaminophen and ibuprofen can be effective for managing mild to moderate pain, reducing the need for oxycodone and other opioids. * Interventional procedures: Techniques like nerve blocks and spinal cord stimulation can provide targeted pain relief, minimizing the risk of opioid-related adverse effects.Conclusion and Final Thoughts
What is oxycodone, and how does it work?
+Oxycodone is a semi-synthetic opioid agonist that works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and body, producing feelings of pain relief, relaxation, and euphoria.
What are the benefits and risks of oxycodone?
+The benefits of oxycodone include effective pain relief, convenience, and flexibility, while the risks include addiction, respiratory depression, constipation, and other adverse effects.
How can I ensure the safe use of oxycodone?
+To ensure the safe use of oxycodone, follow proper dosing instructions, monitor for signs of addiction and adverse effects, store and dispose of the medication securely, and consider alternative treatment strategies.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with oxycodone in the comments below. If you or someone you know is struggling with opioid addiction, please seek help from a qualified healthcare provider or support organization. Together, we can work towards a future where pain management is safer, more effective, and more compassionate.
