Intro
Discover key facts about Pantoprazole, a proton pump inhibitor, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand this medications role in treating acid reflux and stomach ulcers effectively.
Pantoprazole, a medication known for its effectiveness in treating various gastrointestinal issues, has become a staple in the world of gastroenterology. Its widespread use and benefits have sparked interest among both healthcare professionals and patients alike. Understanding the intricacies of pantoprazole can help in harnessing its full potential for therapeutic purposes. Here are some key aspects of pantoprazole that shed light on its importance and application in medical practice.
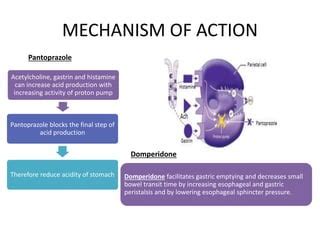
The importance of pantoprazole lies in its ability to reduce stomach acid production, thereby alleviating symptoms associated with conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, and peptic ulcer disease. By inhibiting the H+/K+ ATPase enzyme system at the secretory surface of gastric parietal cells, pantoprazole effectively decreases gastric acidity. This mechanism of action is crucial for the healing of esophageal mucosa and the reduction of ulcer size.
Pantoprazole's efficacy and safety profile have made it a preferred choice among proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). Its pharmacokinetic properties, including oral bioavailability and plasma protein binding, contribute to its therapeutic effectiveness. Furthermore, pantoprazole has been shown to have a favorable interaction profile with other medications, which is essential for patients with comorbid conditions requiring polypharmacy. The drug's long duration of action allows for once-daily dosing, enhancing patient compliance and making it more convenient for those with busy lifestyles.
Introduction to Pantoprazole

Benefits of Pantoprazole
The benefits of pantoprazole are multifaceted. Not only does it provide relief from heartburn and other symptoms of acid reflux, but it also aids in the healing of stomach ulcers. Its ability to reduce stomach acid can prevent future ulcers and allow existing ones to heal more effectively. Moreover, pantoprazole has been shown to improve quality of life for patients suffering from chronic gastrointestinal conditions, enabling them to eat and drink without the constant fear of discomfort or pain.How Pantoprazole Works
Common Uses of Pantoprazole
Pantoprazole is commonly used for several gastrointestinal conditions. These include: - Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): Characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, causing heartburn and discomfort. - Zollinger-Ellison syndrome: A rare disorder marked by excessive production of stomach acid due to high levels of gastrin, a hormone that stimulates acid secretion. - Peptic ulcer disease: Includes both gastric and duodenal ulcers, which are sores that develop on the inside lining of the stomach and the upper portion of the small intestine, respectively. - Erosive esophagitis: Inflammation of the esophagus due to acid reflux, which can lead to erosion of the esophageal lining.Pantoprazole Side Effects and Interactions

Precautions and Warnings
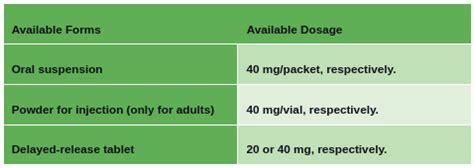
Patients should be aware of several precautions and warnings when taking pantoprazole. These include: - The risk of osteoporosis-related fractures with long-term use, particularly in patients with risk factors for osteoporosis. - The potential for vitamin B12 deficiency, as prolonged use can lead to malabsorption of this essential vitamin. - Increased risk of Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection, a type of bacterial infection that can cause diarrhea and colitis. - The importance of not taking pantoprazole for longer than 14 days without consulting a healthcare provider, as this can lead to rebound acid hypersecretion.Dosing and Administration
Special Considerations
Special considerations are necessary for certain populations, including: - Pregnant women: Pantoprazole should be used with caution, as there is limited data on its safety during pregnancy. - Breastfeeding mothers: The drug is excreted in breast milk, and its effects on infants are not well understood, so caution is advised. - Pediatric patients: The safety and efficacy of pantoprazole in children have not been fully established, and its use should be carefully considered.Alternatives to Pantoprazole
Future Directions
Research into new therapeutic agents and formulations continues to evolve the treatment landscape for gastrointestinal diseases. The development of more targeted therapies with fewer side effects is a key area of focus. Additionally, the role of pantoprazole in treating conditions beyond traditional gastrointestinal diseases, such as its potential effects on the gut-brain axis, is being explored. These advancements promise to further enhance the management of gastrointestinal health and expand the therapeutic arsenal against these prevalent conditions.What is pantoprazole used for?
+Pantoprazole is used to treat conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, and peptic ulcer disease by reducing stomach acid production.
How does pantoprazole work?
+Pantoprazole works by inhibiting the proton pump in the stomach lining, which blocks the final step of acid production, resulting in a decrease in gastric acidity.
What are the common side effects of pantoprazole?
+Common side effects of pantoprazole include headache, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Less common but more serious side effects can include severe allergic reactions, seizures, and kidney damage.
In conclusion, pantoprazole is a valuable medication in the management of various gastrointestinal conditions. Its efficacy, safety profile, and convenience make it a preferred choice for both healthcare providers and patients. As research continues to uncover new aspects of its mechanism and potential applications, pantoprazole is likely to remain a cornerstone in the treatment of acid-related diseases. We invite readers to share their experiences with pantoprazole and explore how it has impacted their lives, contributing to a broader understanding of its role in gastrointestinal health.
