Intro
Discover pelvic organ prolapse symptoms, treatment options, and management strategies to alleviate discomfort and restore pelvic health, addressing bladder prolapse, uterine prolapse, and vaginal prolapse with non-surgical and surgical approaches.
Pelvic organ prolapse is a condition that affects millions of women worldwide, causing discomfort, pain, and disruption to daily life. It occurs when the muscles and tissues that support the pelvic organs, such as the bladder, uterus, and rectum, become weakened or damaged, allowing these organs to bulge or prolapse into the vagina. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including childbirth, menopause, aging, and certain medical conditions. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options for pelvic organ prolapse is essential for women to seek medical attention and regain control over their bodies.
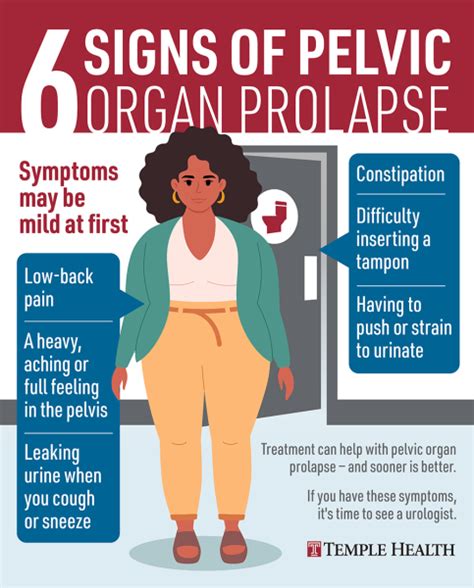
The symptoms of pelvic organ prolapse can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the organs affected. Some common symptoms include a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the pelvic area, discomfort or pain during sex, and difficulty emptying the bladder or bowels. Women may also experience a bulge or lump in the vagina, which can be uncomfortable and embarrassing. In severe cases, pelvic organ prolapse can cause urinary incontinence, constipation, and even affect a woman's ability to engage in physical activities. It is essential for women to seek medical attention if they experience any of these symptoms, as early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve their quality of life.
Pelvic organ prolapse can be diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI. A healthcare provider will perform a pelvic exam to assess the severity of the prolapse and identify any other underlying conditions. They may also ask questions about the woman's medical history, including any previous surgeries, pregnancies, or health conditions. Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options is crucial for women to make informed decisions about their care.
Pelvic Organ Prolapse Symptoms
Treatment Options for Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Treatment options for pelvic organ prolapse depend on the severity of the condition, the woman's overall health, and her personal preferences. Mild cases of pelvic organ prolapse may be treated with lifestyle modifications, such as exercising the pelvic muscles, losing weight, and avoiding heavy lifting. More severe cases may require medical treatment, such as hormone replacement therapy or physical therapy to strengthen the pelvic muscles. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove the prolapsed organ.Pelvic Organ Prolapse Treatment

Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatment options for pelvic organ prolapse include pessary devices, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Pessary devices are small, removable devices that are inserted into the vagina to support the prolapsed organ. Physical therapy can help strengthen the pelvic muscles, improving symptoms and reducing the risk of further prolapse. Lifestyle modifications, such as exercising regularly, losing weight, and avoiding heavy lifting, can also help alleviate symptoms and improve overall health.Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery

Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery and aftercare are crucial components of treatment for pelvic organ prolapse. Women who undergo surgery may need to stay in the hospital for several days to recover. They may experience pain, discomfort, and bleeding during the recovery period. It is essential to follow the surgeon's instructions for post-operative care, including taking pain medication, avoiding heavy lifting, and attending follow-up appointments. Women who do not undergo surgery may need to attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor the progression of the prolapse and adjust treatment as needed.Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prevention

Risk Factors for Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Risk factors for pelvic organ prolapse include pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, aging, and certain medical conditions. Women who have had multiple pregnancies or vaginal deliveries are at higher risk of developing pelvic organ prolapse. Menopause can also increase the risk of pelvic organ prolapse, as the decrease in estrogen levels can cause the muscles and tissues that support the pelvic organs to weaken. Certain medical conditions, such as pelvic inflammatory disease or endometriosis, can also increase the risk of pelvic organ prolapse.Pelvic Organ Prolapse Complications

Living with Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Living with pelvic organ prolapse requires women to make lifestyle adjustments and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen. Women can manage their symptoms by exercising regularly, losing weight, and avoiding heavy lifting. They should also attend regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider to monitor the progression of the prolapse and adjust treatment as needed. Women with pelvic organ prolapse can also benefit from joining support groups or seeking counseling to cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of the condition.Pelvic Organ Prolapse Support

Pelvic Organ Prolapse Resources
Resources for women with pelvic organ prolapse include online educational materials, support groups, and healthcare providers. Women can access online educational materials, such as articles and videos, to learn more about the condition and its treatment options. Support groups, either in-person or online, can provide a safe and supportive environment for women to share their experiences and connect with others who are going through similar challenges. Healthcare providers, including obstetricians, gynecologists, and urogynecologists, can provide medical guidance and support throughout the diagnosis and treatment process.What are the symptoms of pelvic organ prolapse?
+The symptoms of pelvic organ prolapse can include a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the pelvic area, discomfort or pain during sex, and difficulty emptying the bladder or bowels.
How is pelvic organ prolapse diagnosed?
+Pelvic organ prolapse can be diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI.
What are the treatment options for pelvic organ prolapse?
+Treatment options for pelvic organ prolapse depend on the severity of the condition and can include lifestyle modifications, medical treatment, and surgery.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of pelvic organ prolapse, its symptoms, treatment options, and complications. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Remember, seeking medical attention early can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of further complications. Share this article with your friends and family to help raise awareness about pelvic organ prolapse and support those who are affected by this condition.
