Intro
Identify placenta rupture signs, symptoms, and causes. Learn about placental abruption risks, bleeding, and emergency treatment options to ensure maternal and fetal health.
The placenta is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in the development and growth of a fetus during pregnancy. It provides the necessary oxygen and nutrients to the baby and removes waste products. However, in some cases, the placenta can rupture, leading to severe complications for both the mother and the baby. Placenta rupture signs are essential to recognize, as prompt medical attention can help prevent long-term damage and even save lives.
Placenta rupture, also known as placental abruption, occurs when the placenta partially or completely separates from the uterus. This can cause the mother to experience severe abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and other symptoms. In severe cases, placenta rupture can lead to fetal distress, premature birth, and even stillbirth. It is essential for pregnant women to be aware of the signs and symptoms of placenta rupture, as early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Pregnant women who experience any unusual symptoms or discomfort should seek medical attention immediately. Placenta rupture signs can be subtle, and it is crucial to recognize them to prevent severe complications. Some common signs of placenta rupture include vaginal bleeding, severe abdominal pain, and fetal distress. Women who experience any of these symptoms should contact their healthcare provider right away. In this article, we will discuss the signs and symptoms of placenta rupture, its causes, and treatment options.
What is Placenta Rupture?
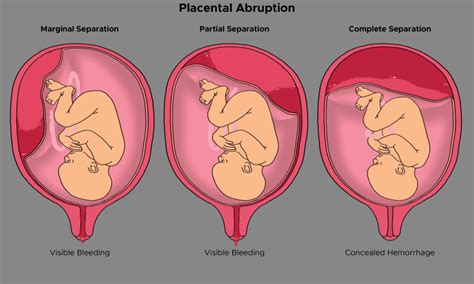
Causes of Placenta Rupture
Placenta rupture can be caused by several factors, including trauma, high blood pressure, and substance abuse. Women who have experienced previous placenta rupture, have a history of high blood pressure, or have a multiple pregnancy are at a higher risk of developing placenta rupture. Additionally, women who smoke or use illicit substances during pregnancy are also at a higher risk of developing this condition.Signs and Symptoms of Placenta Rupture
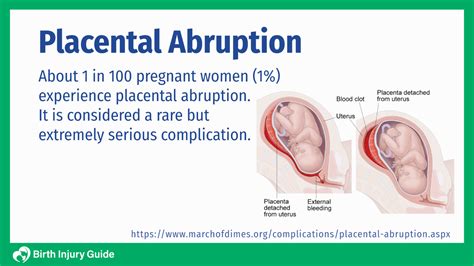
Risk Factors for Placenta Rupture
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing placenta rupture. These include: * Previous placenta rupture: Women who have experienced previous placenta rupture are at a higher risk of developing it again. * High blood pressure: Women with high blood pressure are at a higher risk of developing placenta rupture. * Multiple pregnancy: Women carrying multiple babies are at a higher risk of developing placenta rupture. * Substance abuse: Women who smoke or use illicit substances during pregnancy are at a higher risk of developing placenta rupture. * Trauma: Women who experience trauma during pregnancy, such as a car accident or a fall, are at a higher risk of developing placenta rupture.Diagnosis and Treatment of Placenta Rupture
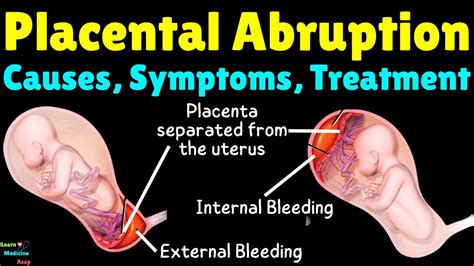
Treatment for placenta rupture depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, the healthcare provider may recommend bed rest and close monitoring of the mother and baby. In severe cases, the healthcare provider may recommend immediate delivery, either vaginally or via cesarean section.
Prevention of Placenta Rupture
While it is not possible to completely prevent placenta rupture, there are several steps that women can take to reduce their risk. These include: * Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle during pregnancy * Avoiding substance abuse during pregnancy * Managing any underlying medical conditions, such as high blood pressure * Avoiding trauma during pregnancy * Attending regular prenatal appointments to monitor the health of the mother and babyComplications of Placenta Rupture

Long-term Effects of Placenta Rupture
Placenta rupture can have long-term effects on both the mother and the baby. Women who experience placenta rupture may be at a higher risk of developing future pregnancy complications, including placenta rupture. Additionally, babies who are born prematurely or experience fetal distress due to placenta rupture may be at a higher risk of developing long-term health problems, including respiratory and neurological disorders.Conclusion and Next Steps
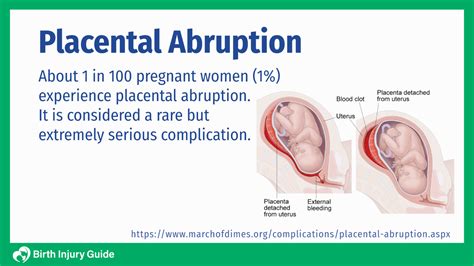
If you have any questions or concerns about placenta rupture, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with your friends and family. Additionally, if you have experienced placenta rupture or know someone who has, we would love to hear your story and provide support and guidance.
What are the symptoms of placenta rupture?
+The symptoms of placenta rupture include vaginal bleeding, severe abdominal pain, and fetal distress. Women who experience any of these symptoms should seek medical attention immediately.
What are the risk factors for placenta rupture?
+The risk factors for placenta rupture include previous placenta rupture, high blood pressure, multiple pregnancy, substance abuse, and trauma during pregnancy.
How is placenta rupture diagnosed?
+Placenta rupture is diagnosed using several tests, including ultrasound, fetal heart rate monitoring, and blood tests.
What is the treatment for placenta rupture?
+The treatment for placenta rupture depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, the healthcare provider may recommend bed rest and close monitoring of the mother and baby. In severe cases, the healthcare provider may recommend immediate delivery, either vaginally or via cesarean section.
Can placenta rupture be prevented?
+While it is not possible to completely prevent placenta rupture, women can reduce their risk by maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle during pregnancy, avoiding substance abuse, managing any underlying medical conditions, and attending regular prenatal appointments.
