Intro
Learn about Placental Abruption Symptoms, causes, and treatment. Identify signs of placental abruption, bleeding, and premature birth risks with related conditions like preeclampsia and fetal distress.
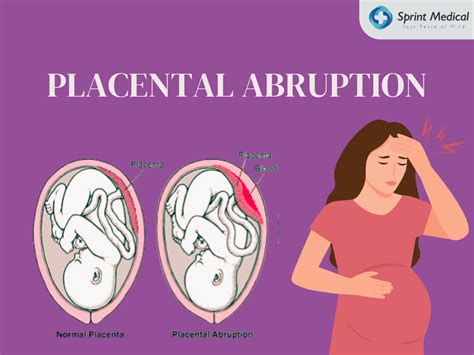
Placental abruption is a serious pregnancy complication that occurs when the placenta partially or completely separates from the uterus. This condition can deprive the baby of oxygen and nutrients and cause severe bleeding that can be life-threatening to both the mother and the baby. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of placental abruption to seek immediate medical attention.
Placental abruption can occur suddenly and without warning, making it crucial for pregnant women to be aware of the signs and symptoms. The condition can be caused by various factors, including trauma, high blood pressure, and substance abuse. Pregnant women who have experienced placental abruption in a previous pregnancy are also at a higher risk of experiencing it again. Understanding the causes and risk factors of placental abruption can help pregnant women take preventive measures and seek medical attention promptly if they experience any symptoms.
Pregnant women who are at risk of placental abruption should be vigilant about their health and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any unusual symptoms. The symptoms of placental abruption can vary in severity and may include vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, and back pain. In some cases, the bleeding may be internal, and the woman may not exhibit any visible symptoms. However, internal bleeding can still be life-threatening, making it essential to seek medical attention promptly if any symptoms are experienced.
What is Placental Abruption?
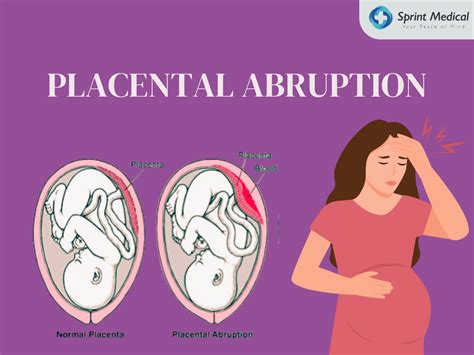
Types of Placental Abruption
There are three types of placental abruption, including: * Mild placental abruption: This type of abruption occurs when the placenta separates from the uterus by less than 20%. * Moderate placental abruption: This type of abruption occurs when the placenta separates from the uterus by 20-50%. * Severe placental abruption: This type of abruption occurs when the placenta separates from the uterus by more than 50%.Symptoms of Placental Abruption
Risk Factors for Placental Abruption
Several factors can increase the risk of placental abruption, including: * High blood pressure: Women with high blood pressure are at a higher risk of developing placental abruption. * Trauma: Women who experience trauma, such as a car accident or a fall, are at a higher risk of developing placental abruption. * Substance abuse: Women who abuse substances, such as cocaine or methamphetamine, are at a higher risk of developing placental abruption. * Previous placental abruption: Women who have experienced placental abruption in a previous pregnancy are at a higher risk of experiencing it again. * Multiple pregnancy: Women who are carrying twins or other multiples are at a higher risk of developing placental abruption.Diagnosis of Placental Abruption
Treatment of Placental Abruption
The treatment of placental abruption depends on the severity of the condition and the gestational age of the baby. In some cases, the woman may be hospitalized for bed rest and monitoring, while in other cases, the baby may need to be delivered immediately. The treatment options for placental abruption include: * Bed rest: The woman may be advised to rest in bed to reduce the risk of further bleeding and to allow the placenta to reattach to the uterus. * Corticosteroids: These medications may be given to the woman to promote fetal lung maturity and to reduce the risk of complications. * Blood transfusions: The woman may require blood transfusions to replace lost blood and to prevent shock. * Delivery: The baby may need to be delivered immediately, either vaginally or by cesarean section, depending on the severity of the condition and the gestational age of the baby.Complications of Placental Abruption
Prevention of Placental Abruption
While placental abruption cannot be completely prevented, there are several steps that women can take to reduce their risk, including: * Maintaining a healthy blood pressure: Women who have high blood pressure should work with their healthcare provider to manage their condition. * Avoiding substance abuse: Women who abuse substances should seek help to quit. * Avoiding trauma: Women should take steps to avoid trauma, such as wearing a seatbelt while driving and avoiding falls. * Getting regular prenatal care: Women should attend all scheduled prenatal appointments to monitor their health and the health of their baby.Conclusion and Next Steps
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with placental abruption in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, you can share this article with friends and family to help raise awareness about placental abruption and its importance.
What are the symptoms of placental abruption?
+The symptoms of placental abruption include vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, back pain, uterine tenderness, and fetal distress.
What are the risk factors for placental abruption?
+The risk factors for placental abruption include high blood pressure, trauma, substance abuse, previous placental abruption, and multiple pregnancy.
How is placental abruption diagnosed?
+Placental abruption can be diagnosed using ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and blood tests.
What are the treatment options for placental abruption?
+The treatment options for placental abruption include bed rest, corticosteroids, blood transfusions, and delivery.
Can placental abruption be prevented?
+While placental abruption cannot be completely prevented, women can take steps to reduce their risk, such as maintaining a healthy blood pressure, avoiding substance abuse, and getting regular prenatal care.
