Intro
Discover stomach polyps causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Learn about gastric polyps, their removal, and prevention, managing digestive health and reducing cancer risk with proper diagnosis and care.
The stomach is a vital part of the digestive system, responsible for breaking down food into nutrients that the body can absorb. However, like any other part of the body, the stomach can be susceptible to various health issues, including the growth of stomach polyps. Stomach polyps, also known as gastric polyps, are abnormal growths that can develop on the lining of the stomach. These growths can be benign or malignant, and it's essential to understand their causes, symptoms, and treatment options to ensure proper management and prevention of complications.
Stomach polyps can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, age, and certain medical conditions. For instance, individuals with a family history of stomach polyps or other gastrointestinal disorders may be more likely to develop stomach polyps. Additionally, certain conditions such as gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and stomach ulcers can increase the risk of developing stomach polyps. It's also worth noting that stomach polyps can be a sign of an underlying condition, such as a gastritis or a stomach infection, which can be treated with antibiotics or other medications.
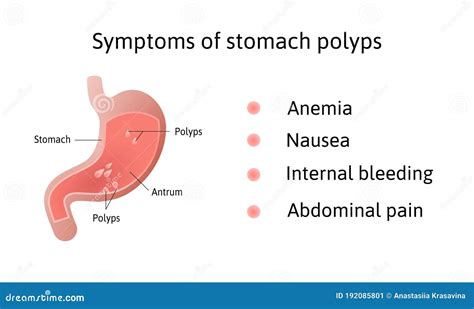
The symptoms of stomach polyps can vary depending on the size, location, and type of polyp. Some common symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss. In some cases, stomach polyps may not produce any symptoms at all, making it essential to undergo regular check-ups and screenings to detect any potential issues early on. If left untreated, stomach polyps can lead to complications such as bleeding, obstruction, and cancer. Therefore, it's crucial to seek medical attention if you're experiencing any symptoms or have a family history of stomach polyps.
Causes of Stomach Polyps

Risk Factors for Stomach Polyps
In addition to the causes mentioned above, there are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing stomach polyps. These include: * Family history: A family history of stomach polyps or other gastrointestinal disorders can increase the risk of developing stomach polyps. * Age: As mentioned earlier, stomach polyps are more common in older adults. * Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as gastritis, GERD, and stomach ulcers, can increase the risk of developing stomach polyps. * Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of developing stomach polyps. * Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing stomach polyps.Symptoms of Stomach Polyps
Diagnosing Stomach Polyps
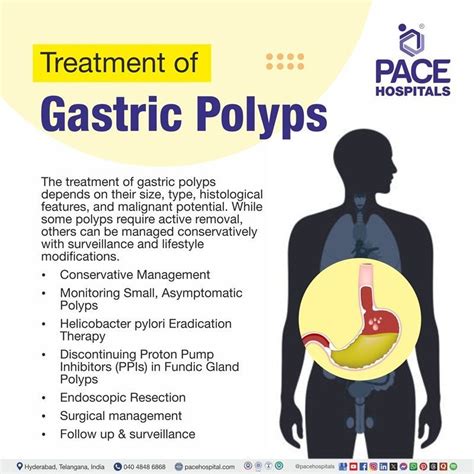
Diagnosing stomach polyps typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Some common diagnostic tests used to diagnose stomach polyps include: * Endoscopy: This is a procedure that involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera and light on the end into the stomach to visualize the polyp. * Biopsy: A biopsy involves removing a sample of tissue from the polyp and examining it under a microscope for signs of cancer or other abnormalities. * Imaging tests: Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans may be used to visualize the polyp and determine its size and location.Treatment Options for Stomach Polyps
Preventing Stomach Polyps
While it's not possible to completely prevent stomach polyps, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing them. These include: * Eating a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce the risk of developing stomach polyps. * Avoiding smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of developing stomach polyps, so quitting or avoiding smoking altogether can help reduce this risk. * Managing stress: Stress can exacerbate stomach polyps, so finding healthy ways to manage stress such as meditation or exercise can help reduce this risk. * Getting regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect stomach polyps early on, when they are easier to treat.What are the symptoms of stomach polyps?
+The symptoms of stomach polyps can vary depending on the size, location, and type of polyp, but common symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss.
How are stomach polyps diagnosed?
+Diagnosing stomach polyps typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as endoscopy, biopsy, and imaging tests.
Can stomach polyps be prevented?
+While it's not possible to completely prevent stomach polyps, making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, avoiding smoking, and managing stress can help reduce the risk of developing them.
In summary, stomach polyps are abnormal growths that can develop on the lining of the stomach, and can be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for stomach polyps is essential for proper management and prevention of complications. By making lifestyle changes and getting regular check-ups, individuals can reduce their risk of developing stomach polyps and improve their overall health and well-being. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with stomach polyps in the comments section below, and to reach out to a healthcare provider if they have any concerns or questions about this topic.
