Intro
Discover 5 ways PPD skin test helps diagnose allergic reactions, patch testing, and sensitivity to paraphenylenediamine, a common hair dye ingredient, ensuring safe cosmetic applications and minimizing adverse effects.
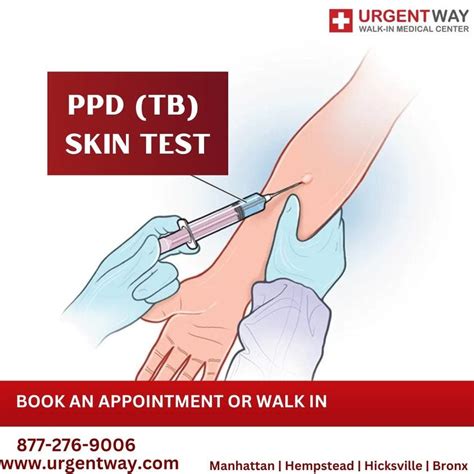
The PPD skin test, also known as the Mantoux test, is a widely used method to diagnose tuberculosis (TB) infection. It involves injecting a small amount of tuberculin, a purified protein derivative (PPD), into the skin, and then observing the reaction after 48-72 hours. The test is crucial for identifying individuals who have been exposed to TB, allowing for early treatment and prevention of the disease. In this article, we will explore the 5 ways PPD skin test is used, its benefits, and the steps involved in the testing process.
The PPD skin test has been a cornerstone in TB diagnosis for decades, and its importance cannot be overstated. With the rise of TB cases globally, the need for accurate and reliable diagnostic methods has become more pressing. The PPD skin test offers a simple, yet effective way to detect TB infection, making it an essential tool in the fight against this disease. Furthermore, the test is not only used for diagnostic purposes but also for screening individuals who are at high risk of contracting TB, such as healthcare workers and individuals living in areas with high TB prevalence.
The PPD skin test is a vital component of TB control programs, and its applications extend beyond diagnosis. It is used to identify individuals who require treatment, to monitor the effectiveness of treatment, and to track the spread of TB in communities. Additionally, the test is used in research settings to study the epidemiology of TB and to develop new diagnostic methods. With its widespread use and importance, it is essential to understand the 5 ways PPD skin test is used, its benefits, and the steps involved in the testing process.
Introduction to PPD Skin Test
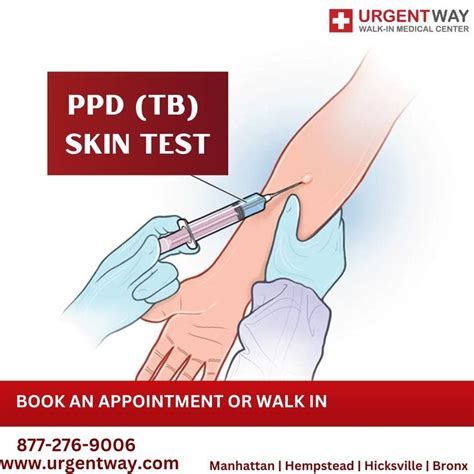
How the PPD Skin Test Works
The PPD skin test works by stimulating an immune response in individuals who have been exposed to TB. When the tuberculin is injected into the skin, it triggers an immune reaction, which causes the skin to become inflamed and swollen. The size of the induration is directly proportional to the amount of tuberculin injected and the individual's immune response. A positive reaction indicates that the individual has been exposed to TB, while a negative reaction suggests that the individual has not been exposed.Benefits of PPD Skin Test
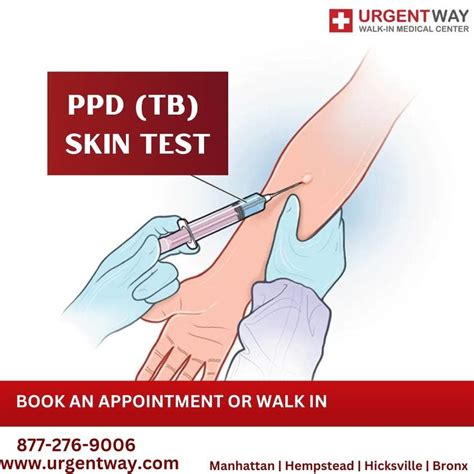
Steps Involved in PPD Skin Test
The PPD skin test involves the following steps: 1. Preparation: The individual's forearm is cleaned and prepared for the test. 2. Injection: A small amount of tuberculin is injected into the skin. 3. Reaction: The individual is asked to return after 48-72 hours for the reaction to be measured. 4. Measurement: The size of the induration is measured and recorded. 5. Interpretation: The results are interpreted based on the size of the induration and the individual's medical history.5 Ways PPD Skin Test is Used
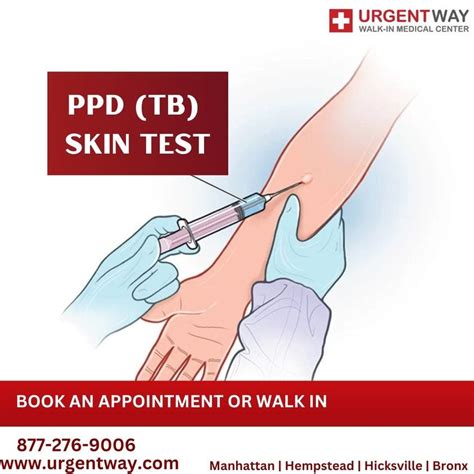
Interpretation of PPD Skin Test Results
The results of the PPD skin test are interpreted based on the size of the induration and the individual's medical history. A positive reaction is typically defined as an induration of 10mm or more, while a negative reaction is defined as an induration of less than 10mm. However, the interpretation of results can vary depending on the individual's risk factors and medical history.Challenges and Limitations of PPD Skin Test
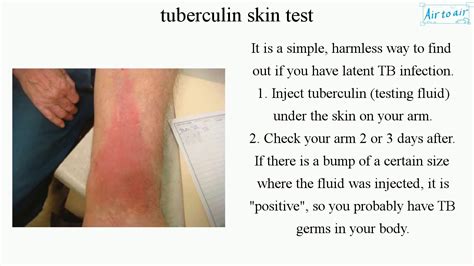
Future Directions for PPD Skin Test
The PPD skin test is an essential tool in the diagnosis and control of TB, but it has several limitations. Future research should focus on developing new diagnostic methods that are more accurate and reliable. Additionally, efforts should be made to improve the interpretation of PPD skin test results and to reduce the variability in test results.Conclusion and Recommendations
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with the PPD skin test. Have you undergone a PPD skin test? What were your results? How do you think the test can be improved? Share your comments and questions below.
What is the PPD skin test used for?
+The PPD skin test is used to diagnose tuberculosis (TB) infection, to identify individuals who require treatment, and to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
How is the PPD skin test performed?
+The PPD skin test involves injecting a small amount of tuberculin into the skin, and then measuring the reaction after 48-72 hours.
What are the benefits of the PPD skin test?
+The PPD skin test offers several benefits, including early detection of TB infection, identification of individuals who require treatment, and monitoring of treatment effectiveness.
