Intro
Pre-diabetes is a condition where an individual's blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. This condition can often be a precursor to type 2 diabetes, and it is essential to recognize the symptoms to take preventive measures. Pre-diabetes is also known as impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that over 88 million adults in the United States have pre-diabetes, and most of them are unaware of their condition.
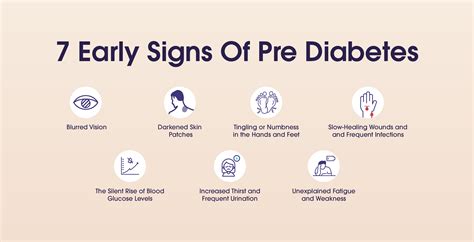
Recognizing the symptoms of pre-diabetes is crucial, as it can help individuals take preventive measures to avoid developing type 2 diabetes. Some common symptoms of pre-diabetes include increased thirst and hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. However, many people with pre-diabetes may not exhibit any noticeable symptoms, which is why it is essential to get regular health check-ups.
Pre-diabetes can be caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet. Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics/Latinos, and American Indians, are also at a higher risk of developing pre-diabetes. Additionally, people with a family history of diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol are more likely to develop pre-diabetes. By understanding the causes and risk factors of pre-diabetes, individuals can take steps to prevent or delay the onset of the condition.
Understanding Pre Diabetes
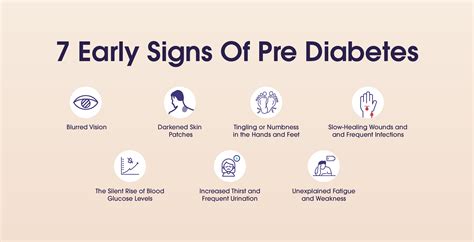
Risk Factors for Pre Diabetes
There are several risk factors that increase an individual's likelihood of developing pre-diabetes. These include: * Age: People over 45 years old are at a higher risk of developing pre-diabetes. * Family history: Having a family history of diabetes increases the risk of developing pre-diabetes. * Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for pre-diabetes. * Physical inactivity: Leading a sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of developing pre-diabetes. * Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics/Latinos, and American Indians, are at a higher risk of developing pre-diabetes. * History of gestational diabetes: Women who have had gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing pre-diabetes.Pre Diabetes Symptoms and Diagnosis
Pre-diabetes can be diagnosed through a simple blood test, which measures the level of glucose in the blood. The most common tests used to diagnose pre-diabetes are:
- Fasting plasma glucose test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood after an overnight fast.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: This test measures the level of glucose in the blood after consuming a sugary drink.
- Hemoglobin A1c test: This test measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2-3 months.
Treatment and Prevention of Pre Diabetes
Pre-diabetes can be treated and prevented through lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. The primary goal of treatment is to reduce the level of glucose in the blood and prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes. Some effective ways to treat and prevent pre-diabetes include: * Losing weight: If an individual is overweight or obese, losing weight can help reduce the level of glucose in the blood. * Increasing physical activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the level of glucose in the blood. * Eating a healthy diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help regulate blood sugar levels. * Getting enough sleep: Getting enough sleep is essential for overall health, and it can also help regulate blood sugar levels. * Managing stress: Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels, so it is essential to find healthy ways to manage stress, such as through meditation or yoga.Complications of Untreated Pre Diabetes

Managing Pre Diabetes with Lifestyle Changes
Managing pre-diabetes with lifestyle changes is essential to preventing the onset of type 2 diabetes. Some effective lifestyle changes include: * Eating a healthy diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help regulate blood sugar levels. * Increasing physical activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the level of glucose in the blood. * Losing weight: If an individual is overweight or obese, losing weight can help reduce the level of glucose in the blood. * Getting enough sleep: Getting enough sleep is essential for overall health, and it can also help regulate blood sugar levels. * Managing stress: Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels, so it is essential to find healthy ways to manage stress, such as through meditation or yoga.Pre Diabetes and Nutrition

Pre Diabetes and Exercise
Exercise is essential for managing pre-diabetes. Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce the level of glucose in the blood, and prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes. Some effective exercises for managing pre-diabetes include: * Aerobic exercise: Aerobic exercise, such as walking or swimming, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the level of glucose in the blood. * Resistance training: Resistance training, such as weightlifting, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the level of glucose in the blood. * High-intensity interval training: High-intensity interval training, such as sprinting or burpees, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the level of glucose in the blood.Pre Diabetes and Stress Management

Pre Diabetes and Sleep
Sleep is essential for managing pre-diabetes. Getting enough sleep can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Some tips for improving sleep include: * Establishing a bedtime routine: Establishing a bedtime routine can help improve sleep quality. * Creating a sleep-conducive environment: Creating a sleep-conducive environment, such as keeping the room cool and dark, can help improve sleep quality. * Avoiding caffeine and electronics before bedtime: Avoiding caffeine and electronics before bedtime can help improve sleep quality. * Getting regular exercise: Getting regular exercise can help improve sleep quality.Pre Diabetes and Mental Health
Pre Diabetes and Medication
In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage pre-diabetes. Some common medications used to manage pre-diabetes include: * Metformin: Metformin is a medication that can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the level of glucose in the blood. * Sulfonylureas: Sulfonylureas are medications that can help stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. * Meglitinides: Meglitinides are medications that can help stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. * Thiazolidinediones: Thiazolidinediones are medications that can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the level of glucose in the blood.What are the symptoms of pre-diabetes?
+Pre-diabetes often does not exhibit noticeable symptoms, but some common symptoms include increased thirst and hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How is pre-diabetes diagnosed?
+Pre-diabetes can be diagnosed through a simple blood test, which measures the level of glucose in the blood. The most common tests used to diagnose pre-diabetes are the fasting plasma glucose test, the oral glucose tolerance test, and the hemoglobin A1c test.
Can pre-diabetes be treated and prevented?
+Yes, pre-diabetes can be treated and prevented through lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, losing weight, and getting enough sleep. In some cases, medication may also be necessary to manage pre-diabetes.
What are the complications of untreated pre-diabetes?
+If left untreated, pre-diabetes can lead to a range of serious health complications, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness.
How can I manage pre-diabetes with lifestyle changes?
+Managing pre-diabetes with lifestyle changes is essential to preventing the onset of type 2 diabetes. Some effective lifestyle changes include eating a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, losing weight, getting enough sleep, and managing stress.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of pre-diabetes, its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. By taking proactive steps to manage pre-diabetes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other serious health complications. If you have any questions or concerns about pre-diabetes, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Share this article with your friends and family to help raise awareness about pre-diabetes and its importance in maintaining overall health and well-being.
