Intro
Prednisone is a corticosteroid medication that is widely used to treat various health conditions, including inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of cancer. While prednisone can be an effective treatment option, it can also interact with other medications, which can lead to adverse effects or reduce the effectiveness of the treatment. In this article, we will explore the importance of understanding prednisone drug interactions and provide a comprehensive guide to help patients and healthcare professionals navigate these interactions.
Prednisone is a commonly prescribed medication, and its use is often accompanied by other medications, including over-the-counter (OTC) medications, supplements, and prescription medications. The potential for drug interactions is high, and it is essential to be aware of these interactions to minimize the risk of adverse effects. Patients taking prednisone should inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking, including OTC medications, supplements, and prescription medications, to ensure safe and effective treatment.
The importance of understanding prednisone drug interactions cannot be overstated. Drug interactions can lead to serious adverse effects, including increased risk of infections, osteoporosis, and adrenal insufficiency. Moreover, drug interactions can also reduce the effectiveness of the treatment, leading to poor health outcomes. By understanding the potential drug interactions, patients and healthcare professionals can take steps to minimize the risk of adverse effects and ensure safe and effective treatment.
Prednisone Mechanism of Action
Prednisone Pharmacokinetics
Prednisone is metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine. The medication has a half-life of approximately 2.5 to 3.5 hours, which means that it takes about 2.5 to 3.5 hours for the medication to be reduced by half in the bloodstream. The pharmacokinetics of prednisone can be affected by other medications, including those that induce or inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzyme system.Prednisone Drug Interactions
- Antibiotics: Prednisone can increase the risk of infections when taken with antibiotics, such as amphotericin B and ketoconazole.
- Anticoagulants: Prednisone can increase the risk of bleeding when taken with anticoagulants, such as warfarin and aspirin.
- Anti-diabetic medications: Prednisone can increase blood sugar levels and reduce the effectiveness of anti-diabetic medications, such as metformin and insulin.
- Anti-seizure medications: Prednisone can increase the risk of seizures when taken with anti-seizure medications, such as phenytoin and carbamazepine.
- Blood thinners: Prednisone can increase the risk of bleeding when taken with blood thinners, such as heparin and clopidogrel.
Prednisone Food Interactions
Prednisone can also interact with certain foods, including:- Grapefruit: Grapefruit and grapefruit juice can increase the levels of prednisone in the bloodstream, leading to increased risk of adverse effects.
- Grapefruit juice: Grapefruit juice can also increase the levels of prednisone in the bloodstream, leading to increased risk of adverse effects.
Prednisone Side Effects

- Increased appetite: Prednisone can increase appetite and lead to weight gain.
- Mood changes: Prednisone can cause mood changes, including anxiety, depression, and irritability.
- Sleep disturbances: Prednisone can cause sleep disturbances, including insomnia and vivid dreams.
- Increased blood sugar levels: Prednisone can increase blood sugar levels and worsen diabetes.
- Osteoporosis: Prednisone can increase the risk of osteoporosis, particularly with long-term use.
Prednisone Contraindications
Prednisone is contraindicated in patients with certain medical conditions, including:- Adrenal insufficiency: Prednisone can worsen adrenal insufficiency, a condition in which the adrenal gland does not produce enough cortisol.
- Cushing's syndrome: Prednisone can worsen Cushing's syndrome, a condition caused by excess levels of cortisol.
- Infections: Prednisone can worsen infections, particularly fungal infections.
Prednisone Dosage and Administration
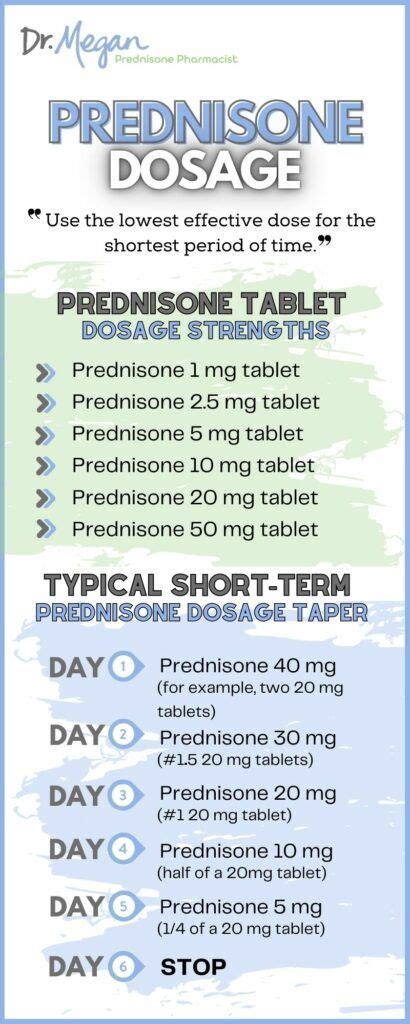
Prednisone Tapering
Prednisone tapering is a gradual reduction in the dosage of the medication to minimize the risk of adverse effects, particularly adrenal insufficiency. The tapering schedule depends on the duration of treatment and the patient's response to the medication.Prednisone Monitoring and Follow-up

Prednisone Patient Education
Patients taking prednisone should be educated about the potential risks and benefits of the medication, including the risk of adverse effects and the importance of adherence to the treatment regimen. Patients should also be informed about the signs and symptoms of adverse effects and the importance of reporting them to their healthcare provider.What are the common side effects of prednisone?
+Prednisone can cause a range of side effects, including increased appetite, mood changes, sleep disturbances, increased blood sugar levels, and osteoporosis.
Can I take prednisone with other medications?
+Prednisone can interact with a wide range of medications, including antibiotics, anticoagulants, anti-diabetic medications, and blood thinners. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking before starting prednisone.
How long does it take for prednisone to start working?
+Prednisone can start working within a few hours of taking the medication, but the full effects may take several days to develop.
Can I stop taking prednisone suddenly?
+No, patients should not stop taking prednisone suddenly, as this can lead to adrenal insufficiency and other adverse effects. Patients should taper off the medication gradually under the guidance of their healthcare provider.
What are the long-term effects of prednisone?
+The long-term effects of prednisone can include osteoporosis, adrenal insufficiency, and increased risk of infections. Patients should be monitored regularly for signs of these adverse effects.
In summary, prednisone is a widely used medication that can interact with other medications, including OTC medications, supplements, and prescription medications. Patients taking prednisone should be aware of the potential drug interactions and inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking. By understanding the potential drug interactions and taking steps to minimize the risk of adverse effects, patients can ensure safe and effective treatment with prednisone. We encourage readers to share their experiences with prednisone and ask questions about the medication in the comments section below. Additionally, readers can share this article with others who may be taking prednisone or who are interested in learning more about the medication.
