Intro
Discover the benefits of a Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plan, offering flexible healthcare coverage with in-network providers, out-of-network care, and cost-sharing options, making it a popular choice for individuals and families seeking affordable medical insurance solutions.
The healthcare landscape is complex and ever-evolving, with numerous options available for individuals and families to manage their medical needs. Among the various health insurance plans, Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) have gained popularity due to their flexibility and comprehensive coverage. Understanding how PPOs work, their benefits, and their limitations is essential for making informed decisions about healthcare.
In the United States, health insurance is a critical component of accessing quality medical care. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has expanded health insurance coverage to millions of Americans, but navigating the different types of health plans can be daunting. PPOs are one of the most common types of health insurance plans, offering a balance between cost and flexibility. They allow policyholders to receive medical care from a network of preferred providers, who have agreed to offer discounted services to plan members.
The importance of understanding PPOs lies in their ability to provide individuals and families with a range of healthcare options, from preventive care to specialized treatments. By choosing a PPO, individuals can ensure they have access to quality medical care while managing their healthcare expenses. Moreover, PPOs often provide additional benefits, such as coverage for mental health services, prescription medications, and wellness programs, making them an attractive option for those seeking comprehensive healthcare coverage.
What is a Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)?
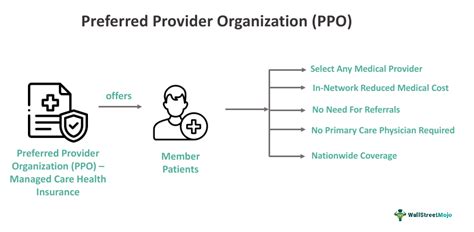
Key Characteristics of PPOs
PPOs have several key characteristics that distinguish them from other types of health insurance plans: * Network of preferred providers: PPOs have a network of healthcare providers who have agreed to offer discounted services to plan members. * Flexibility: PPOs allow policyholders to receive care from both in-network and out-of-network providers. * Cost-sharing: PPOs typically require policyholders to pay a deductible, copayment, or coinsurance for medical services. * Preventive care: PPOs often cover preventive care services, such as annual physicals, screenings, and vaccinations.Benefits of PPOs
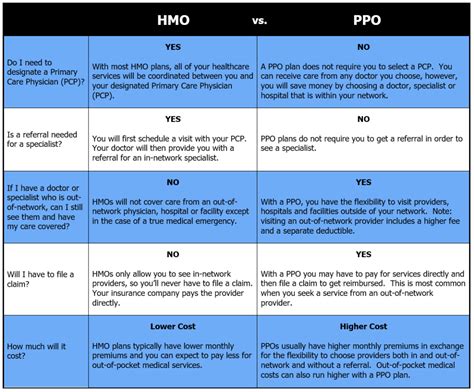
How PPOs Work
PPOs work by contracting with a network of healthcare providers to offer discounted services to plan members. Policyholders pay a premium to the insurance company, which provides access to the network of preferred providers. When policyholders receive care from in-network providers, they typically pay a lower copayment or coinsurance. If policyholders receive care from out-of-network providers, they may pay a higher copayment or coinsurance, or the insurance company may not cover the services at all.Types of PPOs
Advantages and Disadvantages of PPOs
PPOs have several advantages, including flexibility, comprehensive coverage, and cost-effectiveness. However, they also have some disadvantages, such as higher premiums, deductibles, and copayments. Additionally, PPOs may have limitations on coverage, such as pre-authorization requirements or exclusions for certain medical services.How to Choose a PPO
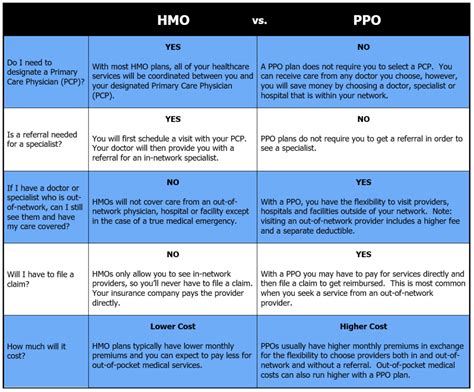
Tips for Using a PPO
To get the most out of a PPO, consider the following tips: * Choose in-network providers: Receive care from in-network providers to reduce out-of-pocket expenses. * Understand the coverage: Review the coverage offered by the PPO and understand what is included and excluded. * Keep track of expenses: Monitor your medical expenses and keep track of your deductible, copayments, and coinsurance. * Take advantage of preventive care: Use the preventive care services offered by the PPO, such as annual physicals, screenings, and vaccinations.PPOs and the Affordable Care Act (ACA)

Essential Health Benefits
The ACA requires PPOs to cover essential health benefits, including: * Ambulatory patient services * Emergency services * Hospitalization * Maternity and newborn care * Mental health and substance use disorder services * Prescription medications * Preventive and wellness services * Rehabilitative and habilitative servicesPPOs and Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance

Group Health Insurance
Group health insurance plans, including PPOs, are often offered by employers to their employees. These plans have several advantages, including: * Lower premiums: Group health insurance plans often have lower premiums compared to individual plans. * Broader coverage: Group health insurance plans may offer broader coverage, including coverage for dependents and retirees. * Simplified administration: Group health insurance plans are often administered by the employer, simplifying the process for employees.Conclusion and Next Steps

What is a Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)?
+A Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) is a type of health insurance plan that offers a network of healthcare providers who have agreed to provide medical services at discounted rates to plan members.
How do PPOs work?
+PPOs work by contracting with a network of healthcare providers to offer discounted services to plan members. Policyholders pay a premium to the insurance company, which provides access to the network of preferred providers.
What are the benefits of PPOs?
+PPOs offer several benefits, including flexibility, comprehensive coverage, and cost-effectiveness. They also often cover preventive care services, hospital stays, and prescription medications.
How do I choose a PPO?
+Choosing a PPO involves several factors, including the network of providers, coverage, cost, and additional benefits. Consider your individual needs and priorities when selecting a PPO.
Can I use a PPO with the Affordable Care Act (ACA)?
+Yes, PPOs are one of the types of health insurance plans available through the ACA marketplaces. The ACA requires PPOs to cover essential health benefits, including preventive care, hospital stays, and prescription medications.
