Intro
Discover key facts about Pregabalin, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand this medications role in treating epilepsy, anxiety, and nerve pain, and learn about its dosage, benefits, and risks.
Pregabalin, a medication primarily used to treat epilepsy, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain, has been a subject of interest for many due to its efficacy and unique mechanism of action. Understanding pregabalin is crucial for both medical professionals and patients who are prescribed this medication. It's essential to delve into the specifics of how pregabalin works, its benefits, potential side effects, and the conditions it treats.
The importance of pregabalin lies in its ability to provide relief to individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions that are often difficult to manage. Chronic pain, whether due to diabetes, shingles, or fibromyalgia, significantly impacts the quality of life, affecting not just the physical well-being but also the mental health of sufferers. Pregabalin offers a ray of hope for these individuals by reducing pain and, in some cases, alleviating associated symptoms like anxiety and sleep disturbances.
As research continues to uncover the full potential of pregabalin, it's vital for patients and healthcare providers to stay informed about the latest findings and guidelines. This includes understanding the proper dosage, potential drug interactions, and the importance of gradual dose adjustments to minimize side effects. By exploring pregabalin in depth, we can better appreciate its role in modern medicine and its potential to improve the lives of many.
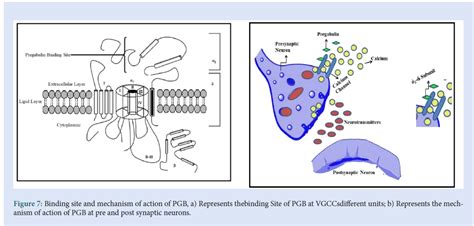
Pregabalin Mechanism of Action
Benefits of Pregabalin
The benefits of pregabalin are multifaceted, making it a valuable option for treating various conditions. Key benefits include: - **Effective Pain Management:** Pregabalin has been shown to significantly reduce chronic pain in conditions like diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and fibromyalgia. - **Anxiolytic Effects:** It has anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) properties, which can be particularly beneficial for patients experiencing anxiety alongside chronic pain. - **Improved Sleep:** Many patients report improved sleep quality while on pregabalin, which is essential for overall health and can be particularly beneficial for those with fibromyalgia.Pregabalin Uses
Potential Side Effects
While pregabalin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, especially when first starting the medication or when the dose is increased. Common side effects include: - Dizziness - Drowsiness - Dry mouth - Edema (swelling) - Weight gainPregabalin Dosage and Administration
Drug Interactions
Pregabalin can interact with other medications, including: - **Opioids:** Increased risk of respiratory depression when used together. - **Benzodiazepines:** Enhanced sedative effects. - **Sleep Aids:** Increased risk of somnolence.Pregabalin and Pregnancy

Pregabalin Withdrawal
Abruptly stopping pregabalin can lead to withdrawal symptoms, which may include: - Insomnia - Nausea - Headache - Diarrhea Gradual tapering of the dose over at least one week is recommended when discontinuing pregabalin.Pregabalin Abuse Potential

Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring is crucial for patients on pregabalin, including: - **Mental Status:** For signs of depression, anxiety, or suicidal thoughts. - **Physical Condition:** Monitoring for edema, weight changes, and other potential side effects. - **Pain Levels:** Assessing the effectiveness of pregabalin in managing pain.Pregabalin Alternatives
Future Directions
Research into pregabalin and its analogs continues, with potential future developments including: - **New Indications:** Exploring its use in other conditions, such as chronic migraine. - **Improved Formulations:** Developing formulations that reduce side effects or improve bioavailability.Pregabalin in Clinical Practice
Patient Education
Educating patients about pregabalin is crucial for its safe and effective use. This includes information on: - **Proper Dosing:** How to take pregabalin as prescribed. - **Side Effects:** Recognizing potential side effects and when to seek medical help. - **Lifestyle Modifications:** How diet, exercise, and stress management can complement pregabalin therapy.What is pregabalin used for?
+Pregabalin is used for the treatment of epilepsy, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain, including diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia.
How does pregabalin work?
+Pregabalin works by binding to the alpha2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, reducing the release of several neurotransmitters and thus reducing neuronal excitability and pain transmission.
What are common side effects of pregabalin?
+Common side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, edema, and weight gain. It's essential to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider.
Can pregabalin be used during pregnancy?
+Pregabalin should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare provider.
How should pregabalin be discontinued?
+Pregabalin should be tapered gradually over at least one week to minimize the risk of withdrawal symptoms.
As we conclude our exploration of pregabalin, it's clear that this medication offers significant benefits for individuals suffering from chronic pain and epilepsy. By understanding its mechanism of action, potential side effects, and proper use, patients and healthcare providers can work together to maximize its therapeutic potential. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about pregabalin in the comments below, and we encourage you to share this article with anyone who might benefit from this comprehensive overview of pregabalin.
