Intro
Learn about Omeprazole, a prescription drug treating acid reflux and heartburn, with information on dosage, side effects, and interactions, helping patients understand this proton pump inhibitor medication.
Omeprazole is a widely used prescription medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). It is primarily used to treat conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, and peptic ulcers. The importance of understanding omeprazole and its uses cannot be overstated, as it has become a staple in the treatment of various gastrointestinal disorders. In this article, we will delve into the world of omeprazole, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and potential side effects.
The significance of omeprazole lies in its ability to reduce the production of stomach acid, which can help alleviate symptoms of acid reflux and other related conditions. By decreasing acid production, omeprazole allows the esophagus and stomach to heal, reducing the risk of further damage and complications. Moreover, omeprazole has been shown to be effective in treating a range of gastrointestinal disorders, making it a versatile and widely prescribed medication.
As we explore the topic of omeprazole, it is essential to understand its history, development, and evolution. Omeprazole was first introduced in the 1980s and has since become one of the most commonly prescribed medications worldwide. Its effectiveness and safety profile have made it a popular choice among healthcare professionals, who often prescribe it to patients suffering from gastrointestinal disorders. With the rise of generic versions and over-the-counter (OTC) options, omeprazole has become more accessible and affordable for patients, further increasing its popularity.
Omeprazole Mechanism of Action
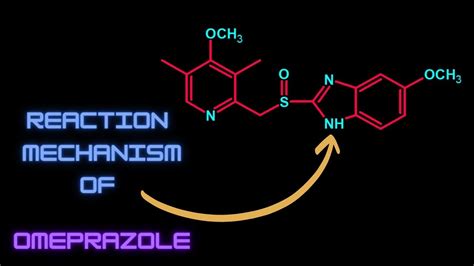
Omeprazole works by irreversibly inhibiting the H+/K+ ATPase enzyme system at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell. This enzyme system is responsible for the production of stomach acid, and by inhibiting it, omeprazole reduces the amount of acid produced. The reduction in acid production allows the esophagus and stomach to heal, reducing the risk of further damage and complications. Omeprazole's mechanism of action is complex and involves several key steps, including the activation of the drug, the binding of the drug to the enzyme, and the subsequent inhibition of acid production.
Benefits of Omeprazole
The benefits of omeprazole are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of using omeprazole include: * Rapid relief from symptoms of acid reflux and other related conditions * Effective treatment of peptic ulcers and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome * Reduced risk of complications and further damage to the esophagus and stomach * Convenience and ease of use, with once-daily dosing and a range of formulations available * Well-tolerated and safe, with a low risk of serious side effectsOmeprazole Uses and Indications
Omeprazole is indicated for the treatment of a range of gastrointestinal disorders, including:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Peptic ulcers
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- Erosive esophagitis
- Duodenal ulcers Omeprazole is also used off-label for the treatment of other conditions, such as dyspepsia and gastroesophageal reflux disease in children.
Side Effects and Interactions
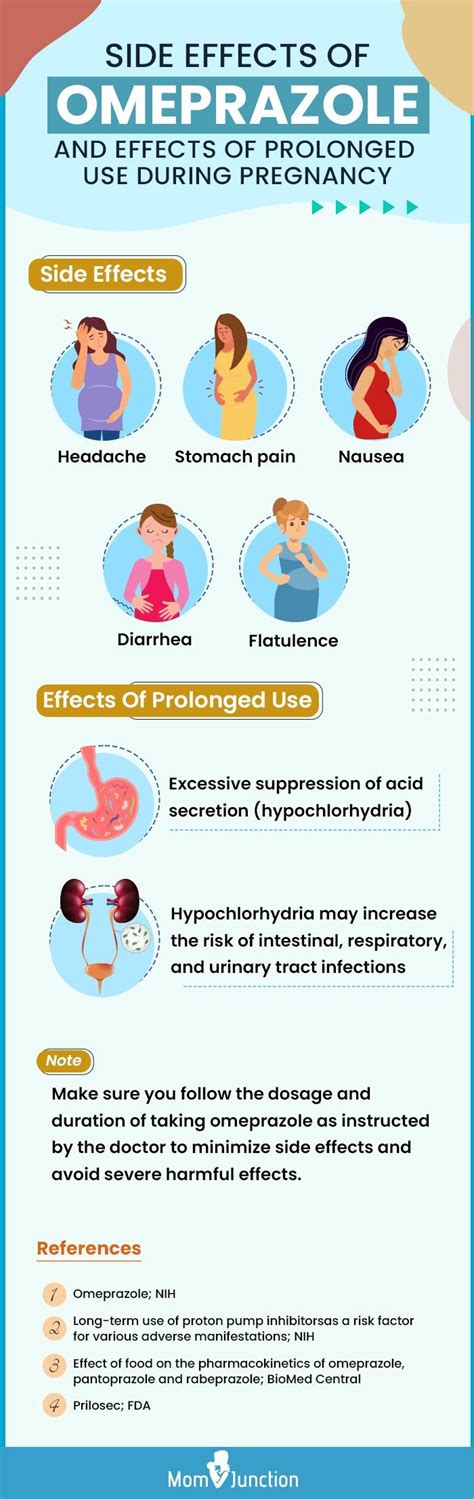
While omeprazole is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some patients. Common side effects include: * Headache * Diarrhea * Abdominal pain * Nausea and vomiting * Dizziness and drowsiness Omeprazole can also interact with other medications, including: * Antacids * Warfarin * Phenobarbital * Phenytoin * Rifampin It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking before starting omeprazole.Omeprazole Dosage and Administration

The dosage and administration of omeprazole vary depending on the condition being treated and the patient's age and weight. Typical dosages include:
- 20-40 mg once daily for adults with GERD
- 20-60 mg once daily for adults with peptic ulcers
- 40-80 mg once daily for adults with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome Omeprazole is available in a range of formulations, including capsules, tablets, and oral suspensions.
Precautions and Contraindications
While omeprazole is generally safe and effective, there are certain precautions and contraindications to be aware of. These include: * Hypersensitivity to omeprazole or other PPIs * Pregnancy and breastfeeding * Liver disease * Kidney disease * Osteoporosis It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about any medical conditions or allergies you have before starting omeprazole.Omeprazole Over-the-Counter (OTC) Options

In recent years, omeprazole has become available over-the-counter (OTC) in many countries. OTC omeprazole is available in lower doses and is intended for short-term use only. While OTC omeprazole can be convenient and affordable, it is essential to follow the instructions carefully and consult with a healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns.
Generic Omeprazole Options
Generic omeprazole is also available in many countries, offering a more affordable alternative to brand-name omeprazole. Generic omeprazole is equivalent to brand-name omeprazole in terms of quality, safety, and efficacy. However, it is essential to ensure that the generic version is manufactured by a reputable company and meets the required standards.Omeprazole and Pregnancy
Omeprazole is generally considered safe during pregnancy, but it should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider. The use of omeprazole during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of certain birth defects, such as congenital heart defects and cleft palate. However, the benefits of omeprazole may outweigh the risks in some cases, and the decision to use omeprazole during pregnancy should be made on a case-by-case basis.
Omeprazole and Breastfeeding
Omeprazole is excreted in breast milk, and its use during breastfeeding is not recommended. The use of omeprazole during breastfeeding has been associated with an increased risk of certain adverse effects in infants, such as diarrhea and vomiting. However, the benefits of omeprazole may outweigh the risks in some cases, and the decision to use omeprazole during breastfeeding should be made on a case-by-case basis.Omeprazole and Interactions with Other Medications
Omeprazole can interact with other medications, including:
- Antacids
- Warfarin
- Phenobarbital
- Phenytoin
- Rifampin It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking before starting omeprazole.
Omeprazole and Side Effects
While omeprazole is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some patients. Common side effects include: * Headache * Diarrhea * Abdominal pain * Nausea and vomiting * Dizziness and drowsiness Omeprazole can also cause more serious side effects, such as: * Allergic reactions * Severe skin reactions * Liver damage * Kidney damage It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these side effects.Omeprazole and Long-Term Use

Long-term use of omeprazole has been associated with an increased risk of certain adverse effects, such as:
- Osteoporosis
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Magnesium deficiency
- Increased risk of infections It is essential to discuss the risks and benefits of long-term omeprazole use with your healthcare provider.
Omeprazole and Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms can occur when omeprazole is stopped suddenly. Common withdrawal symptoms include: * Rebound acid hypersecretion * Diarrhea * Abdominal pain * Nausea and vomiting It is essential to taper off omeprazole gradually to minimize the risk of withdrawal symptoms.What is omeprazole used for?
+Omeprazole is used to treat a range of gastrointestinal disorders, including gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
How does omeprazole work?
+Omeprazole works by irreversibly inhibiting the H+/K+ ATPase enzyme system at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell, reducing the production of stomach acid.
What are the common side effects of omeprazole?
+Common side effects of omeprazole include headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, and dizziness and drowsiness.
Can I take omeprazole during pregnancy?
+Omeprazole is generally considered safe during pregnancy, but it should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Can I take omeprazole while breastfeeding?
+Omeprazole is excreted in breast milk, and its use during breastfeeding is not recommended.
In summary, omeprazole is a widely used prescription medication that is effective in treating a range of gastrointestinal disorders. While it is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects and interact with other medications. It is essential to discuss the risks and benefits of omeprazole with your healthcare provider and follow their guidance carefully. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of omeprazole and its uses. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
