Intro
The prothrombin ratio, also known as the prothrombin time (PT) ratio, is a crucial blood test used to evaluate the blood's clotting ability. It measures the time it takes for blood to clot and compares it to a standard sample. The prothrombin ratio is essential in assessing the risk of bleeding or thrombosis in patients, particularly those taking anticoagulant medications. Understanding the normal range of the prothrombin ratio is vital for healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about patient care.
The prothrombin ratio is calculated by dividing the patient's prothrombin time by the normal prothrombin time, which is typically determined by the laboratory. The result is then multiplied by 100 to express it as a percentage. A normal prothrombin ratio usually ranges from 0.9 to 1.1, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific testing methods used. It's essential to note that the normal range may differ between laboratories, and healthcare professionals should consult the reference range provided by the testing laboratory.
The prothrombin ratio is a critical component of the coagulation cascade, which involves a series of complex interactions between various clotting factors. The prothrombin time measures the activity of factors II, V, VII, X, and fibrinogen, which are essential for the formation of a blood clot. Any abnormalities in these factors can affect the prothrombin ratio, leading to an increased risk of bleeding or thrombosis. Healthcare professionals use the prothrombin ratio to monitor patients with bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, and those taking anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin.
Understanding Prothrombin Ratio Results
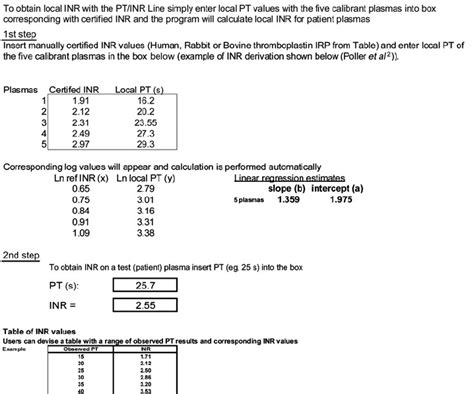
Factors Affecting Prothrombin Ratio Results
Several factors can affect the prothrombin ratio results, including age, sex, and the presence of underlying medical conditions. For example, older adults may have a slightly prolonged prothrombin time due to age-related changes in the coagulation cascade. Additionally, patients with liver disease or vitamin K deficiency may have an abnormal prothrombin ratio due to impaired clotting factor production. It's essential to consider these factors when interpreting prothrombin ratio results to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.Prothrombin Ratio and Anticoagulant Medications
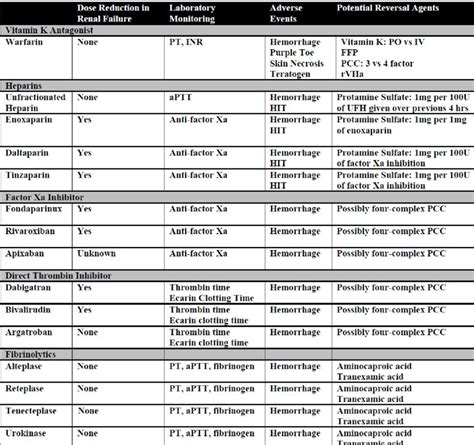
Target Prothrombin Ratio Ranges
The target prothrombin ratio ranges for patients taking anticoagulant medications are as follows: * Warfarin: 2.0-3.0 * Acenocoumarol: 2.0-3.0 * Phenindione: 2.0-3.0 These target ranges may vary depending on the patient's medical condition and the specific medication used. Healthcare professionals should consult the manufacturer's instructions and relevant clinical guidelines to determine the optimal target range for each patient.Prothrombin Ratio and Bleeding Disorders
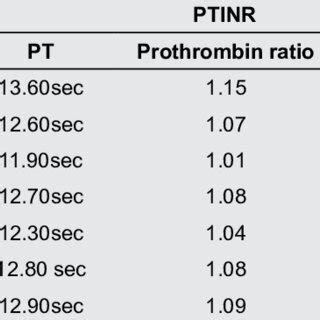
Prothrombin Ratio in Hemophilia
In patients with hemophilia, the prothrombin ratio can be prolonged due to a deficiency in factor VIII or factor IX. The degree of prolongation depends on the severity of the deficiency and the presence of other underlying medical conditions. Healthcare professionals use the prothrombin ratio to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and adjust the dosage of clotting factor concentrates as needed.Prothrombin Ratio and Liver Disease

Prothrombin Ratio in Liver Disease
In patients with liver disease, the prothrombin ratio can be prolonged due to impaired production of clotting factors. The degree of prolongation depends on the severity of the liver disease and the presence of other underlying medical conditions. Healthcare professionals use the prothrombin ratio to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and adjust the dosage of medications as needed.Prothrombin Ratio and Vitamin K Deficiency
Prothrombin Ratio in Vitamin K Deficiency
In patients with vitamin K deficiency, the prothrombin ratio can be prolonged due to impaired production of clotting factors. The degree of prolongation depends on the severity of the deficiency and the presence of other underlying medical conditions. Healthcare professionals use the prothrombin ratio to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and adjust the dosage of vitamin K supplements as needed.Prothrombin Ratio Testing

Prothrombin Ratio Test Results
The prothrombin ratio test results are typically reported as a ratio, with a normal range of 0.9-1.1. The results may be affected by various factors, including the presence of underlying medical conditions, the use of anticoagulant medications, and the quality of the blood sample. Healthcare professionals should interpret the results in the context of the patient's medical history and other laboratory tests.What is the normal range for the prothrombin ratio?
+The normal range for the prothrombin ratio is typically between 0.9 and 1.1, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific testing methods used.
What does a prolonged prothrombin time indicate?
+A prolonged prothrombin time may indicate a deficiency in one or more clotting factors, the presence of a bleeding disorder, or the use of anticoagulant medications.
How is the prothrombin ratio used to monitor patients taking anticoagulant medications?
+The prothrombin ratio is used to monitor patients taking anticoagulant medications by adjusting the dosage of the medication to maintain a target prothrombin ratio range, which varies depending on the specific medication and the patient's medical condition.
What is the target prothrombin ratio range for patients taking warfarin?
+The target prothrombin ratio range for patients taking warfarin is typically between 2.0 and 3.0, although this can vary depending on the patient's medical condition and the specific medication used.
How is the prothrombin ratio affected by liver disease?
+The prothrombin ratio can be prolonged in patients with liver disease due to impaired production of clotting factors, and the degree of prolongation depends on the severity of the liver disease and the presence of other underlying medical conditions.
In conclusion, the prothrombin ratio is a vital blood test used to evaluate the blood's clotting ability and assess the risk of bleeding or thrombosis in patients. Understanding the normal range of the prothrombin ratio and the factors that can affect it is essential for healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about patient care. By interpreting the prothrombin ratio results in the context of the patient's medical history and other laboratory tests, healthcare professionals can diagnose and monitor a range of medical conditions, including bleeding disorders, liver disease, and vitamin K deficiency. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with the prothrombin ratio test, and to ask any questions they may have about this important diagnostic tool.
