Intro
Discover 5 crucial Prothrombin Time Test facts, including coagulation, blood clotting, and bleeding disorders, to understand this vital diagnostic tool for monitoring anticoagulant therapy and liver function.
Prothrombin time tests are a crucial diagnostic tool in the medical field, particularly in assessing the blood's clotting ability. This test is essential for evaluating patients who are at risk of bleeding or thrombosis, and it plays a significant role in monitoring the effectiveness of certain medications. Understanding the basics of prothrombin time tests can help individuals appreciate their importance in healthcare. The prothrombin time test, also known as the protime or PT test, measures how long it takes blood to clot once tissue factor is added. This information is vital for doctors to diagnose and manage various conditions related to blood clotting.
The significance of prothrombin time tests cannot be overstated, especially in emergency situations where rapid assessment of a patient's blood clotting ability is necessary. For instance, in cases of severe injuries or during surgeries, knowing how the blood will react can be the difference between life and death. Moreover, for patients on anticoagulant therapy, regular prothrombin time tests are crucial to ensure that their blood is within the therapeutic range, neither too prone to clotting nor too prone to bleeding. This delicate balance is key to preventing complications such as stroke or pulmonary embolism in patients at risk.
The prothrombin time test is just one of several tests used to evaluate the coagulation pathway, but it is particularly useful because it assesses the extrinsic and common pathways of coagulation. This makes it a valuable tool for identifying deficiencies in factors such as factor VII (part of the extrinsic pathway) and factors X, V, II (prothrombin), and fibrinogen (part of the common pathway). Understanding how these factors interact and how their levels can affect clotting time is essential for diagnosing coagulopathies and monitoring the effects of anticoagulant medications.
What is Prothrombin Time Test

Importance of Standardization
The standardization of prothrombin time results through the INR has significantly improved patient care. It ensures that regardless of where a patient's blood is tested, the results can be reliably compared and used to guide treatment decisions. This is particularly important for patients who travel or receive care in different healthcare settings, as it ensures continuity of care. Moreover, the INR has become a critical component of managing anticoagulation therapy, allowing healthcare providers to adjust medication doses based on a patient's response to treatment, thereby minimizing the risk of adverse events.How Prothrombin Time Test Works
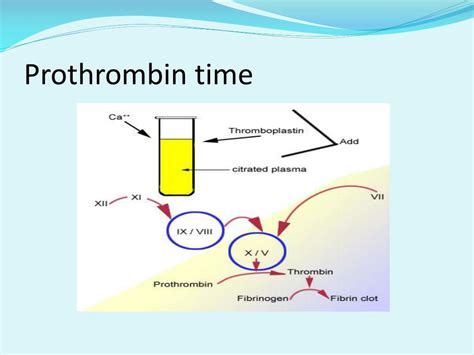
Factors Affecting Prothrombin Time
Several factors can affect the results of a prothrombin time test. These include the use of anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin, which can significantly prolong the prothrombin time by inhibiting the production of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors (II, VII, IX, and X). Other factors such as liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, and the presence of inhibitors (e.g., lupus anticoagulant) can also influence the test results. It is crucial for healthcare providers to consider these factors when interpreting prothrombin time results to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.Benefits of Prothrombin Time Test

Monitoring Anticoagulation Therapy
One of the primary uses of the prothrombin time test is in the monitoring of anticoagulation therapy, particularly for patients on warfarin. By regularly checking the INR, healthcare providers can ensure that the patient's blood is within the therapeutic range, balancing the risk of thrombosis against the risk of bleeding. This monitoring is critical because the therapeutic window for warfarin is narrow, and small changes in dosage or the presence of interacting substances can significantly affect the INR, potentially leading to adverse outcomes.Prothrombin Time Test Procedure

Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting the results of a prothrombin time test requires consideration of the patient's clinical context. A prolonged prothrombin time may indicate a deficiency in one or more of the clotting factors involved in the extrinsic or common coagulation pathways. This could be due to a variety of causes, including liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, or the use of anticoagulant medications. The international normalized ratio (INR) is often used to standardize results, making it easier to compare results over time and between different laboratories. For patients on warfarin, the target INR range depends on the indication for anticoagulation but is typically between 2.0 and 3.0.Common Uses of Prothrombin Time Test
Limitations and Considerations
While the prothrombin time test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has its limitations. It does not assess the intrinsic pathway of coagulation, which involves factors XII, XI, IX, and VIII. Therefore, abnormalities in these factors may not be detected by the prothrombin time test alone. Additionally, the test can be influenced by various factors, including the quality of the blood sample, the type of anticoagulant used in the collection tube, and the presence of certain medications or substances that can affect coagulation.Prothrombin Time Test and Pregnancy

Pregnancy-Related Considerations
Pregnancy-related considerations are crucial when interpreting prothrombin time results. Physiological changes during pregnancy can lead to alterations in coagulation factor levels, potentially affecting the prothrombin time. Additionally, the risk of thrombosis increases during pregnancy, making it essential to closely monitor women with a history of thrombotic events or those on anticoagulant therapy. The management of anticoagulation during pregnancy requires careful consideration of both the mother's and the fetus's health, as anticoagulant medications can have significant effects on fetal development and pregnancy outcomes.Prothrombin Time Test and Liver Disease

Liver Disease and Coagulation
The relationship between liver disease and coagulation is complex. The liver produces the majority of clotting factors, and liver dysfunction can lead to decreased production of these factors, resulting in a coagulopathy. The prothrombin time test, along with other tests such as the partial thromboplastin time (PTT), can help in assessing the severity of liver disease and the risk of bleeding. In patients with advanced liver disease, such as cirrhosis, the prothrombin time can be significantly prolonged, indicating a high risk of bleeding complications.Prothrombin Time Test and Anticoagulant Therapy
Management of Anticoagulation
The management of anticoagulation therapy involves a delicate balance between preventing thrombosis and minimizing the risk of bleeding. The prothrombin time test is essential in this management, as it provides a direct measure of the anticoagulant effect of medications like warfarin. Regular monitoring allows for the early detection of changes in the patient's coagulation status, enabling timely adjustments to therapy. This personalized approach to anticoagulation management can significantly reduce the risk of adverse events and improve patient outcomes.What is the primary use of the prothrombin time test?
+The primary use of the prothrombin time test is to evaluate the extrinsic and common pathways of blood coagulation and to monitor patients on anticoagulant therapy, particularly those taking warfarin.
How is the prothrombin time test result expressed?
+The result of the prothrombin time test is often expressed as the international normalized ratio (INR), which standardizes the results for different thromboplastins used in various laboratories.
What factors can affect the prothrombin time test results?
+Several factors can affect the results of a prothrombin time test, including the use of anticoagulant medications, liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, and the presence of inhibitors such as lupus anticoagulant.
Why is standardization of prothrombin time results important?
+Standardization of prothrombin time results through the INR is important because it allows for reliable comparisons of results from different laboratories, ensuring continuity of care and accurate monitoring of anticoagulation therapy.
How often should the prothrombin time test be performed for patients on warfarin?
+The frequency of prothrombin time testing for patients on warfarin depends on several factors, including the patient's stability on therapy, changes in health status, and the presence of interacting substances. Generally, testing is more frequent when initiating or adjusting warfarin therapy and less frequent for stable patients.
As we conclude our discussion on the prothrombin time test, it is clear that this diagnostic tool plays a vital role in the management of patients with coagulation disorders and those on anticoagulant therapy. Its ability to assess the extrinsic and common pathways of coagulation makes it an indispensable tool in clinical practice. By understanding the mechanisms, benefits, and limitations of the prothrombin time test, healthcare providers can better utilize this test to improve patient outcomes. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with the prothrombin time test, and we encourage further discussion on the importance of accurate and timely diagnostic testing in healthcare. Whether you are a healthcare professional or someone interested in learning more about coagulation disorders, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into the world of prothrombin time testing.
