Intro
Discover 5 crucial PSA test facts, including prostate cancer screening, PSA levels, and biopsy procedures, to understand prostate health and diagnose issues early.
The Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test has been a widely discussed topic in the medical community, particularly among men over the age of 50. As a screening tool for prostate cancer, the PSA test has both its advocates and detractors. Understanding the intricacies of the PSA test is essential for making informed decisions about one's health. In this article, we will delve into the world of PSA testing, exploring its benefits, limitations, and controversies.
The importance of PSA testing lies in its ability to detect prostate cancer at an early stage, potentially improving treatment outcomes. However, the test is not without its drawbacks, and there is ongoing debate about its effectiveness in reducing mortality rates. As we navigate the complex landscape of PSA testing, it is crucial to separate fact from fiction and to consider the latest research and guidelines. Whether you are a healthcare professional or simply looking to educate yourself on the topic, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the PSA test and its role in modern medicine.
As we explore the world of PSA testing, it is essential to consider the various factors that influence the test's accuracy and reliability. From the nuances of PSA levels to the importance of digital rectal exams, there is a wealth of information to digest. By examining the latest studies and expert opinions, we can gain a deeper understanding of the PSA test's strengths and weaknesses, ultimately empowering us to make informed decisions about our health. So, let us embark on this journey of discovery, exploring the intricacies of PSA testing and its significance in the modern medical landscape.
Introduction to PSA Testing

Understanding PSA Levels
PSA levels are typically measured in nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) of blood. A PSA level of 4 ng/mL or lower is generally considered normal, while levels above 4 ng/mL may indicate the presence of prostate cancer. However, it is essential to note that PSA levels can fluctuate over time, and a single elevated reading does not necessarily indicate cancer. Factors such as age, medication, and lifestyle can influence PSA levels, highlighting the need for careful interpretation and consideration of individual circumstances.The Benefits of PSA Testing

Reducing Mortality Rates
Studies have shown that PSA testing can reduce mortality rates from prostate cancer. A landmark study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that PSA testing reduced the risk of death from prostate cancer by 20% over a 14-year period. While these findings are promising, it is essential to note that the study had limitations, and the benefits of PSA testing may vary depending on individual circumstances.The Limitations of PSA Testing
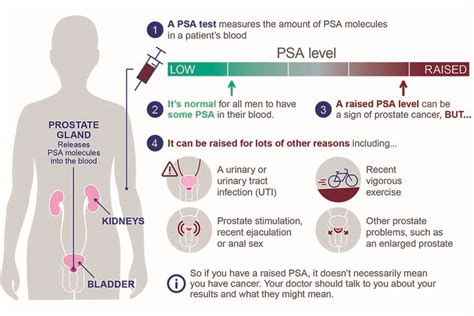
Overdiagnosis and Overtreatment
Overdiagnosis and overtreatment are significant concerns in the context of PSA testing. A study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute found that up to 50% of men diagnosed with prostate cancer may not require treatment, as their tumors are slow-growing and unlikely to cause symptoms. This highlights the need for careful consideration and individualized decision-making when it comes to PSA testing and treatment.PSA Test Facts

Age and PSA Testing
Age is a significant factor in PSA testing. Men over the age of 50 are at increased risk of developing prostate cancer, and PSA testing is often recommended for this age group. However, it is essential to note that PSA testing may not be necessary for younger men, as the risk of prostate cancer is lower. As we consider the role of age in PSA testing, it is crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and to consider individual circumstances.Current Guidelines and Recommendations
Shared Decision-Making
Shared decision-making is a crucial aspect of PSA testing. Men should discuss the benefits and risks of PSA testing with their doctor, considering individual circumstances such as age, family history, and overall health. This approach enables men to make informed decisions about their health, weighing the potential benefits of PSA testing against the risks.Future Directions in PSA Testing

Emerging Biomarkers
Emerging biomarkers, such as the prostate cancer antigen 3 (PCA3) test, may improve the accuracy of PSA testing. These biomarkers can help distinguish between slow-growing and aggressive tumors, reducing the risk of overdiagnosis and overtreatment. As we consider the potential of emerging biomarkers, it is essential to weigh the benefits against the risks and to consider individual circumstances.What is the purpose of PSA testing?
+PSA testing is used to detect prostate cancer at an early stage, potentially improving treatment outcomes and reducing mortality rates.
What are the limitations of PSA testing?
+PSA testing can produce false-positive results, leading to unnecessary biopsies and treatments. Additionally, PSA testing can detect slow-growing tumors that may never cause symptoms or pose a threat to health, leading to overdiagnosis and overtreatment.
What are the current guidelines for PSA testing?
+Current guidelines and recommendations for PSA testing vary depending on the organization and individual circumstances. Men should discuss the benefits and risks of PSA testing with their doctor, considering individual circumstances such as age, family history, and overall health.
As we conclude our exploration of PSA testing, it is essential to remember that this complex topic requires careful consideration and individualized decision-making. By weighing the potential benefits against the risks and considering emerging trends and technologies, we can improve our understanding of PSA testing and its role in modern medicine. If you have any questions or concerns about PSA testing, we encourage you to share your thoughts and engage in the conversation. Together, we can work towards a deeper understanding of this important topic and its significance in the modern medical landscape.
