Intro
Identify Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing, to detect this life-threatening blood clot condition, also related to Deep Vein Thrombosis and lung disease, for prompt medical treatment.
Pulmonary embolism is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a blood clot lodges in the lungs, blocking blood flow. The symptoms of pulmonary embolism can vary widely, and in some cases, they may not be immediately apparent. However, it is essential to recognize the warning signs of pulmonary embolism to seek medical attention promptly. In this article, we will delve into the importance of understanding pulmonary embolism symptoms, the risks associated with the condition, and the measures that can be taken to prevent and treat it.
The importance of recognizing pulmonary embolism symptoms cannot be overstated. Pulmonary embolism is a leading cause of death worldwide, and it is estimated that hundreds of thousands of people die from the condition each year. The symptoms of pulmonary embolism can be similar to those of other conditions, such as heart attack or pneumonia, which can make diagnosis challenging. However, by being aware of the common symptoms of pulmonary embolism, individuals can seek medical attention quickly, reducing the risk of complications and improving outcomes.
Pulmonary embolism is often associated with deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the legs or other parts of the body. The clot can break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. The risk factors for pulmonary embolism include age, obesity, smoking, and family history, among others. Understanding these risk factors and taking steps to mitigate them can help reduce the likelihood of developing pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms and Warning Signs

The symptoms of pulmonary embolism can vary widely, but common warning signs include sudden and severe chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing up blood. Other symptoms may include rapid heart rate, sweating, and feeling lightheaded or faint. In some cases, pulmonary embolism may not produce any noticeable symptoms, which can make diagnosis challenging. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if any of these symptoms occur, as prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Common Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism
Some of the most common symptoms of pulmonary embolism include: * Sudden and severe chest pain or discomfort * Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing * Coughing up blood or pink, frothy mucus * Rapid heart rate or palpitations * Sweating or feeling clammy * Feeling lightheaded or faint * Anxiety or a sense of impending doomCauses and Risk Factors of Pulmonary Embolism
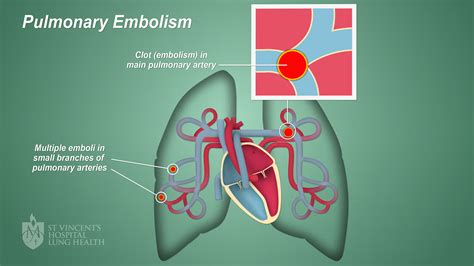
Pulmonary embolism is often caused by a blood clot that forms in the deep veins of the legs or other parts of the body. The clot can break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. The risk factors for pulmonary embolism include:
- Age: Pulmonary embolism is more common in people over 60 years old
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase the risk of blood clots
- Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of blood clots
- Family history: A family history of blood clots or pulmonary embolism can increase the risk
- Surgery: Recent surgery can increase the risk of blood clots
- Cancer: Certain types of cancer can increase the risk of blood clots
- Genetic disorders: Certain genetic disorders, such as factor V Leiden, can increase the risk of blood clots
Preventing Pulmonary Embolism
Preventing pulmonary embolism requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Some of the ways to prevent pulmonary embolism include: * Staying physically active: Regular exercise can help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of blood clots * Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can increase the risk of blood clots * Quitting smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of blood clots * Avoiding prolonged periods of immobility: Prolonged periods of sitting or lying down can increase the risk of blood clots * Wearing compression stockings: Compression stockings can help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of blood clotsDiagnosing Pulmonary Embolism
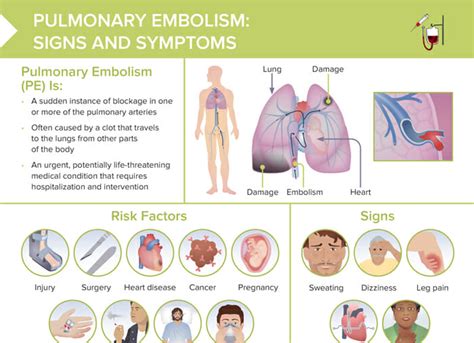
Diagnosing pulmonary embolism can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. However, a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests can help confirm the diagnosis. Some of the diagnostic tests used to diagnose pulmonary embolism include:
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can help rule out other conditions, such as pneumonia
- CT scan: A CT scan can help visualize the lungs and detect any blood clots
- Pulmonary angiogram: A pulmonary angiogram can help visualize the blood vessels in the lungs and detect any blockages
- D-dimer test: A D-dimer test can help detect any abnormal blood clotting
Treating Pulmonary Embolism
Treating pulmonary embolism requires a combination of medications and medical interventions. Some of the treatments used to treat pulmonary embolism include: * Anticoagulants: Anticoagulants can help prevent further blood clotting * Thrombolytics: Thrombolytics can help dissolve any existing blood clots * Oxygen therapy: Oxygen therapy can help improve oxygen levels in the blood * Pain management: Pain management can help reduce any discomfort or painComplications of Pulmonary Embolism
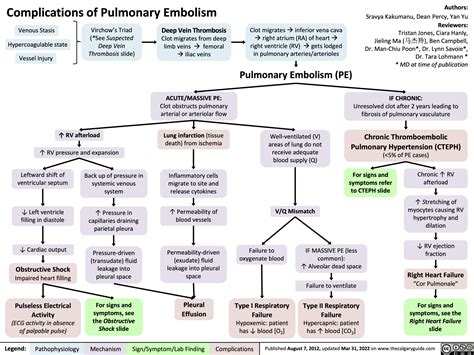
Pulmonary embolism can cause a range of complications, including:
- Respiratory failure: Pulmonary embolism can cause respiratory failure, which can be life-threatening
- Cardiac arrest: Pulmonary embolism can cause cardiac arrest, which can be fatal
- Pulmonary hypertension: Pulmonary embolism can cause pulmonary hypertension, which can increase the risk of further complications
- Recurrent pulmonary embolism: Pulmonary embolism can increase the risk of recurrent pulmonary embolism
Recovering from Pulmonary Embolism
Recovering from pulmonary embolism requires a combination of rest, medication, and lifestyle changes. Some of the ways to recover from pulmonary embolism include: * Getting plenty of rest: Rest can help the body recover from the condition * Taking medication: Medication can help prevent further blood clotting and reduce the risk of complications * Staying physically active: Regular exercise can help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of further complications * Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can increase the risk of further complicationsLiving with Pulmonary Embolism
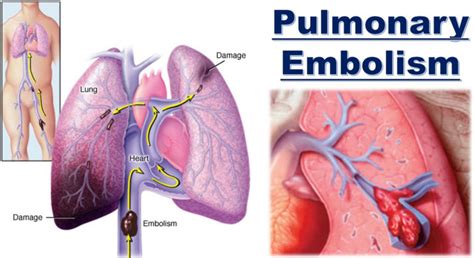
Living with pulmonary embolism requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Some of the ways to live with pulmonary embolism include:
- Staying physically active: Regular exercise can help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of further complications
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can increase the risk of further complications
- Quitting smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of further complications
- Avoiding prolonged periods of immobility: Prolonged periods of sitting or lying down can increase the risk of further complications
Coping with Pulmonary Embolism
Coping with pulmonary embolism can be challenging, but there are several ways to manage the condition. Some of the ways to cope with pulmonary embolism include: * Seeking support: Seeking support from family, friends, and support groups can help individuals cope with the condition * Practicing stress-reducing techniques: Stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help reduce stress and anxiety * Staying informed: Staying informed about the condition and its treatment can help individuals feel more in controlWhat are the symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
+The symptoms of pulmonary embolism can vary widely, but common warning signs include sudden and severe chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing up blood.
How is pulmonary embolism diagnosed?
+Pulmonary embolism is diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as chest X-ray, CT scan, and pulmonary angiogram.
What are the complications of pulmonary embolism?
+Pulmonary embolism can cause a range of complications, including respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, pulmonary hypertension, and recurrent pulmonary embolism.
How can pulmonary embolism be prevented?
+Pulmonary embolism can be prevented by staying physically active, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and avoiding prolonged periods of immobility.
What is the treatment for pulmonary embolism?
+The treatment for pulmonary embolism includes a combination of medications, such as anticoagulants and thrombolytics, and medical interventions, such as oxygen therapy and pain management.
In conclusion, pulmonary embolism is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt medical attention. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and risk factors of pulmonary embolism, individuals can take steps to prevent and treat the condition. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if any symptoms of pulmonary embolism occur, as prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes. We encourage readers to share this article with others, and to take the necessary steps to reduce their risk of developing pulmonary embolism. By working together, we can raise awareness about this critical condition and improve health outcomes for individuals around the world.
