Intro
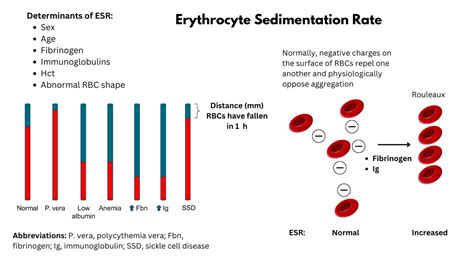
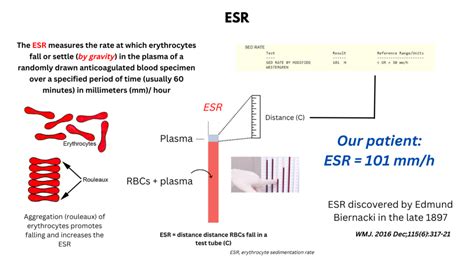
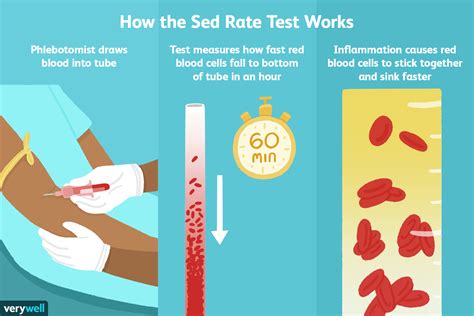
The RBC sedimentation rate, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a blood test that measures how quickly red blood cells (RBCs) settle to the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It is a non-specific test that can indicate the presence of inflammation or infection in the body. The test is often used to monitor the activity of chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, and to detect the presence of infections, such as endocarditis.
The RBC sedimentation rate is an important diagnostic tool because it can provide valuable information about the body's inflammatory response. When the body is experiencing inflammation, the immune system produces proteins that cause red blood cells to aggregate and settle more quickly. By measuring the rate at which red blood cells settle, healthcare providers can gain insight into the level of inflammation present in the body. The test is also useful for monitoring the effectiveness of treatments for chronic inflammatory diseases.
The RBC sedimentation rate is just one of many tests that healthcare providers use to diagnose and monitor diseases. It is often used in conjunction with other tests, such as the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, to provide a more complete picture of the body's inflammatory response. The test is relatively simple and inexpensive, making it a valuable tool for healthcare providers.
RBC Sedimentation Rate Test
How the Test is Performed
The RBC sedimentation rate test is typically performed in a laboratory setting. The test requires a blood sample, which is usually collected from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then placed in a test tube containing an anticoagulant, such as EDTA or citrate. The test tube is then sealed and left to stand for a period of time, usually one hour. After the allotted time has passed, the test tube is examined and the distance that the red blood cells have settled is measured and recorded.Interpreting the Results
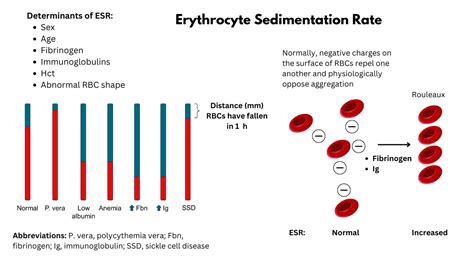
- 0-20 mm/h for men
- 0-30 mm/h for women
- 0-15 mm/h for children
A high RBC sedimentation rate can indicate the presence of inflammation or infection in the body. The test is not specific, however, and can be influenced by a variety of factors, including age, sex, and the presence of certain medical conditions.
Factors that Can Influence the Test
There are several factors that can influence the results of the RBC sedimentation rate test. These include:- Age: The RBC sedimentation rate tends to increase with age.
- Sex: Women tend to have higher RBC sedimentation rates than men.
- Pregnancy: The RBC sedimentation rate can increase during pregnancy.
- Anemia: The RBC sedimentation rate can be affected by the presence of anemia.
- Certain medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and kidney disease, can influence the results of the test.
Clinical Significance
- Monitor the activity of chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Detect the presence of infections, such as endocarditis
- Evaluate the effectiveness of treatments for chronic inflammatory diseases
- Diagnose and monitor certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease and cancer
The test is also useful for monitoring patients who are at risk of developing chronic inflammatory diseases. By detecting inflammation early, healthcare providers can take steps to prevent the development of these diseases.
Limitations of the Test
While the RBC sedimentation rate test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it does have several limitations. The test is not specific, and can be influenced by a variety of factors. It is also not sensitive, and can miss certain cases of inflammation or infection. Additionally, the test can be affected by certain medical conditions, such as anemia, and can produce false-positive results.Comparison with Other Tests
- C-reactive protein (CRP) test: This test measures the level of CRP, a protein that is produced by the liver in response to inflammation.
- Erythrocyte count: This test measures the number of red blood cells in the blood.
- White blood cell count: This test measures the number of white blood cells in the blood.
These tests can provide valuable information about the body's inflammatory response and can help healthcare providers diagnose and monitor certain medical conditions.
Future Directions
The RBC sedimentation rate test is a valuable diagnostic tool that has been used for many years. However, it does have several limitations, and there is a need for more sensitive and specific tests. Researchers are currently exploring new tests that can provide more accurate and reliable results. Some of these tests include:- High-sensitivity CRP test: This test measures the level of CRP in the blood and can provide more accurate results than the traditional CRP test.
- Interleukin-6 (IL-6) test: This test measures the level of IL-6, a protein that is produced by the immune system in response to inflammation.
- Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) test: This test measures the level of TNF-alpha, a protein that is produced by the immune system in response to inflammation.
These tests have the potential to provide more accurate and reliable results than the RBC sedimentation rate test and may become more widely used in the future.
What is the RBC sedimentation rate test used for?
+The RBC sedimentation rate test is used to monitor the activity of chronic inflammatory diseases, detect the presence of infections, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatments for chronic inflammatory diseases.
How is the RBC sedimentation rate test performed?
+The RBC sedimentation rate test is performed by collecting a blood sample from the patient, placing it in a test tube containing an anticoagulant, and measuring the distance that the red blood cells have settled after a period of time.
What are the limitations of the RBC sedimentation rate test?
+The RBC sedimentation rate test is not specific and can be influenced by a variety of factors, including age, sex, and certain medical conditions. It is also not sensitive and can miss certain cases of inflammation or infection.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the RBC sedimentation rate test and its clinical significance. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this topic. By working together, we can promote a better understanding of the importance of diagnostic testing and the role it plays in maintaining good health.
