Intro
Learn about Refeeding Syndrome labs, including electrolyte imbalance, phosphorus, magnesium, and glucose tests, to diagnose and manage this life-threatening condition after starvation or malnutrition.
Refeeding syndrome is a potentially fatal condition that can occur in individuals who are malnourished or have undergone significant caloric restriction, and then begin to eat again. This syndrome is characterized by a range of biochemical and clinical disturbances, including shifts in electrolytes, fluids, and minerals. The importance of understanding refeeding syndrome lies in its potential to cause severe complications, including cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, and even death. Therefore, it is crucial for healthcare professionals to be aware of the risks associated with refeeding and to take appropriate measures to prevent and manage this condition.
The significance of refeeding syndrome extends beyond the individual patient, as it also has implications for public health and healthcare systems. Malnutrition is a widespread problem that affects millions of people worldwide, and the risk of refeeding syndrome is particularly high in vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, children, and those with chronic illnesses. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and management of refeeding syndrome, healthcare professionals can provide better care for their patients and help to prevent this potentially life-threatening condition.
In recent years, there has been growing recognition of the importance of refeeding syndrome, and efforts have been made to raise awareness and improve management of this condition. This includes the development of guidelines and protocols for the safe refeeding of malnourished patients, as well as research into the underlying mechanisms and risk factors for refeeding syndrome. By continuing to advance our understanding of refeeding syndrome, we can work towards reducing the risks associated with this condition and improving outcomes for patients who are at risk.
Introduction to Refeeding Syndrome Labs
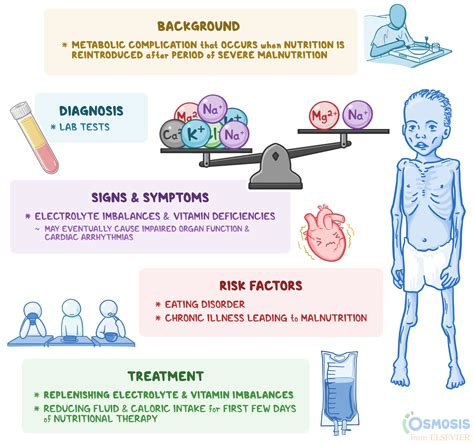
Key Components of Refeeding Syndrome Labs
The key components of refeeding syndrome labs include tests for electrolytes, such as phosphate, magnesium, and potassium, as well as tests for glucose, insulin, and other nutrients. These tests can help to identify patients who are at risk of developing refeeding syndrome, and can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.Some of the key lab tests that are used to diagnose and manage refeeding syndrome include:
- Electrolyte panels, which measure the levels of electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and chloride in the blood
- Phosphate levels, which can help to identify patients who are at risk of developing hypophosphatemia, a common complication of refeeding syndrome
- Magnesium levels, which can help to identify patients who are at risk of developing hypomagnesemia, another common complication of refeeding syndrome
- Glucose and insulin levels, which can help to identify patients who are at risk of developing hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia, both of which can be complications of refeeding syndrome
Interpretation of Refeeding Syndrome Labs
Some of the key factors that must be considered when interpreting refeeding syndrome labs include:
- The patient's nutritional status, including their weight, body mass index, and dietary history
- The patient's medical history, including any underlying conditions that may affect their risk of developing refeeding syndrome
- The patient's symptoms, including any signs of malnutrition, such as weight loss, muscle wasting, or fatigue
- The results of other diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies or other lab tests, which can help to identify underlying conditions that may be contributing to the patient's risk of developing refeeding syndrome
Management of Refeeding Syndrome Based on Lab Results
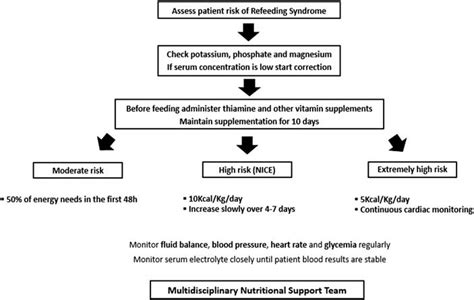
The management of refeeding syndrome based on lab results involves a range of strategies, including nutritional support, electrolyte replacement, and close monitoring of the patient's clinical status. The goal of treatment is to prevent the development of complications, such as cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, and death, and to promote the patient's overall health and well-being.Some of the key strategies that are used to manage refeeding syndrome based on lab results include:
- Gradual introduction of nutrition, starting with small amounts of calories and gradually increasing the amount over time
- Electrolyte replacement, including phosphate, magnesium, and potassium supplements
- Close monitoring of the patient's clinical status, including regular checks of their vital signs, electrolyte levels, and other lab tests
- Use of medications, such as thiamine and other vitamins, to prevent complications and promote the patient's overall health and well-being
Prevention of Refeeding Syndrome
Some of the key strategies that are used to prevent refeeding syndrome include:
- Early identification of patients who are at risk, including those with a history of malnutrition, weight loss, or other conditions that may affect their nutritional status
- Gradual introduction of nutrition, starting with small amounts of calories and gradually increasing the amount over time
- Close monitoring of the patient's clinical status, including regular checks of their vital signs, electrolyte levels, and other lab tests
- Use of nutritional supplements, such as vitamins and minerals, to prevent deficiencies and promote the patient's overall health and well-being
Risk Factors for Refeeding Syndrome
The risk factors for refeeding syndrome include a range of factors, including the patient's nutritional status, medical history, and symptoms. Some of the key risk factors include: * History of malnutrition or weight loss * Presence of underlying conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or kidney disease * Use of certain medications, such as diuretics or laxatives * Presence of symptoms, such as fatigue, weakness, or muscle wastingBy understanding these risk factors, healthcare professionals can take steps to prevent refeeding syndrome and promote the overall health and well-being of patients who are at risk.
Treatment of Refeeding Syndrome

Some of the key strategies that are used to treat refeeding syndrome include:
- Gradual introduction of nutrition, starting with small amounts of calories and gradually increasing the amount over time
- Electrolyte replacement, including phosphate, magnesium, and potassium supplements
- Close monitoring of the patient's clinical status, including regular checks of their vital signs, electrolyte levels, and other lab tests
- Use of medications, such as thiamine and other vitamins, to prevent complications and promote the patient's overall health and well-being
Complications of Refeeding Syndrome
The complications of refeeding syndrome can be severe and even life-threatening. Some of the key complications include: * Cardiac arrhythmias, which can be caused by electrolyte imbalances and other factors * Seizures, which can be caused by electrolyte imbalances and other factors * Death, which can be caused by severe electrolyte imbalances, cardiac arrhythmias, and other complicationsBy understanding these complications, healthcare professionals can take steps to prevent them and promote the overall health and well-being of patients who are at risk.
What is refeeding syndrome?
+Refeeding syndrome is a potentially fatal condition that can occur in individuals who are malnourished or have undergone significant caloric restriction, and then begin to eat again.
What are the risk factors for refeeding syndrome?
+The risk factors for refeeding syndrome include a range of factors, including the patient's nutritional status, medical history, and symptoms.
How is refeeding syndrome treated?
+The treatment of refeeding syndrome involves a range of strategies, including nutritional support, electrolyte replacement, and close monitoring of the patient's clinical status.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of refeeding syndrome labs and their importance in the diagnosis and management of refeeding syndrome. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and management of this condition, healthcare professionals can provide better care for their patients and help to prevent this potentially life-threatening condition. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about refeeding syndrome labs, and to take a proactive approach to managing this condition. Together, we can work towards reducing the risks associated with refeeding syndrome and promoting the overall health and well-being of patients who are at risk.
