Intro
Learn about normal blood glucose levels, blood sugar control, and glucose monitoring to manage diabetes and prediabetes, maintaining healthy glucose levels.
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When blood glucose levels are within a normal range, the body can function properly, and the risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke is reduced. In this article, we will delve into the importance of normal blood glucose levels, the factors that affect them, and the steps that can be taken to maintain a healthy blood glucose range.
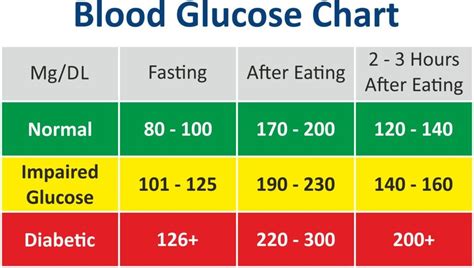
The human body is designed to regulate blood glucose levels within a narrow range, typically between 70 and 110 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). When blood glucose levels exceed this range, it can lead to a range of health problems, including fatigue, blurred vision, and increased thirst and urination. Prolonged periods of high blood glucose levels can also damage organs and tissues, leading to serious complications such as kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness.
Understanding normal blood glucose levels is essential for preventing and managing diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 460 million people worldwide suffer from diabetes, and this number is expected to increase to 700 million by 2045. By maintaining normal blood glucose levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes and its associated complications.
What are Normal Blood Glucose Levels?

Factors that Affect Blood Glucose Levels
Several factors can affect blood glucose levels, including: * Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats can raise blood glucose levels. * Physical activity: Regular exercise, such as walking, can help lower blood glucose levels. * Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can raise blood glucose levels. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood glucose regulation. * Stress: Chronic stress can raise blood glucose levels and worsen insulin resistance.How to Maintain Normal Blood Glucose Levels
Benefits of Maintaining Normal Blood Glucose Levels
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels has numerous benefits, including: * Reduced risk of chronic diseases: Such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. * Improved energy levels: Stable blood glucose levels can help maintain energy levels throughout the day. * Enhanced cognitive function: Normal blood glucose levels can improve concentration, memory, and mood. * Better weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.Diagnosis and Treatment of Abnormal Blood Glucose Levels

Complications of Abnormal Blood Glucose Levels
Abnormal blood glucose levels can lead to a range of complications, including: * Diabetic ketoacidosis: A life-threatening condition that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. * Hypoglycemia: A condition characterized by low blood glucose levels, which can cause confusion, shaking, and loss of consciousness. * Nerve damage: High blood glucose levels can damage nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain. * Kidney disease: High blood glucose levels can damage kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease and kidney failure.Prevention of Abnormal Blood Glucose Levels
Role of Nutrition in Maintaining Normal Blood Glucose Levels
Nutrition plays a critical role in maintaining normal blood glucose levels. The following foods can help regulate blood glucose levels: * Leafy greens: Such as spinach, kale, and collard greens. * Berries: Such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries. * Fatty fish: Such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel. * Whole grains: Such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread. * Legumes: Such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans.Conclusion and Future Directions

As we continue to navigate the complexities of blood glucose regulation, it's essential to prioritize education, awareness, and community support. By working together, we can create a world where everyone has access to the knowledge, resources, and care needed to maintain normal blood glucose levels and live a healthy, fulfilling life.
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions in the comments section below. How do you maintain normal blood glucose levels? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them? Let's start a conversation and support each other in our journey towards optimal health.
What are the symptoms of abnormal blood glucose levels?
+Symptoms of abnormal blood glucose levels may include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How often should I check my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on individual factors, such as medication use and health status. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring schedule for you.
Can I reverse abnormal blood glucose levels through lifestyle changes?
+Yes, lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise modifications, weight loss, and stress management can help improve blood glucose regulation and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases.
