Intro
Discover the 7 RSV symptoms, including runny nose, cough, and fever, and learn about respiratory syncytial virus infection, diagnosis, and treatment options for infants and adults, to recognize early warning signs and prevent complications.
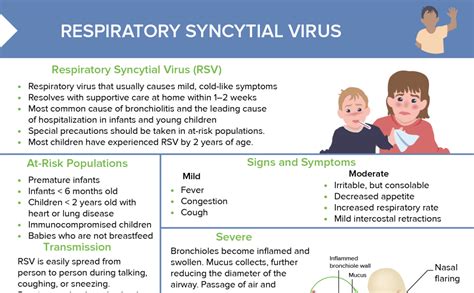
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common and highly contagious virus that affects people of all ages, but it's most severe in young children and older adults. RSV symptoms can range from mild to severe and can be similar to those of other respiratory illnesses, making diagnosis challenging. Understanding the symptoms of RSV is crucial for early detection, proper treatment, and prevention of complications.
RSV is a major cause of respiratory illness in children, and almost all children will have been infected with RSV by the time they are two years old. In adults, RSV can cause mild symptoms, but it can also lead to severe illness, especially in older adults and those with underlying health conditions. The virus spreads through close contact with an infected person, touching contaminated surfaces, and through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
The importance of recognizing RSV symptoms lies in the potential for severe complications, especially in high-risk groups. For instance, premature infants, young children with heart disease or lung disease, and older adults with weakened immune systems are at a higher risk of developing severe RSV disease. Early recognition of symptoms and seeking medical care can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. Moreover, understanding RSV symptoms can help in taking preventive measures, such as practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with anyone who has a cold or other respiratory infection, and ensuring that all family members are up to date on their vaccinations.
Introduction to RSV Symptoms
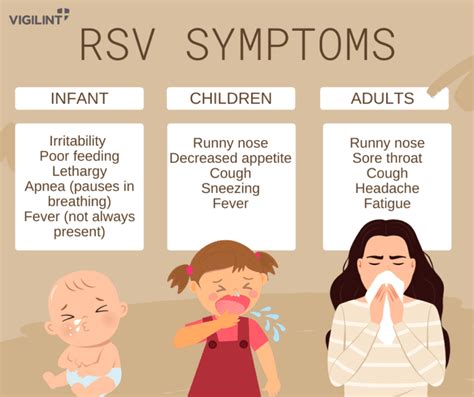
Understanding Mild RSV Symptoms
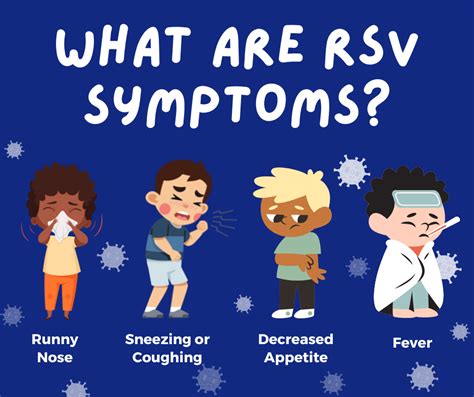
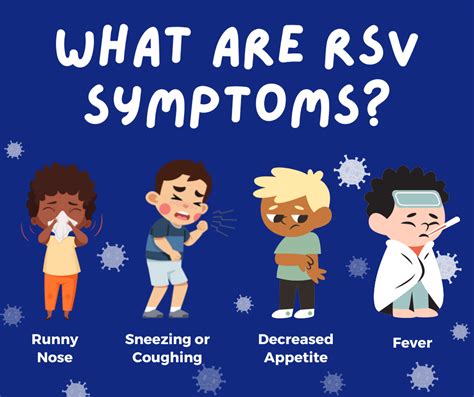
Moderate RSV Symptoms
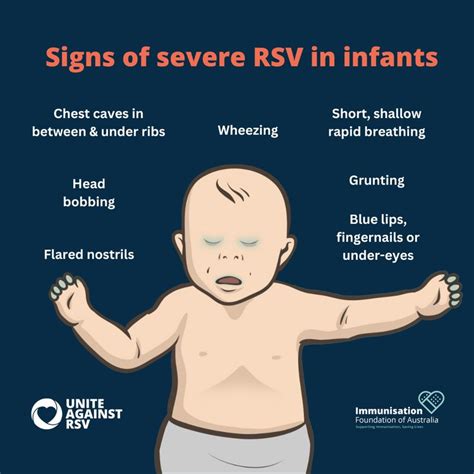
Severe RSV Symptoms
Diagnosing RSV Infection
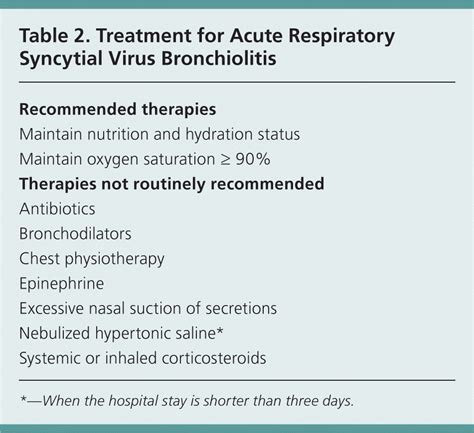
Treatment and Management of RSV
Prevention of RSV Infection

High-Risk Groups for RSV
Certain groups are at a higher risk for severe RSV disease, including: - Premature infants - Young children with heart disease or lung disease - Older adults, especially those with weakened immune systems - Individuals with certain chronic health conditionsComplications of RSV Infection

Understanding the potential complications of RSV infection highlights the importance of early recognition of symptoms and prompt medical evaluation, especially in high-risk groups.
Future Directions in RSV Research
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of RSV infection is crucial for early diagnosis and management, particularly in high-risk individuals. By understanding the range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of infection and its complications. As research continues to advance, the future holds promise for more effective ways to prevent and treat RSV infections.
To further engage with the topic, we invite readers to share their experiences with RSV infections, ask questions, and seek advice from healthcare professionals. The importance of community awareness and education on RSV cannot be overstated, as it plays a vital role in controlling the spread of the virus and supporting those affected.
What are the most common symptoms of RSV infection?
+The most common symptoms of RSV infection include runny nose, coughing, sneezing, fever, and loss of appetite. However, symptoms can vary widely among individuals and may range from mild to severe.
How is RSV infection diagnosed?
+Diagnosing RSV infection typically involves a physical examination and medical history. Healthcare providers may also use tests such as rapid antigen detection tests, molecular tests (e.g., PCR), and chest X-rays to evaluate lung condition.
What are the complications of RSV infection?
+While most people recover from RSV infection without issues, some may develop complications, such as bronchiolitis, pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), otitis media (ear infection), and asthma exacerbation.
How can RSV infection be prevented?
+Preventing RSV infection involves practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently with soap and water, avoiding close contact with anyone who has a cold or other respiratory infection, and ensuring that all family members are up to date on their vaccinations.
What are the future directions in RSV research?
+Research into RSV is ongoing, with a focus on developing effective vaccines and treatments. Several RSV vaccines are in various stages of clinical trials, offering hope for better prevention strategies in the future. Additionally, studies are exploring new antiviral medications that could provide more effective treatment options for those infected with RSV.
