Intro
Learn key Respiratory Syncytial Virus facts, including RSV symptoms, transmission, and prevention methods to protect against this common viral infection, especially in infants and young children, and understand its impact on respiratory health.
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common and highly contagious virus that affects people of all ages, but it's most severe in young children and older adults. RSV is the leading cause of lower respiratory tract infections, such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia, in infants and young children worldwide. In the United States alone, RSV is responsible for approximately 57,527 hospitalizations and 2.1 million outpatient visits among children under the age of five each year. Understanding the facts about RSV is crucial for preventing its spread and managing its symptoms.
RSV is a major public health concern, and its impact on vulnerable populations cannot be overstated. The virus is highly contagious and can spread quickly through close contact with an infected person, touching contaminated surfaces, or through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. RSV can also survive on surfaces for several hours, making it easy to spread in settings like childcare centers, hospitals, and homes. As a result, it's essential to take preventive measures, such as frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with anyone who is sick, and keeping surfaces clean and disinfected.
The importance of understanding RSV facts extends beyond the individual level to the community level. By educating ourselves and others about RSV, we can work together to prevent its spread and protect vulnerable populations. This includes healthcare professionals, caregivers, and family members who can play a critical role in preventing the transmission of RSV and providing supportive care to those who are infected. Furthermore, researchers are continually working to develop effective treatments and vaccines against RSV, and staying informed about the latest developments can help us stay ahead of the curve in managing this common and potentially serious virus.
What is Respiratory Syncytial Virus?
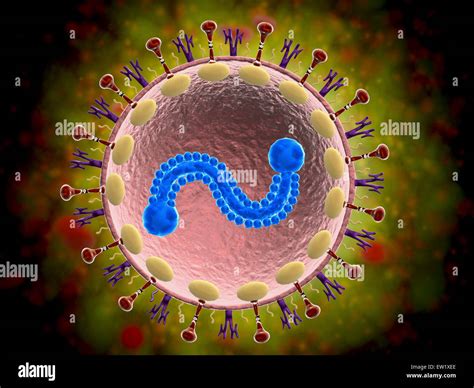
Types of RSV
There are two main subtypes of RSV: RSV A and RSV B. Both subtypes can cause severe illness, but RSV A is more commonly associated with severe disease in young children. RSV A and B can co-circulate during the same season, and infection with one subtype does not provide immunity against the other subtype. This means that individuals can be infected with both RSV A and B during the same season, or in subsequent seasons.RSV Symptoms
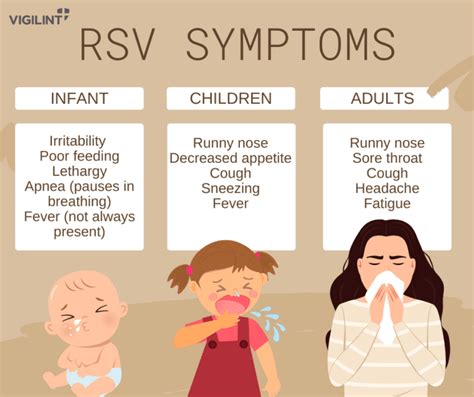
RSV in High-Risk Groups
Certain groups are at higher risk for severe RSV illness, including: * Premature infants (born before 37 weeks gestation) * Young children under the age of two * Older adults (65 years and older) * Individuals with certain underlying health conditions, such as heart disease, lung disease, or immunodeficiency * Those with weakened immune systems, such as people undergoing chemotherapy or taking immunosuppressive medicationsRSV Transmission and Prevention
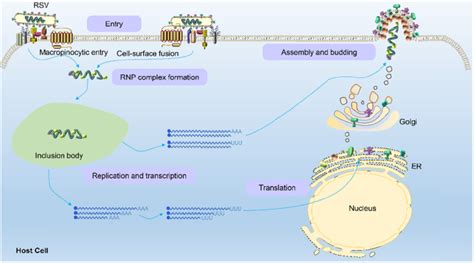
RSV Treatment and Management
There is no specific treatment for RSV, but symptoms can be managed with: * Rest and hydration * Over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to reduce fever and relieve discomfort * Oxygen therapy to help with breathing * Hospitalization may be necessary in severe cases to provide supportive care, such as respiratory support and hydrationRSV Diagnosis and Testing
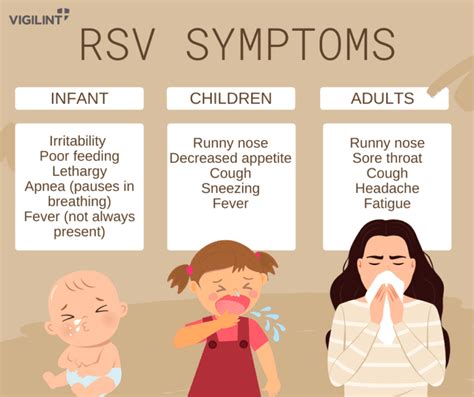
RSV Complications and Long-Term Effects
RSV can lead to complications, such as: * Respiratory failure * Dehydration * Septicemia (blood infection) * Long-term effects, such as: * Recurrent wheezing or asthma * Increased risk of respiratory infections * Developmental delays or disabilitiesRSV Vaccines and Therapies
RSV Seasonality and Epidemiology
RSV typically circulates during the winter months, with peak activity from December to February. However, the exact timing and duration of the RSV season can vary depending on the region and year. Understanding the epidemiology of RSV is crucial for developing effective prevention and control strategies.RSV Global Burden and Economic Impact
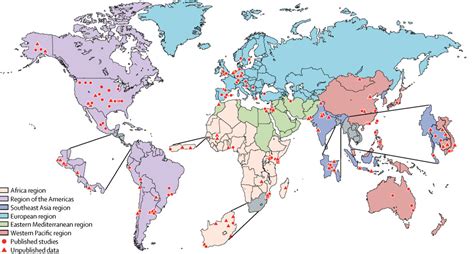
RSV Research and Development
Researchers are continually working to improve our understanding of RSV and develop effective prevention and treatment strategies. This includes: * Basic research to understand the biology of RSV and its interaction with the host * Clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of RSV vaccines and therapies * Epidemiological studies to understand the burden and transmission of RSVWhat is the most common way to get infected with RSV?
+RSV is highly contagious and can spread through respiratory droplets, such as those produced by coughing or sneezing, or by touching contaminated surfaces.
Who is at highest risk for severe RSV illness?
+Certain groups are at higher risk for severe RSV illness, including premature infants, young children under the age of two, older adults, and individuals with certain underlying health conditions.
Is there a vaccine available to prevent RSV infection?
+Researchers are working to develop effective vaccines against RSV, but currently, there is no vaccine available to prevent RSV infection. However, several candidates are in various stages of development.
What are the most common symptoms of RSV infection?
+The symptoms of RSV can range from mild to severe and may include runny nose, coughing, sneezing, fever, loss of appetite, irritability, wheezing, and apnea (pauses in breathing).
How can I prevent the spread of RSV?
+To prevent the spread of RSV, wash your hands frequently with soap and water, avoid close contact with anyone who is sick, keep surfaces clean and disinfected, and avoid sharing utensils, toys, or other personal items.
In conclusion, RSV is a common and highly contagious virus that affects people of all ages, but it's most severe in young children and older adults. Understanding the facts about RSV is crucial for preventing its spread and managing its symptoms. By staying informed and taking preventive measures, we can work together to reduce the burden of RSV and protect vulnerable populations. If you have any questions or concerns about RSV, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others to help spread awareness about this important topic.
