Intro
Discover the implications of a high reticulocyte count, including anemia, blood disorders, and bone marrow function, and learn 5 ways to address elevated reticulocyte levels for improved health outcomes.
The importance of understanding blood cell production cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's overall health. One key indicator of this process is the reticulocyte count, which measures the number of young red blood cells in the bloodstream. A high reticulocyte count can be an indication of various health issues, and it is essential to comprehend the underlying causes and implications of such a result. In this article, we will delve into the world of reticulocyte counts, exploring what they signify, the reasons behind elevated levels, and the potential consequences of ignoring these warning signs.
A reticulocyte count is typically performed as part of a complete blood count (CBC) test, which provides valuable insights into the body's blood cell production. This test is crucial in diagnosing and monitoring various blood disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, and lymphoma. By analyzing the reticulocyte count, healthcare professionals can determine whether the bone marrow is producing red blood cells at an adequate rate. A high reticulocyte count may indicate that the body is trying to compensate for a loss of red blood cells, which could be due to various factors, including bleeding, anemia, or other underlying medical conditions.
Understanding the significance of a high reticulocyte count is vital, as it can help identify potential health issues before they become severe. For instance, a high reticulocyte count in newborns can be an indication of hemolytic disease, a condition where the baby's red blood cells are being destroyed. Similarly, in adults, an elevated reticulocyte count can be a sign of an underlying condition, such as iron deficiency anemia, vitamin deficiency anemia, or other blood disorders. By recognizing the importance of reticulocyte counts, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain their overall health and seek medical attention if they experience any unusual symptoms.
Introduction to Reticulocyte Count
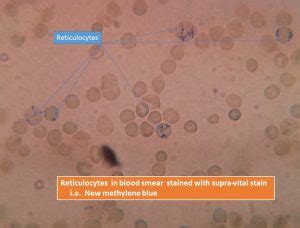
What is a Normal Reticulocyte Count?
A normal reticulocyte count typically ranges from 0.5% to 1.5% of the total red blood cell count. However, this range can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors. In newborns, the reticulocyte count is typically higher, ranging from 2% to 6%, due to the rapid production of red blood cells after birth. In adults, a high reticulocyte count can be an indication of an underlying condition, such as anemia or bleeding, which requires medical attention.Causes of High Reticulocyte Count

Symptoms of High Reticulocyte Count
The symptoms of a high reticulocyte count can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, common symptoms include: * Fatigue: A feeling of tiredness or weakness due to inadequate oxygen delivery to the body's tissues. * Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling winded, even when engaging in light physical activity. * Pale skin: A pale or washed-out appearance, due to inadequate oxygen delivery to the skin. * Headaches: Frequent or severe headaches, due to inadequate oxygen delivery to the brain. * Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy, due to inadequate oxygen delivery to the brain.Diagnosis and Treatment
Prevention and Management
Preventing and managing a high reticulocyte count involves addressing the underlying cause and making lifestyle changes to promote healthy red blood cell production. This may include: * Eating a balanced diet: Rich in iron, vitamins, and other essential nutrients. * Avoiding excessive bleeding: By treating underlying conditions, such as hemolytic disease, and avoiding injuries or trauma. * Managing underlying conditions: Such as anemia, hemolytic disease, or bone marrow disorders, through medication and lifestyle changes. * Getting regular check-ups: To monitor reticulocyte count and address any underlying issues promptly.Complications and Risks

Long-term Outlook
The long-term outlook for individuals with a high reticulocyte count depends on the underlying cause and the effectiveness of treatment. In some cases, a high reticulocyte count can be a sign of an underlying condition that requires ongoing management and treatment. However, with prompt medical attention and lifestyle changes, it is possible to manage a high reticulocyte count and prevent complications.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with us. Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with a high reticulocyte count? What steps have you taken to manage the condition? Share your story in the comments below, and let's work together to promote healthy living and disease prevention.
What is a reticulocyte count?
+A reticulocyte count is a blood test that measures the number of young red blood cells, called reticulocytes, in the bloodstream.
What is a normal reticulocyte count?
+A normal reticulocyte count typically ranges from 0.5% to 1.5% of the total red blood cell count.
What are the causes of a high reticulocyte count?
+The causes of a high reticulocyte count include anemia, bleeding, hemolytic disease, vitamin deficiency, and bone marrow disorders.
How is a high reticulocyte count diagnosed and treated?
+Diagnosing the underlying cause of a high reticulocyte count typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The treatment for a high reticulocyte count depends on the underlying cause, but may include iron supplements, vitamin supplements, blood transfusions, and medications.
What are the complications and risks of a high reticulocyte count?
+A high reticulocyte count can lead to various complications and risks, including anemia, organ damage, infections, and bleeding disorders.
