Intro
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic and often debilitating autoimmune disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation and pain in the joints, which can lead to significant disability and reduced quality of life. Understanding the various factors that contribute to the development and progression of RA is crucial for effective management and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of RA and explore the key factors that play a role in this condition.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a multifactorial disease, and its exact causes are still not fully understood. However, research has identified several genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that can increase the risk of developing RA. These factors can be broadly categorized into two main groups: genetic factors and environmental factors. Genetic factors refer to the inherited traits that can predispose an individual to RA, while environmental factors include external influences that can trigger the onset of the disease.
The impact of RA on daily life cannot be overstated. People living with RA often experience significant pain, stiffness, and fatigue, which can make everyday activities challenging. Furthermore, RA can also increase the risk of developing other health problems, such as cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and depression. Therefore, it is essential to understand the various factors that contribute to RA and to develop effective strategies for managing and treating this condition.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Overview

Genetic Factors
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of RA. Certain genetic variants can increase the risk of developing RA, and research has identified several genes that are associated with the condition. These genes can affect the immune system and increase the risk of autoimmune disorders, including RA. For example, the HLA-DRB1 gene has been shown to be associated with an increased risk of RA, particularly in people of European descent.Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Factors

Environmental Triggers
Environmental triggers can also play a role in the development of RA. These triggers can include: * Infections: Certain infections, such as those caused by bacteria or viruses, can trigger the onset of RA in people who are genetically predisposed to the condition. * Stress: Physical or emotional stress can trigger the onset of RA in some people. * Diet: A diet that is high in processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables may increase the risk of developing RA.Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms

Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis
Diagnosing RA can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. A diagnosis of RA is typically made based on a combination of: * Medical history: A thorough medical history to identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the symptoms. * Physical examination: A physical examination to assess joint pain and stiffness. * Laboratory tests: Laboratory tests, such as blood tests and imaging studies, to confirm the diagnosis.Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment

Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
In addition to medications, lifestyle modifications can also play an important role in managing RA. These modifications may include: * Exercise: Regular exercise to help maintain joint mobility and strength. * Diet: A healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. * Stress management: Stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to help manage stress.Rheumatoid Arthritis Complications

Rheumatoid Arthritis Prognosis
The prognosis for RA varies depending on several factors, including the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. With proper treatment and lifestyle modifications, it is possible to manage the symptoms of RA and slow the progression of the disease.Rheumatoid Arthritis Research
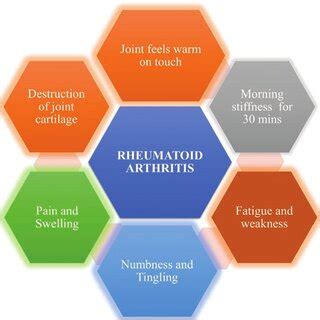
Rheumatoid Arthritis Support
Living with RA can be challenging, but there are many resources available to provide support and guidance. These resources may include: * Support groups: Support groups where people with RA can connect with others who are going through similar experiences. * Online resources: Online resources, such as websites and forums, where people with RA can find information and connect with others. * Healthcare professionals: Healthcare professionals, such as rheumatologists and physical therapists, who can provide guidance and support.What are the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
+The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include joint pain and stiffness, swelling, fatigue, and loss of function.
How is rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed?
+Rheumatoid arthritis is typically diagnosed based on a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
What are the treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis?
+Treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis include medications, such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologics, as well as lifestyle modifications, such as exercise and diet.
Can rheumatoid arthritis be prevented?
+While there is no guaranteed way to prevent rheumatoid arthritis, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, may help reduce the risk of developing the condition.
What is the prognosis for rheumatoid arthritis?
+The prognosis for rheumatoid arthritis varies depending on several factors, including the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. With proper treatment and lifestyle modifications, it is possible to manage the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and slow the progression of the disease.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of rheumatoid arthritis and its various factors. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to reach out. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can raise awareness and promote understanding of this complex condition.
