Intro
Discover how Rheumatoid Factor Test works to diagnose autoimmune disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis, through blood analysis, antibody detection, and inflammation assessment, using diagnostic criteria and medical imaging for accurate results.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints. One of the key diagnostic tools used to detect this condition is the rheumatoid factor test. The rheumatoid factor test is a blood test that measures the levels of rheumatoid factor, an antibody that is often present in the blood of people with rheumatoid arthritis. In this article, we will explore the ways in which the rheumatoid factor test works, its benefits, and its limitations.
The rheumatoid factor test is an important diagnostic tool because it can help doctors diagnose rheumatoid arthritis and distinguish it from other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. The test is also used to monitor the progression of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. There are several ways in which the rheumatoid factor test works, including measuring the levels of rheumatoid factor in the blood, detecting the presence of other antibodies, and monitoring the levels of inflammatory markers.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex condition that can be difficult to diagnose, and the rheumatoid factor test is just one of the tools that doctors use to make a diagnosis. The test is often used in combination with other diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies and physical exams, to confirm the presence of rheumatoid arthritis. In addition to its diagnostic uses, the rheumatoid factor test can also be used to monitor the progression of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment.
What is Rheumatoid Factor?
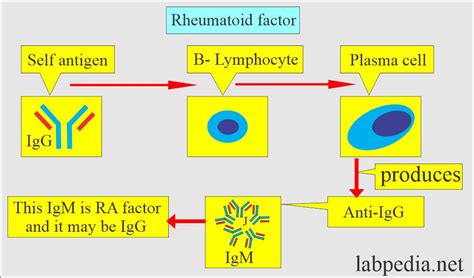
How is Rheumatoid Factor Measured?
The rheumatoid factor test measures the levels of rheumatoid factor in the blood using a technique called enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). This test uses a special plate that is coated with a substance that binds to rheumatoid factor. A sample of blood is added to the plate, and the rheumatoid factor in the blood binds to the substance on the plate. The plate is then washed, and a special enzyme is added that reacts with the rheumatoid factor. The level of rheumatoid factor in the blood is then measured by detecting the amount of enzyme that is present.Types of Rheumatoid Factor Tests

- Qualitative tests: These tests detect the presence or absence of rheumatoid factor in the blood.
- Quantitative tests: These tests measure the levels of rheumatoid factor in the blood.
- IgM rheumatoid factor tests: These tests measure the levels of IgM rheumatoid factor, which is a type of rheumatoid factor that is often present in people with rheumatoid arthritis.
- IgG rheumatoid factor tests: These tests measure the levels of IgG rheumatoid factor, which is another type of rheumatoid factor that is often present in people with rheumatoid arthritis.
Benefits of Rheumatoid Factor Tests
The rheumatoid factor test has several benefits, including:- Helping doctors diagnose rheumatoid arthritis and distinguish it from other conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
- Monitoring the progression of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment.
- Detecting the presence of other antibodies that may be associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Providing information about the severity of the disease and the likelihood of developing complications.
Limitations of Rheumatoid Factor Tests

- The test is not specific for rheumatoid arthritis and can be positive in people with other conditions, such as lupus or scleroderma.
- The test can be negative in people with early rheumatoid arthritis or in people who have a mild form of the disease.
- The test can be influenced by other factors, such as age, sex, and the presence of other medical conditions.
Interpreting Rheumatoid Factor Test Results
Interpreting the results of the rheumatoid factor test requires careful consideration of several factors, including the level of rheumatoid factor in the blood, the presence of other antibodies, and the clinical presentation of the patient. A positive test result can indicate the presence of rheumatoid arthritis, but it is not diagnostic on its own. A negative test result can help rule out rheumatoid arthritis, but it does not exclude the possibility of other conditions that may cause similar symptoms.Rheumatoid Factor Test and Other Diagnostic Tools
Rheumatoid Factor Test and Treatment
The rheumatoid factor test can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and adjust the treatment plan as needed. The test can help doctors determine whether the treatment is working and whether the disease is progressing. The test can also help doctors identify potential complications, such as joint damage or inflammation, and take steps to prevent them.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
The rheumatoid factor test is an important diagnostic tool that can help doctors diagnose and monitor rheumatoid arthritis. By understanding how the test works and its benefits and limitations, doctors can use the test to provide better care for their patients. Further research is needed to improve the accuracy and specificity of the test and to develop new diagnostic tools that can help doctors diagnose and treat rheumatoid arthritis more effectively.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the rheumatoid factor test and its role in diagnosing and monitoring rheumatoid arthritis. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We would be happy to hear from you and provide any additional information you may need.
What is the rheumatoid factor test used for?
+The rheumatoid factor test is used to diagnose and monitor rheumatoid arthritis. It measures the levels of rheumatoid factor in the blood, which can help doctors diagnose the condition and monitor its progression.
How is the rheumatoid factor test performed?
+The rheumatoid factor test is performed by taking a sample of blood and measuring the levels of rheumatoid factor using a technique called enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
What are the benefits of the rheumatoid factor test?
+The benefits of the rheumatoid factor test include helping doctors diagnose rheumatoid arthritis and distinguish it from other conditions that may cause similar symptoms, monitoring the progression of the disease, and detecting the presence of other antibodies that may be associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
